Smith 1 Flashcards
1
Q
View vs projection
A
- View = portion closest to the film cassette
- Porjection = portion which the X-ray beam enters
Anterior-posterior projection can be considered a posterior-anterior view
2
Q
Sesamoids
A
bones within a tendon
sesamoids under the first metatarsal are constant
3
Q
Anterior-posterior (AP) Projection
A
- Structures demonstrated = phalanges, Sesamoids, metatarsals and tarsal bones
- Central ray: (where you shoot)
- angle 15 degrees cephlad
- base of third metatarsal
- Patient position = standing with foot on exposable side of film in angle and base of gain on orthoposer

4
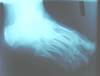
Q
Medial oblique view (MO)
A
- Structures demonstrated = phalanges, metatarsals, tarsal bones and sesamoids
- More lateral structures
- Central ray:
- angle tube 45 degrees aimed at lateral cuneiform
- Patient postion = standing in angle and base of gait on orthoposer
5
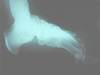
Q
Lateral oblique view (LO)
A
- Structures demonstrated = Phalanges, metatarsals, tarsal bones and sesamoids
- more medial structures
- Central ray:
- angle tube 45 degrees aiming at medial cuneiform
- Patient position = standing in angle and base of gait on orthoposer
6
Q
Lateral projection of the foot
A
- Structures demonstrated = First metatarsal, hallux, medial cuneiform, navicular, talus and calcaneus
- Central ray
- 90 degress or perpendicular to the lateral cuneiform
- Patient position = standing in angle and base of gain on orthoposer

7
Q
Raised Lateral hallux
A
- structures demonstrated = proximal and sital phalanges of the hallux
- central ray
- 90 degrees or perpendicular to the center of the hallux
- Patient position
- standing in angle and base of gait on orthoposer with foam under hallux to decrease overlap of other toes

8
Q
Sesamoid or plantar axial
A
- structures demonstrated = inferior aspect of the metatarsal and sesamoids
- central ray
- perpendicular to the film and aim at inferior heel
- Patient position = standing with foot on block

9
Q
calcaneal axial
A
- Structures demonstrated = subtalar or talocalcaneal joint and the calcaneus
- Central ray
- 45 degrees aimed at the posterior subtalar or talocalcaneal joint
- patient position = patient standing on the film in angle and base of gait

10
Q
anterior-posterior (AP) projection of the ankle
A
- Structures demonstrated = tibia, fibula, talus and ankle joint
- central ray = anterior ankle joint
- Patient position = patient standing on orthoposer with back of leg against the film

11
Q
ankle mortise
A
- structures demonstrated = tibia, fibula, talus and ankle joint
- decrease overlap between tibia and fibula
- Central ray = anterior ankle joint
- Patient position = same as anterior-posterior with foot rotated twoards midline 15 degrees

12
Q
know diffrences of each
- like maltese and ap of ankle
- projection vs view def
- what type of images for looking at anatomical structures
A
13
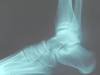
Q
Lateral projection of the ankle
A
- Structures demonstrated = tibia, fibula, talus, calcaneus and ankle joint
- central ray = perpendicular to the film with ray entering lateral malleolus
- Patient position = standing with medial malleolus against film
14
Q
Ottawa rules
A
- uses an instrument for assessment of foot and ankle
- Don’t get an X-ray if:
- ability to walk 4 steps
- no pain in posterior edge or tip of malleoli
- no pain at navivular or base of fifth metatarsal
- Designed to rule out fractures


