Soft lesions & salivary tumors and variant of normal combined-kerr Flashcards
Irritation Fibromas
Composed of
Etiology
Clinical features ;Color
Location
Treatment
- AKA – Fibroma, Traumatic Fibroma
- Composed of dense, scar-like, fibrous connective tissue
- Occurs as a result of chronic trauma
- Clinical Features: Exophytic lesion
- Usually less than a centimeter in diameter
- Color: lighter pink than surrounding mucosa,the surface can be white sometimes bc it’s rubbing and bumping into other oral structures (like teeth), so they get surface keratinization
- Locations: buccal mucosa, tongue, lips, gingiva
- Very common; totally benign soft lesion
- Treatment: You don’t have to remove them, but the surgical Tx = to excise them bc pts will stop biting them and they’ll heal and stop the irritation
What is this clinical finding?

Irritation Fibromas
What is this clinical finding?

Irritation Fibromas
What is this clinical finding?

Chronic Hyperplastic Pulpitis (pulp polyp)

Giant Cell Fibroma
Chronic Hyperplastic Pulpitis
What is it?
Location?
Age?
Clinical Appearance?
Treatment?
• AKA: pulp polyp
• An e_xcessive proliferation of chronically inflamed dental pulp tissue_ – granulation tissue/ fibrous tissue with inflammatory cells (like a little fibroma that
occurs from pulp tissue) ( benign soft tissue leasion)
• Location:
• Teeth with large, open carious lesions
• Primary or permanent molars
• Age: Children & young adults
• Clinical Appearance: A red or pink nodule of soft tissue protruding from the
pulp chamber and fills the entire cavity of the tooth
• Treatment: RCT or extraction of tooth
Giant Cell Fibroma
- Very small form of fibrous tumour that show giant cells
- Age: relatively rare in paediatric patients.
- Clinically it is presented as a painless, sessile, or pedunculated growth which is usually confused with other fibrous lesions like irritation fibromas or Retrocuspid papilla
- Location: Largely occur on lower gingivae and on palate\
What are these clinical findings (what is the name of the syndrome or complex?)

Tuberous sclerosis complex
we see A lot of gingival enlargement – is this overgrowth from disease or from seizure medication? Multi organ system involvement
What is this clinical finding?

Epulis Fissuratum
Cowden Syndrome
- (multiple hamartoma and neoplasia syndrome)
- • Autosomal dominant disorder affecting multiple organ systems
- • Caused by mutations in the phosphatase and tensin homolog gene (PTEN, a tumor suppressor gene)
- • Oral and perioral findings include
- *multiple papules on the lips and gingivae,**
- papillomatosis (benign fibromatosis) of the buccal, palatal, faucial, and oropharyngeal
- mucosae often producing a “cobblestone” effect, and the tongue may also present as pebbly or fissured.
- • Multiple papillomatous nodules (histologically inverted follicular keratoses or
- trichilemmomas) are often present on the perioral, periorbital, and perinasal skin, the pinnae of the ears, and neck.
- • These nodules are often accompanied by lipomas, hemangiomas, neuromas, vitiligo, café au lait spots, and acromelanosis .
- • A variety of neoplastic changes occur in the organs exhibiting hamartomatous lesions,with an increased rate of breast and thyroid carcinoma and gastrointestinal malignancy.
- Squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue and basal cell tumors of the perioral skin have also been reported.
- Incredibly rare ( board loves it)
What is this clinical finding?

Inflammatory Papillary Hyperplasia of the Palate
What is these clinical findings? (what is the name of the syndrome or complex?)
Cowden Syndrome
Very rare!
Tuberous sclerosis complex
• is an inherited disorder caused by mutations in the tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC1 or TSC2) genes
• Characterized by seizures and mental retardation associated with hamartomatous glial proliferations and neuronal deformity in the central nervous system.
• Fine wart-like lesions (adenoma sebaceum) occur in a butterfly distribution over the cheeks and forehead, and histologically similar lesions (vascular fibromas) have been described intraorally.
• Characteristic hypoplastic enamel defects (pitted enamel hypoplasia)
occur in 40 to 100% of those affected.
• Rhabdomyoma of the heart and other hamartomas of the kidney,
Epulis Fissuratum
AKA
Cause
Location
Clinical presentation
Composed of
Treatment
• AKA: denture-induced fibrous hyperplasia, fibrous inflammatory hyperplasia
• Cause: ill-fitting denture
• Location: vestibule (maxilla or mandible), along the
denture border
•Clinical presentation: Arranged in elongated folds of tissue into which the
denture flange fits; • Surface ulceration within the folds is common
• Composed of dense fibrous connective tissue
• Treatment: surgical excision (scalpel vs CO2 laser -laser is better)
and reline then remake of denture
What is the clinical finding?

Pyogenic Granuloma
We can see the corresponding radiograph;
-although the radiograph suggests generalized bone loss, there is a lot of calculus on
the distal of #16 > it makes sense that this is a pyogenic granuloma

What is this clinical finding?

Pyogenic Granuloma:
Pyogenic Granuloma
Histology
They are filled with blood vessels so they’re very very rich
in vascularization > they tend to bleed easily

What is this clinical finding?

A parulis
It is not a pyogenic granuloma
A parulis is a proliferation of granulation tissue at the opening of a sinus tract
When the infection breaks through the alveolar bone and presents itself,
it will sometimes cause this proliferation of granulation tissue
Inflammatory Papillary Hyperplasia of the Palate
Majority occur with what disease?
Associated with what?
Clinical appearance
Treatment
- Majority occur with denture stomatitis
- Associated with a removable full or partial denture or orthodontic
- appliance (Something you see in patients who wear denture all the time, don’t take it out, chronic denture wear)
-
Clinical Appearance: Palatal vault is covered by multiple erythematous papillary projections (fibrous connective tissue surfaced by epithelium) –(papillary but no papilla, instead it’s bumpy and bosselated)
- Granular or cobblestone appearance
- Erythema is usually due to superinfection with candida
- Treatment:Treat underlying candidiasis, fix denture. These bumps can be removed, take electrosurgery loop, and scrape off the bumps – heals well
What is this clinical finding?

Peripheral Ossifying or Cementifying Fibroma
Lesion in the image is pedunculated – put a periodontal probe on normal gingiva and glide along underneath it, there’s a stalk
Peripheral Ossifying Fibroma
Histology
- When sessile, when removing it, take scalpel blade and just cut into it
- If has a little bone or cementum formation inside it, you can feel the bone with the scalpel

What is this clinical finding?

Peripheral Giant Cell Granuloma
Peripheral Giant Cell Granuloma
Histology
Giant cells inside the lesion

What are the 3P
or 4P?
• Pyogenic granuloma/pregnancy tumor
• Peripheral ossifying**_or_**cementifying fibroma
• Peripheral giant cell granuloma
• Peripheral fibroma (4P)
Memorize these well!
All benign soft tissue lesions
Pyogenic Granuloma
What a differential diagonsis to consider if we see it
- if it’s on the gingival tissues, take a radiograph
- always consider SCC as a differential diagnosis
What is this clinical finding?

