Depression Flashcards
What is Depression?
Features of depressive disorders
Patient usually have the symptoms continually for 2 weeks and consist of
• CORE SYMPTOMS
– Low mood
– Lack of energy
– Lack of enjoyment & interest
• Depressive thoughts
• Somatic symptoms/Biological symptoms
Difference between a ‘normal’ adjustment reaction and clinical depression
Examples of illnesses that can cause depressive symptoms
There are many illnesses that can cause depressive symptoms including:
• Hormone disturbance such thyroid dysfunction
- Vitamin deficiencies such as vitamin B12
- Heart and lung diseases
- Blood vessels not functioning well
- Kidney disease
- Liver disease
2 things if misused can cause depressive symptoms?
- People drinking too much over a period is a well known cause of developing depressive symptoms
- A number of recreational drugs cause depressive symptoms, especially drugs that initially induce a feeling of happiness and wellbeing such as XTC or amphetamines.
Brain structures involved in depressive symptoms
• Limbic system
- Frontal lobe
- Basal ganglia
What causes people to become clinically depressed?
There are many different causes that can be categorised as follows:
- Predisposing: Genetics, childhood experiences, female gender
- Perpetuating (maintaining factors): A stressful job, studies, relationship difficulties, substance misuse, financial strain, housing, unemployment
- Precipitating factors: Life events often related to losses such as loss of someone you love, loss of health and break up of relationships.
3 Predisposing factors of depression
- Genetic
- Childhood experiences
• Female gender
Childhood experiences causing depression
- Quality of attachment
- Quality of parental relationships
- Loss of a parent
- Bullying
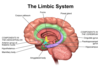
Limbic System laebl

• Cingulate gyrus
- Hippocampus
- Amygdala
- Hypothalamus
• Septum
- Olfactory Bundle
- Dentate gyrus
- Anterior nucleus of the thalamus
• Mammillary bodies
Main 3 functions of the limbic system
- Emotion
- Motivation
• Memory
Frontal lobe functions (what fraction of the whole cortex does it form?)
The frontal lobe form 2/3 of the total cortex
- Motor function
- Language (Broca’s area)
- Executive functions (purposeful goal directed behaviours)
- Attention
- Memory
- Mood
- Social and moral reasoning

how is mood is determined in the brain?
The main hypothesis is that mood is determent by functional circuits between these brain areas. E.g. the frontal lobe projects to parts of the limbic system which in turn connects to the basal ganglia and the brainstem. This affects:
• Cognitive processed (thoughts)
- Sympathetic output
- Parasympathetic output
- Motor systems
The 2 main neurotransmitters for depressive disorders?
- NE
- Serotonin
Other neurotransmitters important in psychiatric conditions include:
- Dopamine
- Acetylcholine
- GABA
• Glutamate
NE functions in brain?
Functions in the brain:
• Mood
• Suggests a role in behaviour (arousal and attention)
• Implicated in memory functions
Made in the locus coeruleus in the brainstem and transported to several areas of the cortex

recepters of the NE system!
- 4 types of receptors: α1 and 2 and β1 and 2
- The function of the β receptors in the brain is not very clear as yet
- It is likely that α receptors play a role in arousal and mood
- See for a schematic picture of receptors next slide
evidence that NE beingimplicate din causation of depression in the brain?
serotonin function in the brain
where is it made?
- Sleep
- Impulse control
- Appetite
- Mood
Produced in the brain stem (Raphe nuclei) and transported to cortical areas and limbic system
recepters of the seretonin
Complex, there are many different pre and post serotonergic receptors.
reasons for implicating 5HT in depression?
5HIAA depletion in CSF (a metabolite of serotonin) in patients with depression
Tryptophan depletion (precursor for serotonin) causes depression
PET studies
SPET studies
Reserpine (depletes nerve endings from mono amines)
Anti-depressant: SSRI, TCA, SNRI’s, MAOI
2 ‘CORE’ SYMPTOMS OF DEPRESSION
- During the last month have you often been bothered by feeling down, depressed, or hopeless?
- Do you have little interest or pleasure in doing things?
for how long should the 2 core symptoms be present? if so? what else to ask?
- Fatigue/loss of energy.
- Worthlessness/excessive or inappropriate guilt.
- Recurrent thoughts of death, suicidal thoughts, or actual suicide attempts.
- Diminished ability to think/concentrate or indecisiveness.
- Psychomotor agitation or retardation.
- Insomnia/hypersomnia.
- Significant appetite and/or weight loss.

Differential diagnosis:
- Hypothyroidism
- Menopause
- Chronic disease


