SM 117a/130a/131a - ECG I, II, III Flashcards
Depolarization of the ventricles leads to which ECG manifestation?
The QRS complex

Which ECG leads will provide information about the function of the left circumflex artery?
- Lateral leads
- V5
- V6
- High lateral leads
- I
- aVL
- Sometimes inferior
- II
- III
- aVF

Which ECG lead goes from the chest to the left leg?
aVF
(- in chest to + in left leg)
In which ECG leads is a Q-wave always pathologic?
Lead III, aVR
(If in both - may be normal if only in Lead III?)
- “It is normal for small q waves to be present in III: a q-wave in III and no other lead rarely represents an MI • There are normally SMALL q-waves in V5 and V6 (the “septal q-waves” that are part of normal activation of the ventricles: look at a V5 or V6 of a normal ECG) • Q-waves should be present in at least 2 contiguous leads (i.e. 2 inferior leads, 2 anterior leads, 2 lateral leads) “*
- Thank you @Caroline Kratka :)*
Where is V2 placed?
Which coronary artery supplies this lead?
4th intercostal space, left sternal border
Supplied by the LAD (Septal lead)

What must be true for a Q wave to be pathological?
Duration > 0.03 seconds (1.5 small boxes) or 0.02 seconds in V2 or V3
AND
Amplitude > 0.1 mV (1 small box)
AND
Present in at least 2 contiguous leads (ex: 2 inferior, or 2 anterior, or 2 lateral)
Note: Small Q waves are normal in III, V5, V6
Describe the stages of STEMI and associated ECG findings
-
Hyperacute phase: mins after acute occlusion, may last hrs
- Tall, peaked, hyperacute T-waves, with or without ST elevation
- Usually over by the time the patient gets to the ER -
Acute phase: Begins hrs after occlusion, may last days
- Elevated ST segment
- T waves are less tall than hyperacute phase
- Q waves may appear -
Later
- T waves begin to invert
- ST segment may remain elevated, or may return to baseline -
Even later (old MI)
- Q waves present: hallmark of myocardial scarring (can be avoided with proper treatment!)
What is the rule for determining heart rate using the little boxes?
1500/(# of little boxes) = heart rate
Which component of the ECG corresponds with the AV delay?
PR interval
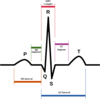
Which ECG lead is perpendicular to lead II?
aVL
Where is V1 placed?
Which coronary artery supplies this lead?
4th intercostal space, right sternal boarder
Supplied by the LAD (V1 is a septal lead)

Which ECG finding is the “hallmark of myocardial scarring,” indicative of an old MI?
Q wave
If you see inverted T waves and elevated ST segments on a patient’s ECG, which stage of STEMI are they likely in?
After the acute phase (or the later portion of the acute phase)
Depolarization of the atrium corresponds with which ECG feature?
P-wave

If there is ischemia in the lateral wall of the LV, in which ECG leads would you see abnormalities?
Which coronary artery?
aVL, V4, V5, V6
Circumflex branch
Which ECG lead goes from right arm to left leg?
Lead II
(- on right arm to + on left leg)
Repolarization of the ventricles results in which ECG component?
T-wave

Which ECG lead goes from the abodomen-area to the right arm?
aVR
(- in abdomen to + on right arm)
Which lead has its (+) endpoint at position D?

Lead II

Which ECG interval measures the sum of the total action potential duration in the ventricles?
QT interval
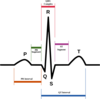
What creates the ECG wave form?
Potential differences between cells that are activated and inactivated create current flow from more negative to more positive areas
The current flow is recorded by electrodes; current traveling toward an elctrode results in an up wave
What does left axis deviation look like on ECG?
Between 0 and -90
QRS complex…
Up in Lead 1
Down in AVF
Which ECG interval meausres the plateau of the cardiac action potential?
ST segment

If there is ischemia in the inferior wall of the LV, in which ECG leads would you see abnormalities?
Which coronary artery?
II, III, aVF
Right coronary artery
What is normal for the QRS interval?
<0.10 seconds
Where is V3 placed?
Which coronary artery supplies this lead?
Midway between V2 and V4 (place it after applying V4)
Supplied by the LAD (Anterior Lead)

What causes the U-wave on an ECG?

The U-wave only occurs in some people
It is a positive deflection emmediately after a T-wave
May be normal or pathological
Which lead has its (+) endpoint at position F?