Inflammatory Gingival Enlargement
Example of someone with true hyperplastic gingivitis
Maybe related to very poor plaque control
In this case, either porcelain or porcelain fused to metal full coverage restorations that have very
bulky margins, and that may play a role for food to pick up
Pyogenic Granuloma
What is it?
Etiology
Assossiated with which demographics?
Location?
Treatment?
- What is it? Reactive connective tissue hyperplasia - exuberant granulation tissue; Misnomer – not pyogenic and not a true granuloma
- Etiology: Response to injury - calculus or overhang restoration
- Assosiated with? Often occurs in pregnant women (“pregnancy tumor”), also associated with puberty
- Treatment: Excision and removal of irritant (eg calculus, overhanging restorations)
What is the Differential diagnosis of gingival enlargement
Acute Myelogenous Leukemia (AML)
Wegener’s Granulomatosis
Kaposi Sarcoma
Plasma Cell Gingivitis
Generalized gingival enlargement – all different cases and diseases

How to differentiate Pyogenic Granuloma from the other 2Ps ?
(Peripheral ossifying or cementifying fibroma & Peripheral giant cell granuloma)
- They often occur in the gingival, but can occur in multiple areas
- that’s the one thing that distinguishes this from the other 2 P’s: pyogenic granuloma can occur on ANY oral site, most commonly on the gingival tissues
What is this clinical finding?

Hereditary Gingivofibromatosis

Infantile
Hemangioma
(“strawberry” hemangioma).
Infant with two red, nodular masses on
the posterior scalp and neck
Neville Cr
Pyogenic Granuloma
Clinical appearance
Location
Size
Developing rate
Age:
- Clinical appearance
- Usually ulcerated
- Soft exophytic lesion, either sessile or pedunculated
- Deep red to purple in color, bleeds easily
-
Location:
- Most common – gingiva
- Also occurs in other areas of the oral mucosa ( can happen anywhere)
- Size: small to large (millimeters to centimeters)
- Develop rapidly and then remain static
- Age: Any age
How to recogonize a capillary Malformation?
When you apply pressure to it, it evacuates the lesion (disappears!), when you pull away, it refills and you see it again – that tells you it’s a vascular lesion

What is this clinical finding?

Capillary
Malformation (Low
flow)
How to differentiate between
Venous
malformation (low
flow)
from
Arteriovenous or
arteriolar malformations
(High flow)
Venous malformation
(Low flow)
No bruit, non-pulsatile
vs
Arteriovenous or
arteriolar malformations
(High flow)
Bruit and pulsatile
In other word, Venous lesion = Does not have pulse
Histopathologically they look different too
Treatment:
-Don’t biopsy this unless it’s rapidly growing, if it is rapidly growing then suspect ► angiosarcoma? ( unlikely)
-can be surgically treated by oral surgeons -clamping off the blood vessel and dissecting it out, or putting a sclerosis agent

What is this clinical finding?

Venous
malformation (low
flow)
Many pts can live with this without treatment
What are these clinical findings ( which syndrome or complex is this)?

Osler-Weber-Rendu
Syndrome
What are these clinical findings? (What is the syndrome or complex)?

Sturge-Weber
Angiomatosis
Sturge-Weber syndrome
What are these clinical findings (What is the syndrome or complex)?
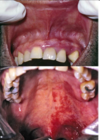
Sturge-Weber
Angiomatosis
Sturge-Weber syndrome
Notice how the vascular malformation is only one side..
Remember: Vascular changes follow trigeminal nerve, so it doesn’t cross midline
What is this clinical finding?

Lymphangioma
What is this clinical finding?

Cystic Hygroma
a type of Lymphangioma
Peripheral Ossifying or Cementifying Fibroma
What is it?
Clinical appearance
Derived from
Age
Sex
Reccurance rate
Treatment
- a reactive benign soft tissue lesion
- Clinical appearance: Well-demarcated, sessile or pedunculated lesion that appears to originate from the gingival interdental papilla
- Derived from: cells of the periodontal ligament
- Age: children and young adults
- Sex: females more than males
- Recurrence rate – about 16%
- Treatment: Surgical excision
What is this clinical finding?

Neuroma
(Traumatic Neuroma)
Not a benign true neoplasm, it’s reactive lesion
This is an edentulous patient, so resorbed bone, so flange of denture is impinging in the area of mental foramen – develop from repeated trauma
Sometimes have to cut into nerve, peel the neuroma from nerve, careful not to sever nerve

What are these clinical findings (Which syndrome or complex)?

Multiple Endocrine
Neoplasia (MEN)
Syndrome
What is this clinical finding?

neurofibroma
-it looks like lymphoepithelial cyst, but this is further anterior and not where you would get
lymphoid tissue – so it’s not lymphoepithelial cyst, it’s neurofibroma
Yellow – nerves typically yellow
What is this clinical finding?

neurofibroma
Peripheral Giant Cell Granuloma
What is it?
Location?
Age?
Clinical appearance:
Radiographic finding?
- What is it? Probably a reactive lesion due to local irritating factors (giant cells develop inside the lesion which is a benign soft tissue lesion)
- Location: Gingiva, usually anterior to the molars
- Age: Most frequently seen between 40-60 years old
- Clinical appearance: dusky purple, sessile or pedunculated, smooth-surfaced, dome-shaped papule or nodule. Most lesions are less than 1.5 cm in diameter, though infrequently, may grow as large as 5 cm in greatest dimension
- Radiographic Features: Usually none, but superficial destruction of the alveolar bone may occur
What are these clinical findings (which syndrome or complex)?

Neurofibromatosis syndrome
von Recklinghausen’s Disease
- Lisch nodules on iris, pigmented (eye picture)
- Neurofibromatosis in mouth (bottom left picture)
- Café au lait (bottom right picture)

What is the clinical finding?

Schwannoma/ Neurilemoma
What is this clinical finding?

Schwannoma/ Neurilemoma
Schwannoma/ Neurilemoma
Histology
Antoni A and Antoni B.
Streaming fascicles of spindle-shaped Schwann cells characterize Antoni A tissue.
These cells
often form a palisaded arrangement around central acellular, eosinophilic areas known as Verocay bodies. Antoni B
tissue is less cellular and less organized; the spindle cells are randomly arranged within a loose, myxomatous stroma.
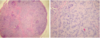
What is this clinical finding?

Granular Cell Tumor
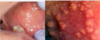
What is this clinical finding?
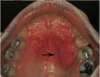
Granular Cell Tumor
Granular Cell Tumor
Histology
Has pseudoepitheliomatus hyperplasia of epithelium (seen on left picture)
Characteristic feature are the granular cells on the right picture
Infiltrate down into the muscle layers, that’s when pathologist confirms granular cell tumor

Diagnosis and Treatment
of the 3Ps
•Diagnosis: All 3 “P” lesions usually occur on gingival interdental papillae ( however pyogenic granuloma can occur anywhere)
• Since they can look similar clinically, excisional biopsy necessary to
determine diagnosis
• Treatment: complete excision and removal of local irritant (scaling
and root planing)
What is this clinical finding?

