SM 106a - Heart and Mediastinum Anatomy (Incl. Lab Objectives) Flashcards
Which part of the heart is cut open in this picture?
How do you know?

Left ventricle and Left Atrium
Ventricle has thick muscular walls, no opening for coronary sinus to drain into
Left atrium sits on top of left ventricle

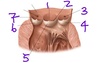
What structure is labeled by #8?

Costal Pleura

What structure is labeled by #1?

Ascending Aorta

Which structure is labeled by #16

Right ventricle

Which structure is labeled by #13?

Pectinate muscles (in the left auricle)

Which structure is labeled by #10?

Left atrium

Which structure is labeled by #7?

Opening of inferior vena cava and valve

Which of the three major coronary arteries supplies blood to the left ventricle?
Front and bottom of LV: Anterior interventricular artery (aka Left anterior descending artery)
Back and side of LV: Circumflex artery
Where is the Aortic Semi-Lunar Valve?
Where do you place your stethoscope to listen?
Valve: Between the left ventricle and the aorta
Stethoscope: In the second intercostal space to the right of the patient’s sternum
(Circled A)

Which structure is labeled by #14?

Right coronary artery

What is cardiac tamponade?
Cardiac tamponade = fluid in the pericardial cavity that compresses the heart
Parietal pericardium has low compliance; increased volume in the sac puts pressure on the heart, rather than expanding the pericardial sac.
Describe the pathway of sympathetic innervation of the heart
- Presynaptic neuron
- Spinal cord
- Lower cervical or uppor thoracic sympathetic trunk
- Synapse in sympathetic trunk
- Cell body is here in the stellate ganglion
- Postsynaptic neuron
- Sympathetic trunk
- Cardiopulmonary splanchnic nerves
- Plexus at the bifurcation of the trachea
What structure is labeled by #12?

Right Ventricle

What structure is labeled by #9?

Left Internal Jugular Vein

Which structure is lableled by #7?

Right coronary artery

Which coronary artery suplies the left atrium?
Circumflex artery
Why does angina sometimes radiate down a person’s arm?
The left ventricle is supplied by nerves from T1
Nerves from T1 also supply the brachial plexus
Therefore, anginal pain can be referred to nerves in the arm
Which structure is labeled by #5?

Interventricular septum

Which structure is labeled by #1?

Ligamentum Arteriosum

What structure is labeled by #16?

Right Brachiocephalic Vein

Which part of the lung does the heart interface on the…
Left side?
Right side?
Right side = middle lobe of the right lung
Left side = lingula of the upper lobe of the left lung
What structure is labeled by G?

Left subclavian artery

Which structure is labeled by #3?

Opening of the left coronary artery
List the differences between the left and right ventricles
- Smooth top of chamber
- Left is called the aortic vestibule
- Right is called the conus arteriosus
- Left is round with thicker walls
- Right is bellow-shaped with thinner walls
Which structure is labeled by #7?

Cusp of bicuspid aka mitral aka left atrioventricular valve

Visceral sensory fibers from which spinal segment supply the ventricles?
T1
Which structure is labeled by #11?

Anterior cusp of the tricuspid valve (right atrioventricular valve)

Which structure is labeled by #9?

Apex of the heart

Which structure is labeled by #2?

Crista Terminalis

What structure is labeled by #5?

Cervical Pleura

What structure is labeled by #1?
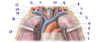
Left Phrenic Nerve

Describe the general flow of blood into and out of the azygous vein
From left side
- Left posterior intercostal veins
- Hemiazygous vein
- Azygous vein
- Superior vena cava
- Must arch over root of the right lung to get here
From right side
- Intercostals drain directly into azygous vein
Which structure is labeled by #6?

Right cusp of the aortic semi-lunar valve

Which structure is labeled by #1?

Nodule of the posterior cusp of the aortic semi-lunar valve

What structure is labeled by #4?

Left Subclavian Artery

Which structure is labeled by #4?

Left ventricle

Which structure is labeled by #14?

Conus arteriosus

Which structure is labeled by #12?

Right atrium

Which structure is labeled by #3?

Remnants of foramen ovale

Which structure is labeled by #3?

Marginal branch of the right coronary artery

What structure is labeled by #15?

Right Vagus Nerve

Which structure is labeled by #10?

Chordae tendineae

What is the function of the papillary muscles?
Located in the ventricles
Stabilize the AV (tricuspid and bicuspid) valves via chordae tendineae to prevent flaps from swinging into the atrium when the ventricle contracts
Which structure is labeled by #13

Right pulmonary veins

What is the name of the valve shown in this picture?
What is the name of this valve on the other side of the heart?

Shown (left side): Bicuspid aka Mitral aka Left Atrioventricular Valve
Other (right) side: Tricuspid aka Right Atrioventricular valve

Which structure is labeled by #8?

Remnants of the fossa ovalis

Describe the structure and function of the atrioventricular valves
-
Structure:
- Flat cusps that are stabilized by papillary muscles and chordae tendineae
- Right: Tricuspid = 3 flaps
- Left: Bicuspid (mitral) = 2 flaps
-
Function:
- Prevent backflow into the atrium during ventricular contraction
Which blood vessel is cut open in this picture?
How do you know?

The aorta
The pulmonary trunk woudl look similar, but the aorta has openings for the left and right coronary arteries

Describe the pathway of visceral sensory innervation of the heart
- Heart
- Cardiopulmonary splanchnic nerves
- Sympathetic trunk
- Joins spinal nerve
- Enters spinal curve via dorsal root
- Cell body is in the dorsal root ganglion
What structure is labeled by #10?

