Streptococcus Flashcards
(80 cards)
Is streptococcus gram positive or gram negative?
Is it anaerobic or aerobic?
Is it Motile or Non Motile?
Does it form spores?
Is it catalase positive or negative?
- Gram positive cocci arranged in chains
• Facultative anaerobe …O2 availability is not critical for survival
• Non-motile and non-spore forming (like Staphylococcus) - Catalase negative.
What is streptococcus arranged as? W hat kind of Bacteria (Rods, Cocci, etc)
Gram positive cocci arranged in chains
What kind of bacteria is seen in this image? Why?

Streptococcus Genus
Gram positive cocci arranged in chains
What is streptococcus’ growth requirement? Can it live outside the host? Is it catalase positive or negative?
Fastidious growth requirement (unlike Staphylococcus) i.e. requires a nutritionally rich media for growth
• Thus, they cannot survive for long away from the animal host
• Cannot grow in media containing high salt (> 6.5%) (unlike the salt
resistant Staphylococcus)
• Catalase negative (unlike Staphylococcus that is catalase + and
arranged in grape-like appearance)
What are the 2 widely used culture media for growth of streptococcus?
- Blood agar
- Edward media for selective
isolation and identification of
Streptococci
What can you determine about streptococcus when using blood agar?
✓ Allows determination of
the type of hemolysin toxin produced by the isolates (beta, alpha, gamma)

In this image what kind of streptococcus is seen?
A.) Alpha
B.) Beta
C.) Gamma

B.) Beta

In this image what kind of streptococcus is seen?
A.) Alpha
B.) Beta
C.) Gamma

A.) Alpha

In this image what kind of streptococcus is seen?
A.) Alpha
B.) Beta
C.) Gamma

c.) gamma

On this image of Streptococcus on an Edward Media, what is occuring?

Growth of Streptococci on Edwards media showing esculin hydrolysis.
Which Streptococcus group is more pathogenic ?
✓ Beta-hemolytic group
➢ most pathogenic streptococci
Which streptococcus on this plate is the alpha hemolysis group? How can you tell?
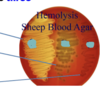
✓Alpha-hemolysis group
➢partial and incomplete hemolysis with green color (viridiant)
This is the one in the center of this image.
Which streptococcus on this plate is the beta hemolytic group?

It would be the one on the left ( bright yellow) this shows complete hemolysis.
Which streptococcus on this plate is the gamma hemolytic group?

The one on the right is the gamma hemolysis. It shows no hemolysis.
Where does Alpha Hemolysis Streptococcus usually infect? Gamma?
Alpha: Respiratory tract
Gamma: Fecal ( enterococcus faecalis.
How can you serogroup streptococcus by using a common cell wall carbohydrate?
- )Add 1 drop of extraction reagent # 1 into test tube.
- ) Add 1 bacterial colonu
- ) Add one drop of extraction reagent # 2
- ) Mix
- ) Add 5 drops extraction reagent # 3
- ) Mix well. Cell wall carbohydrate is extracted and ready to mix with antibody.
- ) Mix 1 drop of the bacterial extract with one drop of the antibody kit (A, B, C, D, F or G) in the relevant circle on the card.
- ) Correct combination of antibody and antigen (carbohydrate) causes agglutination.
What streptococci serogroups are of human and veterinary clinical importance?
✓ Of the 19, sero-groups A, B, C, D, E, and G are clinically important in human and veterinary medicine
What are your methods of diagnosis of streptococcus isolates from suspected cases? What is the order in which you will do this?
- ) Gram Stain: Gram positive or negative
- ) Catalase test ( 1 drop H2O2 + bacterial innoculation) If the drop bubbles then the bacteria is catalase positive. Streptococcus is not.
- ) Blood Agar hemolysis to determine group.
- ) Lancefied serogrouping.
Group A streptococcus Serotypes have what kind of hemolysis? What is the bacteria species, what animals does it typically infect?
Group A
- Beta hemolytic ( complete hemolysis)
Species: S. Pyogenes
Species: Children/ Humans
Group B streptococcus Serotypes have what kind of hemolysis? What is the bacteria species, what animals does it typically infect?
Group B
Hemolysis Type: Beta
Species: S. agalactiae
Animal: Humans and animals ( dogs cats, vaginal tract.)
Group C streptococcus Serotypes have what kind of hemolysis? What is the bacteria species, what animals does it typically infect?
Hemolysis Type:
Species:
Animal Affected:
Group C
Hemolysis Type: Beta
Species: S. Equi, S. equilismullis, S. zooepidemicus, S. dysgalactiae
Primary Animal Affected: Horses
Group D streptococcus Serotypes have what kind of hemolysis? What is the bacteria species, what animals does it typically infect?
Group D
Hemolysis Type: gamma hemolytic
Species: Enterococcus
Animal Affected: Bovine, Canine, ect
Group E streptococcus Serotypes have what kind of hemolysis? What is the bacteria species, what animals does it typically infect?
Group D
Hemolysis Type: Beta hemolytic
Species: S. porcinus
Animal Affected: Pigs
Group G streptococcus Serotypes have what kind of hemolysis? What is the bacteria species, what animals does it typically infect?
Group G
Hemolysis: Beta hemolysis
Species: S. canis
Animals Affected: Canines and Felines