Congenital Epulis
Gingival Enlargement
Etiology
- Response to chronic inflammation
- Hormonal changes (pregnancy/puberty)
- Immune-mediated/plasma cell gingivitis
- Drug induced
- Genetic/ Inherited
NOTE: Gingival enlargement is not always hyperplastic tissue
What is this clinical finding?

Neuroectodermal tumor of infancy
look how they removed it here surgically
is rare, rapidly growing, pigmented neoplasm of neural crest origin. It is generally accepted as a benign tumour despite of its rapid and locally destructive growth.

Lipoma
What is it?
Location?
Cliniclly?
Histologically?
Treatment?
- What is it: Benign tumor of mature fat cells; Relatively rare
- Location:Won’t see on gingival tissue, will see on buccal mucosa, on the tongue, and floor of the mouth
- Clinically appears as a yellowish mass surfaced by thin overlying epithelium, When you feel it, it’s soft
- Histologically: a well-delineated tumor composed of mature fat cells with a thin capsule
- Treatment: surgical excision,does not recur

What is this clinical finding?

Lipoma
Usually very orange looking lesion in site where there’s adipose tissue
Very obvious, nothing as orange as lipoma
Drug Induced Gingival
Enlargement
What are the famous drugs that are known to cause it?
- Phenytoin: (or Dilantin) – the drug that used to be given to every single
- person that had seizures
- Calcium-channel blockers
- Nifedipine not as prescribed anymore
- Dilitiazem still prescribe
- Amlodipine: is prescribed as one of the first line therapy for hypertension (very commonly prescribed); it doesn’t typically cause gingival overgrowth except in some selected patients, usually
those with pretty poor oral hygiene
- Cyclosporine A (used for for bone marrow transplant, graft vs
host disease, solid organ transplant)- Cyclosporine is universally recognized as causing gingival hyperplasia
- Cyclosporine is largely replaced with Tacrolimus, which typically doesn’t cause gingival overgrowth
- Cyclosporine A is largely replaced with Tacrolimus, which typically doesn’t cause gingival overgrowth
Some drugs have more connective tissue component, others have more epithelial component
Not all identical under the microscope - Cyclosporine provides more epithelial change, Dilantin causes more of a connective tissue change
What is this clinical finding?

Vascular leiomyoma
High-power view showing spindle-shaped cells with bluntended
nuclei. Immunohistochemical analysis shows
strong positivity for smooth muscle actin (inset).

What is this clinical finding?

Rhabdomyoma

Will see the striated muscle
Differential diagnosis… looks like granular cell tumor – don’t know til you remove it
If patient presents with relatively slow growing tumor like this, will I get incisional biopsy or
excisional biopsy? Hard to say
If confident benign tumor and it’s this size and I don’t think it’s vascular (no pulse, can do
aspiration), feels firm – try to excise it
If it looks different, like you think it’s malignant minor salivary gland neoplasm (won’t find it in this
site, but if it’s on hard palate) – incision?
What is this clinical finding?

Leiomyosarcoma
Hereditary Gingivofibromatosis
What causes it?
How common?
what effects on oral cavity?
Treatment?
What causes it?
- Various genes that are implicate (Putative inherited mutations are in the SOS1 or CAMK4 genes.) Linked to both autosomal dominant and recessive patterns of inheritance
How common?
- Very rare
what effects on oral cavity?
- Sometimes gingival overgrowth will completely obliterate the teeth, grow around entire tooth
- Enlargement may be present at birth or may become apparent only with
the eruption of the deciduous or permanent dentitions. - Tooth migration, prolonged retention of the primary dentition, and
diastemata are common, and enlargement may completely cover the
crowns of the teeth, resulting in compromised oral function.
Treatment
- Need surgical (usually laser) treatment – just grows back, so have to get it done periodically
What are these clinical findings?

Rhabdomyosarcoma
In this case, hasn’t broken through epithelium
They don’t all break through
Infantile
Hemangioma
When do they appear?
Rate of Development
Clinical presentation
Treatment
- When do they appear? They are rarely present at birth, infants are Born with this in place.
- Rate of development: the tumor will demonstrate rapid development that occurs at a faster pace than the infant’s overall growth in the first few weeks of life,
-
Clinical presentation: Either superficial or deeper tumors
- Superficial tumors of the skin appear raised and bosselated with a bright-red color (“strawberry” hemangioma); They are firm and rubbery to palpation, and the blood, cannot be evacuated by applying pressure.
- Deeper tumors may appear only slightly raised with a bluish hue.
- May be left with a pink or magenta macule in site where hemangioma occurred after its involute
- Treatment: Typically will involute with time, Some cases don’t involute, so need to be removed
- It is a vascular Anomaly
What is this clinical finding?

Fibrosarcoma

Capillary
Malformation (Low
flow)
- a type of vascular anomaly
- CMs are commonly known as port wine stains.
- They look like a pink, red or purple patch of skin
- occur in 1 in 300 newborns.
What is this clinical finding?

Kaposi Sarcoma
Solitary vascular lesion on hard palate – it was so small so he decided to just excise it in this case^
What are these clinical findings?

Kaposi Sarcoma
- Widespread Kaposi, can see cutaneous lesions
- Oral images of this patient: on palate, starts with macule on patient’s left posterior palate –macular stage
- Then in becomes proliferative – exophytic nodular stage (seen on patient’s right anterior palate,surrounding canine and some incisors)
- Can see engorged blood vessels in area on histology slide
What is this clinical finding?

Plasmacytoma in Multiple Myeloma
- They already had multiple myeloma then developed plasmacytoma
- When you biopsy this, it’s filled with plasma cells bc they’re producing the abnormal immunoglobulins, which are the cause of the devastating issues of multiple myeloma

Acute myelogenous
leukemiawith
granulocytic
sarcoma

- *Complaining of lump inside of her cheek**
- *Notsomuch worried about her gingiva**, despite her overgrowth – leukemic infiltrates that got into gingival tissues
- *Left buccal mucosa**, kept biting on it, feeling incredibly fatigued though she was always working out
- *Oral surgeon biopsied** her buccal mucosa and read by pathologist as pyogenic granuloma
- *Physician** sent her for bloodwork, dental school sent her for bloodwork too
What is this clinical finding?

Lymphoma
- Well circumscribed ulceration in area
- Associated swelling in periphery
- White change in the patient’s left area
- Been there for 3 weeks
- It’s lymphoma
What is this clinical finding?

