Spinal Cord, ANS, CNS, Neurons Flashcards
What do B nerve fibers do?
- Small
- Myelinated
- Conduct less rapidly than A
- Preganglionic autonomic
What is a chemical synapse?
Chemical neurotransmitters are released
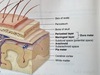
What is the dura mater and where is it located?
- Outer, tough, fibrous membrane
- Attached to inner surface of cranium
- Forms falx and tentorium

What does a neurons axon do?
- One-way conduction
- Conducts impulses away from the cell body
What pathways are in the descending fiber system?
Motor pathways
What pathways are in the ascending fiber system?
Sensory pathways
What do the Corticospinal Tracts do?
- Voluntary muscle control
(descending - motor pathway)
What are the 4 types of A nerve fibers?
- Alpha
- Beta
- Gamma
- Delta
What does cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) do?
- Mechanical support (cushions brain)
- Controls brain excitability by regulating ionic composition
- Aids in exchange of nutrients and waste
What do projection neurons do?
Carry impulses to other parts of the CNS
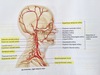
What structures make up venous drainage from the head and neck?
- Cerebral Veins
- Dural venous sinuses

What signals do Beta nerve fibers send?
- Touch
- Pressure
(A fiber type)
What signals do Gamma nerve fibers send?
- Motor to muscle spindles
(A fiber type)
The vertebral arteries join to form what artery in the brain?
- Vertebral arteries arise off the subclavian arteries and unite to form the basilar artery
- Bifurcates into two posterior cerebral arteries

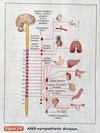
What does the Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) do?
Innervations of involuntary structures:
- Smooth muscle
- Heart
- Glands
Helps maintain homeostasis
The vertebral arteries supply what parts of the brain?
- Brainstem
- Occipital lobes
- Cerebellum
- Parts of Thalamus
What do the Spinorericular Tracts do?
- Deep and Chronic Pain
(ascending - sensory pathway)
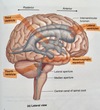
What are the ventricles in the brain for?
How many are there?
- Filled with CSF and communicate with each other and with the spinal cord
- 4 ventricles or cavities

What do the Tectospinal Tracts do?
- Assists in head-turning responses to visual stimuli
What do the Spinocerebellar Tracts do?
- Proprioception from muscle spindles, golgi tendon organs, and touch and pressure receptors to cerebellum for control of voluntary movements
(ascending - sensory pathway)
What is the subarachnoid space and where is it located?
- Contains cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and cistern (major arteries)
- Between arachnoid and pia mater

What signals do Alpha nerve fibers send?
- Proprioception
- Somatic Motor
(A fiber type)
What do the Rubrospinal Tracts do?
- Assist in Motor Function
What is a neuron cell body?
Genetic center with dendrites to receive information