Lead III

What causes the P-wave of the ECG?
Atrial depolarization
Right Atrium= beginning part
Left Atrium = latter part

With respect to depolarized (+) and nondepolarized (-) cells, where does current flow?
Current flows from (+) to (-) cells
Which lead has its (+) endpoint at position E?

aVF

What causes the QRS complex in the ECG?
Depolarization of the ventricles

Which leads are considered the anterior ECG leads?
Which coronary artery do they correspond with?
V3
V4
Foront of the heart: Supplied by the LAD

If a patient’s PR interval is too short, would you expect cardiac output to increase or decrease?
Decrease; During the PR interval, the ventricle fills with blood from the atirum
If the PR interval is short, the conduction signal from the atrium is not delayed long enough for the ventricles to properly fill. This is likely to decrease cardiac output
What does a normal axis look like on ECG?
Between 0 and +90
QRS complex…
Up in Lead 1
Up in AVF
Where is V4 placed?
Which coronary artery supplies this lead?
5th intercostal space, mid-clavicular line
Supplied by LAD (Anterior lead)

How many big boxes on the Y-axis of an ECG correspond with 1.0 mV?
2 big boxes
What does the QT interval represent?
How is it measured on and ECG?
The sum of the total duration of ventricular action potential
On an ECG, it is from the beginning of the QRS complex through the end of the T wave

Which ECG leads will provide information about the function of the right coronary artery?
- Inferior leads
- II
- III
- aVF

Which lead has its (+) endpoint at position B?

aVL

What happens to the ST segment in NSTEMI?
Why?
ST segment depression (or no change)
The ischemia is subendocardial. During the action potential plateau, current flows from the healthy epicardium to the ischemic subendocardium, away from a surface electrode. The net current flow is away from the electrode, resulting in ST segment depression

What is happening to the heart during the PR interval?
Conduction is delayed in the AV node
The atrium is contracting and the ventricle is relaxed; this allows time for ventricular filling
Which ECG lead goes from the abdomen to the left arm?
aVL
(- in abdomen to + on left arm)
Which ECG leads will provide information about the function of the LAD?
- Septal leads
- V1
- V2
- Anterior Leads
- V3
- V4
- Lateral Leads
- V5
- V6

Which ECG lead is perpendicular to lead aVL?
Lead II
If you see tall, peaking T-waves on an ECG, which stage of STEMI is the patient likely in?
Hyperacute phase (earliest: minutes - hours after occlusion)
Usually this phase is gone by the time the patient gets to the ER
Where is V5 placed?
Which coronary artery supplies this lead?
Horizontal with V4, in the anterior axillary line
(V4 is in the 5th intercostal space, mid-clavicular line)
Supplied by LAD, LCx

Describe the ECG presentation of right atrial enlargement
- Lead II: increased amplitude of P wave (>2.5 mm)
- *OR**
- Lead V1: Increased amplitude of P wave (>2.5 mm)
Because the right atrium depolarizes first, these changes are likely to be in the beginning of the P wave
Which ECG leads involve the right leg?
None; the electrode on the right leg is the “ground”
What is normal for the PR interval?
0.12 -0.2 seconds
Which lead has its (+) endpoint at position C?

Lead I

What happens to the ST segment in STEMI?
Why?
ST segment elevation
The ischemia is transmural. During the action potential plateau, current flows from the healthy tissue to ischemic tissue (from more + charged to less + charged). Because of the curvature of the heart (?) the net current flow is toward the surface, where the electrode is. This results in ST segment elevation

Which leads are considered the inferior ECG leads?
Which coronary artery do they correspond with?
II
III
aVF
They look at the bottom wall of the heart, supplied by the right coronary artery (Sometimes LCx)

Which ECG lead goes from left arm to left leg?
Lead III
(- on left arm to + on left leg)
Describe the ECG presentation of left ventricular enlargement
- V1 S wave + V5 or V6 R wave = >35 mm
- May be normal in patients <35 years old
- Lead I R + Lead III S = > 25 mm
- R in aVL > 12 mm
What is the equation for correcting the QT interval?
Why is this necessary?
Normally, the QT interval changes with heart rate (shortens as heart rate increases). Correcting for the QT interval helps physicians determine if there is a pathology at different heart rates
Use Bazett formula
RR = time between consecutive QRS complexes

Which ECG lead is perpendicular to lead III?
aVR
What causes a given ECG lead to “see” a positive (up) signal?
A wavefront traveling toward the positive end of a lead will “see” and “up” signal, which will show on that lead of the ECG
For example, a wavefront traveling in the direction of the arrow would appear up in leads aVL, I, and II

What ECG changes are you likely to find in a patient with pericarditis?
- ST elevation in multiple leads
- PR segment depression (sometimes)
- Clinical findings of pericarditis
- Chest pain that varies with postural changes (relief leaning forward)
- Sequential ECG changes are different from those of MI
In which ECG leads are small Q waves normal?
III, V5, V6
Describe the ECG presentation of left atrial enlargement
- Lead II: Increased width of P wave (> 3mm)
- *OR**
- Lead V1: Area of (-) P wave component > 1mm2
Because the left atrium depolarizes after the right, these changes are likely to be in the end of the P wave
What causes the T-wave on an ECG?