Looks like it could be a salivary gland neoplasm, but it’s not
It was another lymphoma
Manifest in a number of different ways
Case
40 year old male
Completely healthy otherwise
Not taking any medications
Presents with bump on the tongue
First question: did you do anything that might have led to this? Bite your tongue?
“possible I bit my tongue, or it could be when I had a dental procedure, maybe they accidentally
cut into the side of my tongue” – then it developed
This tells us, is this a reactive lesion?
Is it pedunculated or sessile? It’s pedunculated, larger at the top than the base
Let’s look at the surface: it’s ulcerated
When palpating, it’s only on the surface - don’t feel any submucosal presentation
Tongue underneath feels relatively normal
This bump is kind of firm and it bleeds like crazy when you touch it
When you look at teeth, no area where they’re too sharp

Do you think it’s a fibroma? No. Why?
Fibroma is covered with normal coloring epithelium – sometimes see a little white change on surface or see tiny traumatic ulcer on surface This is not like that, this is completely ulcerated
Not fibroma; fibroma is a chronic bump that patient is aware of
Is it squamous cell carcinoma? Interesting, it is indeed very friable; but no
Sometimes SCC can develop and can be exophytic and don’t have deep invasion, But this is pedunculated, SCC would not be pedunculated
History says there could be some kind of trauma, biting, or nick with bur – not squamous cell
Mucocele? No
Would you typically develop mucocele on lateral border of tongue? No
Not going to be as many mucoceles in this area, but there are the glands of Blandin and Nuhn, so it’s possible to develop on ventral surface of tongue
This bump doesn’t look like a fluid filled bump though, it has surface ulceration, redness ;Mucoceles have intact surface, would not bleed, or be red
Granular cell tumor? No
Granular cell tumor would have normal overlying epithelium (it’s pushing up from underneath)
This does not have normal overlying epithelium
Hemangioma reserved for congenital; not a vascular malformation either
Neurofibroma? No, not the same surface
Salivary gland neoplasms? Possible, there are salivary glands in that area; keep this in differential
The one that this is is pyogenic granuloma: usually red, ulcerated, and bleeds easily

Osler-Weber-Rendu
Syndrome
AKA
What is it and its clinical appearance
Type of Herditary and Etiology
What can it cause?
Location?
AKA
• Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia
What is it and its clinical appearance
• disorder of development of the vasculature characterized by telangiectases and
arteriovenous malformations in specific locations. These are essentially endothelial cell issue – get tafted area of abnormal blood vessels multiple different organ systems – causes complications
Type of Herditary and Etiology
•Autosomal dominant with mutations i_n at least five gene_s but mutations in two genes (ENG and ACVRL1/ALK1) cause approximately 85% of cases.
What can it cause?
• Can cause hemorrhage
Location?
often on fingers, lips,tongue, but always look at the fingers!
Sturge-Weber
Angiomatosis
Sturge-Weber syndrome
- Rare, non-hereditary developmental condition
- Vascular proliferation involving tissues of the brain and face
- Face: Unilateral distribution along one or more segments of the trigeminal nerve ( unilateral means don’t cross the midline) known as port wine stain/ nevus flammeus – they are deep-purple color.
- Intracranial calcifications; neurological disorders
- Intraoral involvement is common
Lymphangioma
What is it?
Types
Locations:
Treatment
What is it?
• Benign tumor of lymphatic vessels
Types
- Microcystic
- Mixed
- Cystic hygroma (macrocystic)
Location
- Most frequent extra-oral location: posterior triangle of the neck;
- intraoral location: tongue
Treatment:
monitor, surgery if needed, recurrence common
Neuroma
AKA
What is it?
Clinical presentation
Location
AKA
- traumatic neuroma
What is it?
- Reactive (ie not a true neoplasm) proliferation of nerve tissue after injury, usually extraction or other surgical procedure
Clinical presentation
- They are smooth-surfaced, nonulcerated nodules.
- May be painful (30% of cases) and sometimes associated with altered nerve sensations that can range from anesthesia to dysesthesia to overt pain
Location
- mental foramen area, tongue, lower lip
Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia (MEN) Syndrome
What is it?
Inhertiance type?
Which type is associated with multiple mucosal neruoma?
What other presentations?
Increase risk of which cancer?
What is it?
Group of rare conditions
Inhertiance type?
Autosomal dominant
Which type is associated with multiple mucosal neruoma?
Type 2B associated with multiple mucosal neuromas (one of the first
visual signs)
What other presentations?
• Marfanoid features
• Multiple tumors and hyperplasias of endocrine organs (ie
pheochromocytoma)
Increase risk of which cancer?
• Increased risk for medullary thyroid cancer (prophylactic thyroidectomy)
Common board questions
Neurofibroma
What is it?
Clinical presentation?
Location?
Treatment?
Mailgnancy?
What is it?
- A benign tumor arising from peripheral nerve tissue
Clinical presentation:
- Slow growing, painless lesion
- Smooth-surfaced, nodular mass that varies in size
- Skin more commonly involved than oral mucosa
Location:
- Common oral mucosal sites: tongue and buccal mucosa
- May develop centrally in bone
Treatment: surgical excision
Malignant transformation reported, but rare
Neurofibromatosis syndrome
Most common form?
intheritance type?
Clinical presntation?
Malignant transformation?
Most common form?
Several forms, type I is most common (von Recklinghausen’s Disease)
intheritance type?
• 85-97% of cases inherited as autosomal dominant trait, chromosome 17 (NF1 gene)
Clinical presentations:
- Skin nodules (neurofibromas)
- Café au lait pigmentation on skin
- Lisch nodules very diagnostic (a pigmented hamartomatou in the iris of the eyes)
Malignant transformation
- reported in 5% of cases (neurofibrosarcoma)
Schwannoma/ Neurilemoma
What is it?
Age?
Location?
Clinical presentation?
Treatment?
malignant
transformation ?
What is it?
• Benign neoplasm of Schwann cell origin
• Uncommon lesion: 28-48% occur in the
head and neck
Age?
• Most common in young and middleaged
adults
Location?
• Most common intraoral location:
tongue
Clinical presentation?
• The solitary schwannoma is a slow-growing, encapsulated
tumor that typically arises in association with a nerve trunk.
• May present with pain
• Treatment
• surgical excision
malignant
transformation
reported, but rare
Granular Cell Tumor
What is it?
Location?
Age?
Treatment?
What is it?
Benign tumor derived from
Schwann cells
Location?
• Oral cavity is the most common
location
• Vast majority of cases seen on
dorsal tongue
Clinical presentation?
- Typically an asymptomatic sessile nodule that is usually 2 cm or less in size (firm)
- The mass is typically pink, but some granular cell tumors appear yellow.
- The granular cell tumor is usually solitary, although multiple, separate tumors sometimes occur, especially in black patients.
- The lesion often has been noted for many months or years, although sometimes the patient is unaware of its presence.
Age:
40-60, rare in children
Treatment
• Treated by surgical excision (Be careful with excision! no need
to get all of it out, just most of it)
rarely recurs
Congenital Epulis
AKA
Cell resemble?
Cell origin?
Clinical features & location
Treatment?
• AKA: Congenital epulis of the newborn
• Cells resemble cells of the granular cell tumor
• Cell of origin is unknown, not derived from nerve
• Clinical features:
- Sessile or pedunculated mass, usually found on
- *the anterior** gingiva/ alveolar mucosa
- Almost always occurs in baby girls
- Present at birth
• Treatment:Surgical excision, does not recur
Neuroectodermal tumor of infancy
Location?
Rate of development?
Treatment?
Origin?
Clinical presentation?
Location?
Often occur as soft tissue mass largely in anterior maxilla
Rate of development?
So fast developing that it envelops and moves the teeth
Treatment?
Needs to be surgically excised
Origin?
Thought to be of neuroectodermal source
Clinical presentation?
Pigmented change in tissue
Lipoma vs Lipofibroma
- Sometimes lipomas can be mixed with fibrous tissue, can be lipofibromous
- Two lesions that look almost identical but one is lipoma, one is lipofibroma
- Only difference is that one has fibrous tissue in it, no other difference
Benign Tumors of Muscle
• Leiomyoma
• Benign tumor of smooth muscle
• Vascular Leiomyoma
• Benign tumor of smooth muscle walls of
blood vessels
• Rhabdomyoma
• Benign tumor of skeletal muscle
They are SUPERRR rare
If become malignant, they become leiomyosarcoma or rhabdomyosarcoma – malignant even
more rare
Leiomyosarcoma
- a type of rare cancer that grows in the smooth muscles.
- So, so rare
- Diseases that move rapidly, because they’re malignancies
- You might see surface ulcerations, they’re moving so fast, they break through the epithelium
Rhabdomyosarcoma
- is a type of sarcoma.
- Rhabdomyosarcoma usually begins in muscles that are attached to bones and that help the body move, but it may begin in many places in the body
What is Sarcoma ?
Sarcoma is cancer of soft tissue (such as muscle), connective tissue (such as tendon or cartilage), or bone.
Fibrosarcoma
what is it?
Age?
Rate of growth?
Treatment?
Survival rates?
•What is it? Malignant tumor of fibroblasts
• Age? Most common in young adults and
children
• Rate of growth? Slow growing lesion that is usually not
painful (Can be slow growing, can be rapidly growing – different criteria determining high or low grade)
• Treatment: surgical excision, recurrence is common(Aren’t always easy to surgically remove, because already metastasized into other reservoirs, spread into contiguous areas) Aren’t always radiosensitive, don’t always respond to radiation treatment
• 5-year survival rates range from 40-70%
Vascular Malignant Neoplasms
• Angiosarcoma
• Malignant tumor of blood vessels
• Lymphangiosarcoma
• Malignant tumor of lymphatic vessels
• Kaposi’s sarcoma
- Malignant neoplasm associated with endothelial cells
- Seen predominantly in poorly controlled HIV infected patient population (not exclusively)
- Elderly people can develop Kaposi
Kaposi Sarcoma
Etiology
Types
Treatment
Etiology:Caused by HHV-8 (human herpesvirus 8) /part of herpes family
Types:
- Classic: late adult life, Italian and Jewish men, skin of lower extremities
- Endemic: African form
- Iatrogenic immunosuppression-associated: most often occurs in recipients of organ transplants
- AIDS-related
Treatment
- Surgical excision, radiation therapy or systemic chemotherapy for multiple nonoral lesions, if it gets large, dose-radiation therapy!
Plasmacytoma in Multiple Myeloma
Presents as soft tissue lesion
It is possible that a patient can present with plasmacytoma that would be the first sign of multiple
myeloma (it would be a rare sign, but it can happen)
Lymphoma
- Lymphoma is a general term for a complex group of heterogeneous lymphoreticular malignancies.
- Lymphoma is the sixth most common malignancy and the second most common neoplasm of the head and neck after squamous cell carcinoma and accounts for 50-59% of head and neck neoplasms in children.
- They constitute approximately 3-5% of all known malignancies and are generally divided into two morphologically distinct types: Hodgkin’s lymphoma (HL) and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (NHL).
- These malignancies typically arise within the lymphatic tissues and can progress to extranodal disease as in NHL.
- Cervical lymph node involvement can be present in any type of lymphoma.
- HL extends by means of contiguous nodal spread whereas NHL tends to disseminate hematogenously and is typically a systemic diagnosis.
- Within the head and neck, Waldeyer’s ring is the most common site of involvement, accounting for more than half of all extranodal head and neck lymphomas.
- Oral involvement by lymphoma may represent a localized disease process but is more often part of a systemic process that secondarily involves the cervical lymph nodes.
- Lymphoma arising within the oral cavity accounts for less than 5% of all oral malignancies, and approximately 85% of these lesions involve the pharyngeal tonsil and the palate
- Extralymphatic sites include the salivary glands, paranasal sinuses, oral cavity, and larynx.
ADENOMA
benign tumor
of glandular origin
Characteristics of a Benign Tumor:
Encapsulated ‐ distinguishable from surrounding tissues
Freely movable ‐ not fixed
Slow growing
Non tender ‐ patients do not complain of pain
BENIGN SALIVARY GLAND
TUMORS
(list 3)
Pleomorphic adenoma aka mixed tumor
Monomorphic adenomas
o Canalicular adenoma
o Basal cell adenoma
Warthin tumor (papillary cystadenoma lymphomatosum)
PLEOMORPHIC ADENOMA
(MIXED TUMOR)
- This tumor comes in many forms/shapes
- Most common salivary gland tumor
- Painless, slowly growing, firm mass
- Adults (30‐50 years old) ; slight female predilection
- Sites:
- 50% to 77% of parotid tumors (most commonly found in parotid-2/3rd to 3/4th of parotid tumors)
- Minor SG: palate>upper lip>buccal mucosa> other site (most common intraoral site is the palate)
- Malignant transformation possible in long standing lesions (about 5% cases) ‐> called Ca ex PA
What is this clinical finding?

