CVB SAS/Misc Review Flashcards
Many questions and images are taken from Dr. Mutharasan's SAS and lecture slides (111 cards)
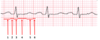
On an ECG, the QRS axis is -45 degrees.
Direction of QRS in Lead I:
Direction of QRS in Lead aVF:
What kind of deviation is this?
Direction of QRS in Lead I: Up
Direction of QRS in Lead aVF: Down
Left Axis Deviation
Which segments make up the PR interval?

1 + 2

What is the effect of reduced aortic compliance on pulse pressure?
Pulse pressure increases
- SBP increases and DBP decreases
How is ejection fraction calculated?
(EDV-ESV)/EDV
What is the most likely etiology of a II/IV decrescendo diastolic murmur best heard at the base of the heart?
Aortic regurgitation
Which layer of the ventricle has the longest refractory period?
Midmyocardium
Which segments make up the QT interval?

3 + 4 + 5
On an ECG, the QRS axis is +45 degrees.
Direction of QRS in Lead I:
Direction of QRS in Lead aVF:
What kind of deviation is this?
Direction of QRS in Lead I: Up
Direction of QRS in Lead aVF: Up
No deviation: 0 to +90 = normal ECG axis
Which of the receptors on macrophages recognize modified LDL?
Scavenger receptors
Note: These receptors are NOT downregulated the way normal LDL receptors are
Point 0 represents LV End Diastolic Pressure (LVEDP) at baseline.
Which point best represents the LVEDP in a stiff left ventricle?

The blue line in general
A stiffer left ventricle would result in increased pressure at every volume (especially higher volumes), becuase the ventricle cannot stretch as well to accomodate volume

Which chamber of the heart rests against the esophagus?
Left Atrium
Your patient presents with symptoms of heart failure. You determine that the Point of Maximal Impulse is located in the 6th intercostal interspace and is 3.5 cm in diameter.
A. Pulmonary Hypertension
B. Mitral Stenosis
C. Dilated Cardiomyopathy
D. Amyloidosis
C. Dilated Cardiomyopathy
What ligand does Gp IIb/IIIa bind to?
Fibrinogen
Which structure labels the pulmonary valve?

A

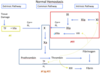
Which factor belongs in the orange box?

Fibrinogen

Compared to the Hgb concentration earlier in the morning before the trauma, what is the Hgb concentration immediately upon blood loss?
Hgb concentration immediately upon blood loss remains the same
Mechanisms that would increase blood volume (but dilute Hgb concentration) have not yet kicked in
Which factor belongs in the orange box?

Prothrombin

Describe the aPPT test
How is the assay performed?
Which coagulation pathway is activated?
Mix plasma with silicate to activate factor XII and initiate the intrinsic coagulation pathway. Adding calcium results in conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin in 30 to 40 seconds.
Which ECG feature is labeled by segment 2?

PR Segment

During exercise, what happens to pulmonary vascular resistance?
PVR decreases
Which structure labels the aortic valve?

B

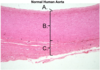
Which of the following pictures shows a large vein?

C - Has longitudinal smooth muscle
(Arteries have concentric smooth muscle)

What is the mechanism behind enoxaparin’s (a LMWH) anti-coagulant effects ?
LMWH is a factor Xa inhibitor (with some Factor IIa activity)
This inhibits the clotting cascade (after the intrinsic and extrinsic pathways converge, so therefore it inhibits both)
What does aortic regurgitation do to preload and afterload?
Aortic regurgitation increases both preload and afterload