Repolarization of the ventricle
The action potentials of the first part of the ventricle to depolarize are longer than the action potentials of the parts that depolarize later, resulting in the T-wave
Describe the ECG presentation of right ventricular enlargement
- V1: R wave > S wave
- *And/Or**
- V6: S wave >= R wave
- Limb leads: right axis deviation
- Usually accompanied by right atrial P-wave abnormality
List 6 key characteristics of a normal ECG
- P wave is upright in lead II
- Axes: QRS axis, T wave axis normal
- Normal sinus rhythm (HR normal, a QRS complex follows every P wave)
- Horizontal lines: TP, PR, and ST sements are all at the same level
- P waves, T waves, QRS complexes all point in the same direction (may vary by lead)
- From V1 to V6, the QRS complex makes a smooth transition from down to up
- Most down in V1, most up in V6
If there is ischemia in the anterior wall of the LV, in which ECG leads would you see abnormalities?
Which coronary artery?
V1, V2, V3, V4 (Septal and anterior leads)
These leads monitor the LAD (left anterior descending artery)

How would you determine an axis on ECG?
Look at the direction of QRS complexes in leads I and aVF
- Normal: Between 0 and +90
- Lead I: Up
- aVF: Up
- Left axis deviation: Between 0 and -90
- Lead I: Up
- aVF: Down
- Right axis deviation Between +90 and +180
- Lead I: Down
- aVF: Up
If you have an ischemic patient and you see abnormalities in ECG leads II, III, aVF…
Which coronary artery is most likely blocked?
Which tissue is infarcted?
Right coronary artery (Inferior leads)
Inferior wall of the left ventricle

A waveform with an axis of +0 would be “up” in which leads?
Down?
Flat?

Up: aVL, I, II (B, C, D)
Down: aVR, III (A, F)
Flat: aVF (E)

If you see elevated ST segments without very tall T waves on an ECG, what stage of STEMI is the patient likely in?
Acute phase (2nd: hours to days after occlusion)
Q waves may also be present
Which ECG lead goes from right arm to left arm?
Lead I
(- on right arm to + on left arm)
What time interval corresponds with the little box on an ECG?
The big box?
Little box = 0.04 seconds
Big box = 0.2 seconds
Which ECG lead is perpendicular to lead I?
aVF
If there are 4 large boxes between QRS complexes, what is the patient’s heart rate?
~75 bpm
(300 150 100 75 60 50)
What does a right axis deviation look like on ECG?
Between +90 and 180
QRS complex…
Down in Lead 1
Up in AVF
Which ECG lead is perpendicular to lead aVF?
Lead I
Which lead has its (+) end at position A?

aVR

Which ECG lead is perpendicular to lead aVR?
Lead III
In which ECG leads is a Q-wave normal?
Small Q waves may be normal in all leads except V1 through V3, where they are always pathologic. Q waves of any size may be normal in leads III and aVR.
If you see abnormal Q waves in an otherwise normal ECG, what stage of STEMI is the patient likely in?
The MI is old; Q waves are the hallmark of myocardial scarring due to previous MI
Where is V6 placed?
Which coronary artery supplies this lead?
Horizontal with V4, mid-axillary line
(V4 is in the 5th intercostal space, mid-clavicular line)
Lateral lead: supplied by the LAD or LCx

Depolarization of the AV node corresponds with which ECG component?
PR interval

Besides transmural ischemia, what may cause ST elevation?
- Normal variant
- ST elevation in multiple leads
- ST ususally concave
- Ventricular aneurysm
- Scar that bulges during systole due to muscle death
- Pericarditis
- ST elevation in multiple leads
What is “normal” for a QT interval?
<1/2 of the interval between 2 consecutive QRS compelxes
More precisely, the QTc should be ~0.45 in men and ~0.46 in women
Which component of the ECG is created by depolarization of the SA node?
None;
Depolarization of the SA node is silent on ECG because it is too small to be recorded extracellularly
If you have an ischemic patient and you see abnormalities in ECG leads aVL, V4, V5, and/or V6
Which coronary artery is most likely blocked?
Which tissue is infarcted?
LCx (High lateral and lateral leads)
Lateral wall of the left ventricle

What mechanism causes Q waves?
Normally, the QRS complex is up because activation of the LV is outward, from endocardium to epicardium. The wave of depolarization travels toward the surface electrode
If there is an infarct in the free wall of the left ventricle, it will generate less electrical activity.
The QRS complex points down, or has a downward deflection before going up because there are more vectors pointing away from the surface electrode, both through the IV septum (L to R), and through the free wall of the right ventricle (subendocardium to epicardium)

Which leads are considered the High Lateral ECG leads?
Which coronary artery do they correspond with?
I
aVL
Left Circumflex artery

Which leads are considered the Lateral ECG leads?
Which coronary artery do they correspond with?
V5
V6
Left Circumflex artery

If you have an ischemic patient and you see abnormalities in ECG leads V1, V2, V3, and/or V4…
Which coronary artery is most likely blocked?
Which tissue is infarcted?
Left anterior descending artery (Anterior leads)
Anterior wall of the left ventricle

Which leads are considered the septal ECG leads?
Which coronary artery do they correspond with?
V1
V2
LAD (left anterior descending)

What is the basis for ST segment changes during ischemia?
- In ischemic tissues, patchy areas of depolarized (+) cells coexist with healthy cells
- Current flows from (+) to (-)
- At rest: flow from ischemic cells to healthy cells
- At plateau of AP: Flow from healthy cells to ischemic cells
- This means that the first cell to depolarize is also the first to repolarize, causing ST segment abonormalities