PLEOMORPHIC ADENOMA
(MIXED TUMOR)
What is this clinical finding?

PLEOMORPHIC ADENOMA
Classic presentation: includes swelling in the parotid region
(MIXED TUMOR)
What is this clinical finding?

PLEOMORPHIC ADENOMA
Palatal presentation: since salivary glands are only in lateral sides of the palate, usually
swellings are in one side and not the midline. Lateral swelling is a clue that you are
looking at a salivary gland lesion (left pics)
On the right pic, it involved midline and crossed over to other side, so there are
exceptions. But more commonly found in lateral side of the palate.
(MIXED TUMOR)
What is this clinical finding?

PLEOMORPHIC ADENOMA
- Upper lip presentation: sometimes swelling can be seen extra orally and intraorally.
- Remember the swelling will be movable, not tender, not fixed to underlying structures.
(MIXED TUMOR)
What is this clinical finding?

Untreated pleomorphic adenoma
slow growing, but can grow to enormous sizes
Pleomorphic adenoma
histology
This is a mixed tumor with myxoid component (right) and
fibrous/epithelial component(left)
This type of tumor can produce a lot of different tissues, since the origin is from myoepithelial cells aka plasmacytoid cells, which are pluripotent cells which means they can differentiate into many different lineages of cells such as

What is this clinical finding?

Canalicular Adenoma
What is this clinical finding?

Canalicular Adenoma
- Mucocele might look this way, but what would make it lower on
- differential diagnosis is the location of the swelling. Mucocele is mostly seen on lower lip and this pic shows upper lip. Salivary gland tumors and mucoceles
- can have the same clinical presentation, so always do a biopsy for formal histopathology diagnosis.
Basal Cell Adenoma
- Basaloid appearance of the tumor cells
- Primarily parotid lesion
- predominantly in women over 50 years of age. It is uncommon in young adults.
(Basal cells are located in epithelium that is adjacent to interface with the connective tissue and they are separated from the CT by a basement membrane, stem cells of epithelium are located in basal cell layer)
Basal cells are typically Blue in appearance and cuboidal,

What is this clinical finding?
Basal Cell Adenoma

What is this clinical finding?

