Session 1: CSF, ventricular system Flashcards
(16 cards)
label


what structres r deep to the insula?
putamen and globus pallidus, caudate nucleus
part of basal ganglia

label

Caudate> C-shaped structure
appears twice

image

what is red dot? why is it squashed

3rd ventricles, due to the thalamus on either side!

label
what r the white mater strucutres?

corpus callosum & v-shaped internal capsule

where does corpus callosum run?
above the lateral ventricles
what is this? fucntion? location

internal capsule
connects cerebral cortex w/ the rest of the nervous system
its a major white matter pathway!
its sandwhiched w=btw 2 majir grey matters!
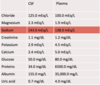
composition on CSF?
- Normal CSF is clear and colourless and contains very little protein (15 to 45 mg/dL)
- little immunoglobulin
- only one to five cells (leukocytes) per ml.
- hyperosmolar compared to plasma!
Changes from these normal values are useful in the diagnosis of a variety of disease processes
CSF circulation

what is the ventricles of the brain?

cavities in brain are known as the brain ventricles, contain choroid plexus, makes a total of 600-700ml of CSF per day

where does CSF circulate before being reabsorbed at the arachnoid granulations?
CSF circulates through the ventricular system and subarachnoid space before being reabsorbed at the arachnoid granulations
what supplies the ventricles with blood?
internal carotid artery

Hydrocephalus
types?
‘Accumulation of CSF is thought to be due to an imbalance between production & absorption of CSF w/ enlargement of brain ventricles’’
◦ Non-communicating/obstructive
- CSF is obstructed w/ in the ventricles or between the ventricles subarachnoid space.
◦ Communicating
- There is communication btw the ventricles & subarachnoid space.
- problem lies OUTSIDE of the ventricular system
- Due to reduced absorption or blockage of the venous drainage system.
- It may also be due to increased CSF production.
Non-communicating/obstructive Hydrocephalus
- common cause?
- CT scan features?

CSF is obstructed within the ventricles or between the ventricles and the subarachnoid space.
- Most commonly due to aqueduct blockade
- Can be congenital or acquired
- Also due to tumours ex: meningioma
4th ventricle _smaller_ than 3rd>> u can tell there is a blockage in aqueduct

Communicating - Hydrocephalus
- common cause?
- less common causes?
- CT?
- there is communication between the ventricles and the subarachnoid space, problem lies outside of the ventricular system*
- Mostly to POST-MENINGITIS
◦ Bacterial, fungal, TB
- Subarachnoid haemorrhage
- Trauma + neoplastic infiltration of subarachnoid space
Less common mechanisms include:
◦ excess CSF production - choroid plexus papilloma


