session 1: reflex. tracts, seizures Flashcards
Draw a labelled diagram showing the complete reflex arc

what could cause a loss in the tendon reflex?
caused by a lesion anywhere along the spinal reflex path. The reflex lost indicates its level
what r the 2 types of reflexes, what type of reflex is the knee jerk?
What spinal level(s) mediate(s) the knee jerk reflex?
monosynaptic and polysynaptic
knee jerk is monosynaptic>> involves a single synapse!
L3-L4
(stretch reflex is the only monosynaptic relfex!)

Which structures detect muscle stretch when the tendon hammer is applied to the patellar ligament?
Muscle spindle detect stretch

What is the generic term for the neurone that receives information from the structures named above?
What is the generic term for the neurone that sends impulses to the skeletal muscle in a reflex arc?
Afferent neuron
Motor neuron
what enhances reflex activity? what should be done before a reflex is recorded as absent.
Distraction of the patient’s attention, clenching teeth or pulling interlocked fingers enhances reflex activity
(Jendrassik manœuvre)
Such reinforcement manœuvres should be done before a reflex is recorded as absent.

what is the Jendrassik manoeuvre?
Distraction of the patient’s attention, clenching teeth or pulling interlocked fingers enhances reflex activity

recap

explain how the Somatic sensory cortex is organized in the brain
The somatic sensory or somaesthetic cortex occupies the entire postcentral gyrus
- superior parts of the body r at the inferior parts of the cortex
& vise versa

define encephalisation
an evolutionary increase in the complexity or relative size of the brain, involving a shift of function from non-cortical parts of the brain to the cortex.
Course of Corticospinal tract/pyramdial tract
The corticospinal tract descends through the corona radiata and posterior limb of the internal capsule to reach the brainstem.
It continues through the crus (cerebral peduncle) of the midbrain > basilar pons > medulla>> here it forms the pyramid
Just above the spinomedullary junction:
- 80% of fibres cross in midline in pyramidal decussation > these fibres descend on the contralateral side of the spinal cord as the lateral corticospinal tract
- 20% of fibres that DONT decussate continue to descend in the ventral portion of the spinal cord.
Targets of the corticospinal tract
- no crossing over > ventral /anterior corticospinal tract
occupies the ventral/anterior funiculus at cervical and upper thoracic levels, supply motor neurons serving muscles in anterior & posterior abdominal walls.
- cross over > lateral corticospinal tract
Distal limb motor neurons, skilled movements
What is a T1 MRI scan, & how does it differ from a T2 scan?
By altering the sequence of pulses to which the protons are subjected, different properties of the protons can be assessed. These properties are referred to as the “weighting” of the scan.
By altering the pulse sequence and the scanning parameters, T1-weighted images and T2-weighted imagescan be obtained.
These two types of imaging sequences provide differences in image contrast, which accentuate and optimize different tissue characteristics.

What is a T1 MRI scan, and how does it differ from a T2 scan?
T1-weighted images show dark fluid and bright fat—ex: in the brain the CSF is dark;
T2-weighted images demonstrate a bright fluid and intermediate signal from fat—ex: in brain the CSF appears white.
REMEMBER> T2 H<strong>2</strong>0
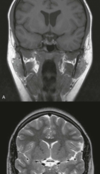
What is it & which tissue might it derive from?

Which structures in the cerebral hemisphere is the lesion compressing?
Meningioma
tumors that arise from meningothelial cells
may become malignant, invading the brain and eroding the skull. In such cases, prominent edema may be present in the brain parenchyma, to the extent that the extra-axial nature of the tumor is no longer obvious.
temporal lobe
Why does gadolinium (Gd) enhance the lesion?
Enhancement with exogenous contrast material is now a routine part of MRI.
The material most widely used is a gadolinium chelate.
The gadolinium atom is strongly paramagnetic & acts to shorten the T1 relaxation time of nearby water protons in blood. it doesn’t pass the blood-brain barrier> very useful in detecting disruption of the blood-brain barrier by neoplasm, infection, trauma, and infarction.
The T1-shortening effect is also used for rapid MRA, which is performed in a fast scanning protocol after the bolus injection of a contrast agent. In the brain, bolus injection of gadolinium with repeated echo planar imaging (EPI) has been used to image perfusion 31 and the blood volume of tumors
what to do if someone is having a tonic clonic epileptic seizure
You cannot stop a person’s seizure, the seizure will usually stop naturally on its own
After the seizure has stopped, put them into the recovery position and check that their breathing is returning to normal.
Gently check their mouth to see that nothing is blocking their airway such as food or false teeth. If their breathing sounds difficult after the seizure has stopped, call for an ambulance.

Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus denotes an excessive accumulation of the CSF in the intracranial compartment