PAPILLARY
CYSTADENOMA
LYMPHOMATOSUM
(WARTHIN TUMOR)
MUCOEPIDERMOID
CARCINOMA
Charcterstics?
Location
Clinical appearance in minor gland
Can be mistaken for
Histopahtology
Most common malignancy of salivary glands
Most common malignant SG tumor in children
Locations
Palate, most common intraoral site
Rare primary intrabony (jaws) tumors
Most common in parotid
Minor SG: palate 2nd
Clinical appearance in minor gland: asymptomatic fluctuant swelling; blue or red colored
Can be mistaken for mucocele
Histopathology: note the cells growing into adjacent tissue, showing infiltration

Monomorphic Adenomas
What is it?
Types?
Treatment?
What is it?
Proliferation of 1 type of cell makes up the tumor.
Types? Includes:
o Canalicular Adenoma
o Basal Cell Adenoma
Treatment for all monomorphic adenomas is surgical excision & diagnosis is done with biopsy
What is this clinical finding?

MUCOEPIDERMOID
CARCINOMA
What is this clinical finding?

MUCOEPIDERMOID
CARCINOMA
Request all for biopsies!
What is this radiographical finding?

CENTRAL
MUCOEPIDERMOID
CARCINOMA
- Intrabony presentations, may have extraoral swelling depending on the stage
- Started as small swelling and progressed rapidly:, need to pick it up early!
- Patient recovered, but might need radiation, lost salivary glands, needed reconstruction of palate
Canalicular Adenoma
- Almost exclusively in minor SG
- Striking predilection for upper lip (>75%)
- Nearly always occurs in older adults
- Slowly growing, painless mass
- One clue for visualization of soft tissue swellings is increased vascularity with blue‐ish tint in the area.
What is the clinical finding?

ACINIC CELL
ADENOCARCINOMA
What is the clinical finding?

ACINIC CELL
ADENOCARCINOMA
blue‐ish tint
What is this clinical finding?

Untreated acinic cell adenocarcinoma
Because it is slow growing, and a low grade tumor, the
patient is alive and not dead with a tumor this size.
Similar presentation to pleomorphic adenomas, but there is a lot of ulceration on the surface and prominent vascularization in acinic cell
adenocarcinoma.
Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma
High grade salivary gland malignancy ( very bad cancer to get)
Adults
Palatal mass; ulcerations
Spread through perineural invasion ‐ tumor wraps itself around nerves and spreads through perineural spaces
Grows slowly in the beginning and then picks up speed
Histology: Duct like proliferation with cystic spaces

What is this clinical finding?

Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma
What are these clinical findings?

Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma
What are these clinical findings?

Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma
Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma
Swiss cheese appearance, cribriform pattern (full of holes aka cystic spaces)

Perineural invasion Histology
Perineural invasion: nerve nuble in the
center and is wrapped by tumor

What is this clinical presentation?

Polymorphous
Adenocarcinoma
What is this clinical presentation?

Polymorphous
Adenocarcinoma
What is this clinical finding?

Carcinoma Ex Pleomorphic
Adenoma
PAPILLARY
CYSTADENOMA
LYMPHOMATOSUM
(WARTHIN TUMOR)
- finger‐like projections, benign, cystic spaces, aggregates oflymphocytes)
- Vast majority occur within the parotid gland
- Very rare intraorally
- Predominantly in men
- Typically between 5th and 8th decades
- Strong correlation with cigarette smoking
- Most common SG tumor to occur bilaterally (bilateral parotid swelling), but can be unilateral
- Etiology: Thought to arise within lymph nodes as a result of entrapment of
- salivary gland elements early in development
-
Clinical Features:
- swelling that has more subtle presentation
- Doughy to cystic mass
- In the inferior pole of the gland, adjacent and posterior to the angle of the mandible
- Treatment: surgical excision, responds very well to it
Summary for benign
tumors
Encapsulated, freely movable, not fixed to underlying structure, not tender, patients do not complain of pain, slow growing
There is one tumor of the ones discussed that does have a risk of malignant transformation (only 5% and will take many, many years) and that is Pleomorphic adenoma
MALIGNANT SALIVARY
GLAND TUMORS
List 5
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma
Acinic cell carcinoma
Adenoid cystic carcinoma
Carcinoma ex‐mixed tumor/malignant mixed tumor
Polymorphous adenocarcinoma
CLINICAL FEATURES OF
ADENOCARCINOMAS
(malignant gland tumors)
Infiltrative
Fixed to underlying structures, not moveable
Rapid or slow growth, depending on grade and type of malignant salivary
gland tumor
Larger, rapidly growing lesions may cause pain and/or paresthesia
Ulcerated overlying mucosa
MUCOEPIDERMOID
CARCINOMA
What are its compoenents?
Within jaw prognosis
Treatment
Prognosis
Therapy by gene?
What are its compoenents? Mixture of mucus‐producing cells and epidermoid or squamous cells
May arise within jaws from odontogenic epithelium of dentigerous cysts
• More common in the mandible than maxilla
• Molar‐ramus area
Treatment: Usually treated by surgical excision
Prognosis:
• Overall prognosis is fairly good
• 10% of patients die, due to local recurrence or metastasis
Low‐grade tumors have good prognosis (>90% are cured)
High‐grade tumors the prognosis is guarded (Only 30% survive)
Therapy by gene?
CRTC1–MAML2, CRTC3‐MAML2 gene fusions (targeted therapy)
ACINIC CELL
ADENOCARCINOMA
- Occurs predominantly in major SGs,
- Found in all age groups, peak incidence in 5th and 6th grade
- No gender predilection
- Malignancy with serous acinar differentiation
- Most common in the parotid (since 90% serous acini)
- Variable microscopic appearance
- May even appear encapsulated, since it is SLOW growing
- Better prognosis than salivary gland malignancies
Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma
Location
Growth rate
Clinical presentation
Treatment
Prognosis
Location:
Approx. 50% occur within the minor SG ‐ palate most common site
Growth rate
Usually a slowly growing mass
Clinical presentation
Pain is a common and important early finding, occasionally occurring before there is noticeable swelling (described at annoying pain)
Tendency to show perineural invasion, corresponds to pain
Treatment
Excision usually the treatment of choice ‐ but edges of tumor may have perineural invasion and remain undetected ‐ makes tumor dangerous
Prognosis
5‐year survival rate as high as 70% (maybe 90%)
By 20 years, only 20% ‐ poor long term prognosis
Polymorphous
Adenocarcinoma
Location
Gender
Appearance
growth patterns
Treatment
- Location:
- Almost exclusively in the minor SG
- 60% on the hard or soft palate
- Gender”
- 2/3rds in females
- Appearance:
- Tumor cells have deceptively uniform appearance
- Growth patterns:
- Different growth patterns – polymorphous
- Perineural invasion ‐ common ‐ but considered low grade tumor
- Treatment: Wide surgical excision; overall prognosis relatively good, with 80% cure rate
Carcinoma Ex Pleomorphic
Adenoma
What is it?
Mean age?
Growth pattern
Treatment?
Prognosis
What is it? (benign tumors that have underwent malignant transformation‐ takes a lot time, 15 to 20 years)
Mean age about 15 years greater than benign counterpart
Growth patterns: Mass present for many years with recent rapid growth with associated pain or ulceration
Treatment: Best treated by wide excision, with local node dissection and radiation
Prognosis: guarded, with 50% local recurrence or metastases and dying Prognosis is case to case scenario, may transform to high grade tumor
What are the FREQUENCY OF SALIVARY
GLAND TUMORS BY
LOCATION
Lower lip
o Mucocele
o Mucoepidermoid Ca
o Pleomorphic Adenoma
What are the FREQUENCY OF SALIVARY
GLAND TUMORS BY
LOCATION
upper lip
o Canalicular Adenoma
o Salivary Duct Cyst*
o Pleomorphic Adenoma
What are the FREQUENCY OF SALIVARY
GLAND TUMORS BY
LOCATION
Parotid
o Pleomorphic adenoma
o Warthin’s tumor
o Basal cell adenoma
o Mucoepidermoid ca
o Acinic cell ca
o Adenoid cystic ca
o Ca ex mixed tumor
What are the FREQUENCY OF SALIVARY
GLAND TUMORS BY
LOCATION
Palate
o Pleomorphic adenoma
o Adenoid cystic ca
o Mucoepidermoid ca
o PLGA
o Monomorphic adenoma
SG Tumors: Summary of
Key Points
Involve both major and minor glands
Benign and malignant tumors both have similar
clinical presentation
Most malignant salivary gland tumors do not show histopathologic
characteristics associated with malignancy
Most occur in adults
Warthin Tumor seen in parotid, may be bilateral
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma
o Can occur in children
o May occur centrally in bone
Palatine Torus/Torus Palatinus
- Tori are incredibly common, a normal of variant
- Part of physical exam is to visualize as well as running index finger over the hard palate every time
- Sometimes, torus palatinus is quite small and unnoticeable until you touch it (feel a hard bump and it’s just a bony growth)
- Sometimes, they are pedunculated; Sometimes, they get so large they become traumatized; vascular supply on surface can sometimes form ulcerations and even get a little bone exposure.
- If patient with history of use of bisphosphonates (bone modifying agents given to women who have osteoporosis or osteopenia and to prevent metastesis for certain cancers), he will remove that dead bone, and it will slowly heal. That’s one of the perils of having an enlarged palatine torus
What is this clinical finding?

Palatine Torus/Torus Palatinus
What is this clinical finding?

Palatine Torus/Torus Palatinus
What is this clinical finding?

Mandibular Torus:
Torus Mandibularis
What is this clinical finding?

Mandibular Torus:
Torus Mandibularis
What is this clinical finding?

Buccal Exostoses
Mandibular Torus: Torus Mandibularis
- Sometimes pt’s tori are so large that the sublingual frenum gets stuck underneath
- repeated irritation/trauma can create a little white rim on the tori
- these tori are rock hard and may grow overtime, but we don’t really understand why people get them
What is this clinical finding?

Unencapsulated Lymphoid Aggregates
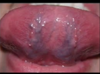
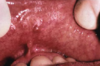
What is this clinical finding?

Lymphoepithelial
cyst
we see a tiny yellowish cyst. we see the blood vessels on the surface; this is quite characteristic.
What is this clinical finding?

Unencapsulated
Lymphoid
Aggregates
Post-tonsillectomy
Can even develop these on area of tonsils.
(left pic) Red/salmon is a lymphoid aggregate (unencapsulated lymphoid tissue). This is someone
who had a tonsillectomy , and you can see these
lymphoid aggregates on posterior pharyngeal wall (salmon color).They move around the area.
(right pic) It grew back even in post-tonsillectomy patients.
What is this clinical finding?
Fordyce Granules
What is this clinical finding?

Fordyce Granules
Buccal Exostoses
- Sometimes patient develops exostoses (another word for torus).
- Can get buccal exostoses, all just bone. Can pick these up on radiograph, the bone is a lot denser.
Why does it happen?
- Maybe it’s related to parafunctional habits – but don’t really understand the
- basis for the exostosis.
- They’re going to be bilateral. If it’s unilateral, we start thinking about other bony diseases
a variant of normal
What is this clinical finding?

Fimbriated
fold/Plica
semiluminaris
What is this clinical finding?

Frenal tag
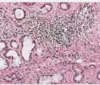
Unencapsulated Lymphoid Aggregates
- the lymphoid aggregates are part of the foliate papillae (they contain some taste buds as well).
- This is lymphoid tissue -- when you get a cold or upper respiratory tract infection, sometimes these areas can become hyperplastic in response to infection – can become a little enlarged.
- These are usually bilateral.
- a variant of normal
What is this clinical finding?

Sublingual Varices
What is this clinical finding?
Sublingual Varices
What is this clinical finding?

Sublingual Varices
What is this clinical finding?

Circumvallate papillae
What is this clinical finding?

Parotid Papillia (Stenson duct)
What is this clinical finding?

Parotid Papillia (Stenson duct)
What is Lymphoepithelial
cyst?
a cystic structure.develops in that area where there are already unencapsulated lymphoid tissue.
This is not normal – Pathologic
Sometimes when you get a cyst in this area – because of lymphoid tissue, you can develop lymphoepithelial cyst – a tiny yellowish cyst. we see the blood vessels on the surface; this is quite characteristic.
What is this clinical finding?

Linea Alba
What is this clinical finding?

Leukoedema
Fordyce Granules
- Occurs on the buccal labial mucosa, retro molar pad and tonsillar area and lips
- They are white or yellow ectopic sebaceous glands
- They can be present in small or large quantity
- Why do we have sebaceous glands in mouth? we dont know, evolutionary advantage? we don’t really understand.
- a variant of normal
What is this clinical finding?

Palatal Rugae
Fimbriated
fold/Plica
semiluminaris
- Some patients have more obvious fimbriated folds or plica semilunaris in their mouths than others
- When you look at the ventral surface of the tongue, you’ll sometimes be able to pick these up.
- These are duct opening from a series of salivary glands, minor glands, but they’re a little bit different than other minor glands in the mouth.
- They produce more of a viscous type of saliva, and they are the glands of the Blandin and Nuhn
- a variant of normal
What is a Frenal tag?
- Frenal attachments are thin folds of mucous membrane with enclosed muscle fibers that attach the lips to the alveolar mucosa and underlying periosteum.
- Most often, during the oral examination of the patient the dentist gives very little importance to the frenum, for assessing its morpholology and attachment.
- Sometimes occur; essentially normal of varient
Sublingual Varices
- Tortuous dilated vessels (enlarged engourged veins) on the ventral surface of the tongue, and sometimes stretch onto lateral border
- Appears bluish purple in color
- More prominent with increasing age; we don’t see it in younger pts.
- Nothing to be concerned about, a variant of normal
Circumvallate papillae
- Located in the posterior region of the tongue; dividing the body from the base
- They are mushroom shaped and arranged in V-shape formation
- Although they are usually not apparent in most patients, you may be able to visualize them in some
- a variant of normal
Parotid Papillia (Stenson duct)
- Located in right and left buccal mucosa at the level of the occlusal plane close to the maxillary first and second molar.
- This structure may appear as a small dot or have a prominent pink to red papillae presence.
- This is the parotid papilla, and It is the opening of the parotid duct which drains saliva from the parotid gland.
A normal of variant
Linea Alba
•a white line or keratotic area that present along occlusal plane in some patients
- due to some friction In that area. (the buccal mucosa)
- It varies in thickness and opacity
- Can be seen in some patients who have bruxism
- a variant of normal
Leukoedema
- A bluish and white filmy opalescence of the mucosa is observed
- In order to differentiate it from other white lesions à gently stretch the patient’s cheek forward and the leukoedema will disappear or partly fade and appears less apparent
- It is commonly found in people of color and some smokers.
- a variant of normal
Palatal Rugae
- Raised ridges or folds
- Located in the anterior palate on either side of the mid-palatine raphe behind the incisive papilla
- They vary in number and size
- May increase with age
- a variant of normal
Inflammatory/Reactive Lesions of the Salivary Glands
List 5
- mucocele/mucous cyst
- ranula
- necrotizing sialometaplasia
- sialolithiasis
- sialadentitis
Mucocele
Definition
Clinical features
Location
Histological features
Treatment
• definition: a lesion that forms when a salivary gland duct is severed & secretion spills into the adjacent CT
• a pseudocyst (not lined by epithelium) — mucous builds up in the CT & causes a bump
• clinical features:
- swelling in the tissue that may increase & decrease in size
- may have a bluish hue, fluctuant on palpation — fluid filled, soft, compressible
• location: lower lip most common site, but may form in any area where there are minor salivary glands
• histologic features:
- a cyst-like space in soft tissue
- lined by compressed granulation tissue
- lumen filled with mucin, foamy macrophages & inflammatory cells
• treatment: surgical excision, removal of associated minor salivary glands
• may recur if don’t remove all associated injured minor salivary glands

What is this clinical finding?

Mucocele
What is this clinical finding?

Mucous Cyst
What is this clinical finding?

Ranula
Notice how it’s unilateral
on the floor of the mouth
What is this clinical finding?

Ranula
- Notice how it’s unilateral*
- on the floor of the mouth*
Necrotizing Sialometaplasia
Definition
Predisposing factors
Clinical features
Histologic features
Treatment
• Definition: locally destructive inflammatory condition — looks malignant but is benign
• salivary gland ischemia — “heart attack of the palate”; blood flow is interrupted
• predisposing factors:
- local trauma
- palatal injection of local anesthesia
- previous surgery
- many are idiopathic..
• usually a clinical diagnosis based on history & how fast — palate uncommon for SCC
• clinical features:
- initially appears as a non-ulcerated swelling of the palate
- often associated with pain or paresthesia
- within 2-3 weeks, necrotic tissue sloughs off & becomes a crater-like ulcer
- patient may say: “a chunk of the roof of my mouth fell out”
• histologic features:
- necrosis of the salivary glands — coagulative necrosis (green circles in histology —>)
- salivary gland duct epithelium is replaced by squamous epithelium — appear as islands of squamous epithelium deep in the CT & resembles SCC (arrows in histology —>)
• Treatment: no treatment, spontaneously resolves within 6 to 10 weeks
• irrigating & debriding the area can reintroduce vascularity & help healing

What is this clinical finding?

Necrotizing Sialometaplasia
Sialolithiasis
Definition
Location
Origin
Clinical features
Radiological features
Histological features
Treatment
Definition: lith = stone ;; sialolith: a salivary gland stone
Location: occur in both major & minor salivary glands
• floor of the mouth is most common location (Wharton’s duct is a common place)
• often causes obstruction of the duct
Origin: arise from desposition of calcium salts around nidus of debris within the duct lumen
- *clinical features:**- minor glands: hard yellowish structure in soft tissue
- may be visible on a radiograph
- recurrent swelling (due to the obstruction)
- episodic pain & swelling during times of increased salivation
- can be palpated if the stone is located toward the terminal portion of the duct
- *Radiological features** : may be viewed as a radiopacity on an occlusal x-ray–well defined radiopacity
- *Histological features-** concentric rings of calcification, color of it in stain depends on level of calcificatio
- *Treatment**: promote passage of stone (massage, sialogogues, increase fluid intake) or surgical removal

What is this clinical finding?

Sialolithiasis
What is this clinical finding?
Sialolithiasis
Notice how it can appear radiographically as a well defined radiolucency

What is this Radiographical finding?

Sialolithiasis
Mucous Cyst
Definition
Clinical features
Histological features
Treatment
•Definition: a pseudocyst
• microscopicallly appears as an epithelial lined cystic structure that is actually a dilated duct
• clinically you CANNOT tell the difference between a mucocele & mucous cyst
• clinical features:
- same as a mucocele
• histologic features:
- same as mucocele but will see an epithelial lining (but actually a dilated duct)
treatment: same as mucocele; surgical excision
What is this clinical finding?

Sialadenitis
Acute: parotid papilla purulent discharge
What is this clinical finding?

Sialadenitis
Chronic: caused fibrosis
Summery
of inflmattory salivaory conditions
Mucocele
- fluctuant swelling
- bluish hue
- lower lip most common
Ranula
- fluctuant swelling
- floor of mouth
Sialolithisis
• major glands: episodic pain &
swelling of affected gland
• minor glands: asymptomatic/
local swelling or tenderness
• if superficial - firm to palpation
& yellowish color
Necrotizing
Sialometaplasia
• initial painful swelling
• later necrotic ulcer
• posterior lateral hard
palate & soft palate
Sialadenitis
• painful swelling of
affected gland
• purulent discharge if
acute infection

Ranula
Definition
Associated with
Clinical features
Treatment
• Definition: mucocele-like lesion that forms unilaterally on the floor of the mouth
• may break through the mylohyoid muscle & enter neck space = “plunging ranula”
• associated with: the ducts of the sublingual & submandibular glands
• clinical features:
- must be on floor of the mouth for it to be considered a ranula
- big & have deep blue color if exophytic
- sometimes can grow downward/deep & won’t see blue as much
• treatment: surgical excision
Sialadenitis
definition
causes:
clinical features:
histologic features:
Treatment:
• definition: acute or chronic inflammation in major or minor salivary glands
• causes:
• obstruction of a salivary gland duct (sialolith)
• infection (mumps [viral], staph aureus [bacterial, most common], candida [fungal])
• decreased salivary flow (Sjogren’s, sarcoidosis)
• parotid gland = parotitis
• clinical features:
- acute: most common in parotid, swollen & painful gland, erythematous & warm overlying mucosa/skin, purulent discharge, low-grade fever
- chronic: caused by recurrent or persistent ductal obstruction, periodic swelling & pain
• histologic features:
- acute or chronic inflammatory cell infiltrate in the salivary gland
- in chronic cases = salivary gland replaced by fibrous CT & fat
- cells: acute = neutrophils ;; chronic = lymphocytes, plasma cells, macrophages
• Treatment: antibiotics, rehydration, surgical drainage, or surgical removal of gland