Esophagus

What structure is labeled by #13?

Right Phrenic Nerve

List the differences between the right and left atria
- Right has the crista terminalis
- Contains pace maker tissue
- Right recieves blood from systemic circulation (vena cavae)
- Left receives blood from the pulmonary circulation
Which structure is labeled by #5?

Anterior papillary muscle

What structure is labeled by B?

Thymus

Which structure is labeled by #1?

Right atrial “nodal” branch of the right coronary artery

What structure is labeled by #11?

Left Ventricle

What structure is labeled by #3?

Right Phrenic Nerve

Which structure is labeled by #9?

Left ventricle

Which structure is labeled by #11?

Trabeculae carneae

What structure is labeled by #3?

Diaphragm

What structure is labeled by #7?

Left Subclavian vein

Which section of the mediastinum contians the heart?
Middle mediastinum
Which structure is labeled by #5

Left atirum

What is the coronary sinus?
An endothelial-lined venous channel imbedded in the cardiac muscle in the posterior AV groove
(Not a vein)
What structure is labeled by D?

Trachea

What is epicardium?
Viscerial pericardium
Which structure is lableled by #4?

Great cardiac vein

Which structure is labeled by #2?

Pulmonary semi-lunar valve

Which structure is labeled by #4

Pulmonary arteries

What structure is labeled by C?

Superior vena cava

Which structure is labeled by #3?

Aortic arch

Which structure is labeled by #6?

Opening of coronary sinus and valve

What structure is labeled by #13?

Right Atrium

Trace the flow of blood through the heart
- Enters via superior and inferior vena cavae
- Right atrium
- Through tricuspid valve
- Right ventricle
- Through pulmonary semi-lunar valve
- Pulmonary trunk
- Pulmonary arteries
- Lungs (Lobes -> Bronchopulmonary segments)
- Pulmonary veins
- Left atrium
- Bicuspid (mitral) valve
- Left ventricle
- Aortic semi-lunar valve
- Aorta
- Systemic circulation
What is the effect of sympathetic innervation on the hearth/
Increase heart rate by stimulating the SA node
Act on myocardial cells to increase force of contraction
- Increase myocyte metabolism
- Dilate coronary arteries
- Increase blood flow to muscles
Sympathetic innervation = helps us run away from scary things
What is the effect of parasympathetic innervation on the heart?
Decrease heart rate by inhibiting the SA node
Parasympathetic = rest and digest
Trace the pathway of the conductive system that regualtes the heart beat
- SA node = pacemaker
- Three nodal pathways
- AV node = backup pacemaker
- AV bundle (bundle of hiss)
- Right and left branch bundle (septal branch)
- Right and left purkinje fibers
- Right and left ventricular muscle
What structure is labeled by #11?

Trachea

Where does blood from the coronary sinus drain into?
Right atrium
Which structure is labeled by #2

Left inferior pulmonary vein

What structure is labeled by #12?

Right Internal Jugular Vein

What structure is labeled by #7?

Aortic Arch

What structure is labeled by #4?

Serous Visceral Pericardium (Epicardium)

What structure is labeled by #7?

Descending Aorta

Which structure is labeled by #7 (the space)?

Aortic sinus (there are 3 sinuses shown in this picture)

What structure is labeled by #17?

Superior Vena Cava

What structure is labeled by B?

Manubrium of the sternum

Which structure is lableled by #6?

Right marginal artery and vein

Where is the Tricuspid valve?
Where do you place your stethoscope to listen?
Valve: Between the right atrium and the right ventricle
Stethoscope: Left 5th intercostal space
(Circled T)

What are the arrows pointing to?

Right (lower arrow) and left (upper arrow) phrenic nerves

What structure is labeled by I?

Esophagus

Which structure is labeled by #10?

Brachocephalic trunk

Which structure is labeled by #5?

Circumflex branch of the left coronary artery

What is the name of the colored structure as a whole?

Pericardial Sac

Which structure is labeled by #9?

Anterior papillary muscle

Which ventricle is the right?
Which is the left?
How do you know?

A = Left; thicker walls, round
B = Right; thinner walls, crescent shaped
Which structure is the red arrow pointing to?

Pulmonary Trunk

What structure is labeled by #8?
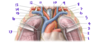
Left Phrenic Nerve

What structure is labeled by E?

Esophagus

Which structure is labeled by #1?

Left superior pulmonary vein

List the structures of the heart supplied by the right coronary artery
Posterior of the heart
- Right atrium and ventricle
- Posterior part of the left ventricle (adj. to IV septum)
- Posterior 1/3 of IV septum
- SA and AV nodes (usually)
Which structure is labeled by #7?

Membranous interventricular septum

Which structure is lableled by #2?

Left coronary artery

Which side of the heart is shown in this picture?
How do you know?

Left
The ventricle has a thick muscle layer

Which structure is labeled by #13?

Supraventricular crest

Which structure is labeled by #8?

Posterior papillary muscles

Which coronary artery typically supplies the SA and AV nodes?
Right coronary artery
What structure is labeled by D?

Left brachiocephalic vein

Which structure is labeled by #6?

Anterior interventricular branch of the left coronary artery

Which structure is labeled by #8?

Posterior papillary muscle

Which structure is labeled by #4?

Posterior papillary muscle

Which structure is labeled by #7?

Circumflex artery

What does the left coronary artery divide into?
Circumflex artery & Left anterior descending artery
Which structure is labeled by #11

Superior vena cava

Which structure is labeled by #2?

Posterior cusp of the mitral valve

Which structure is labeled by #7?

Septomarginal trabecula (aka moderator band)

Which structure is labeled by #3

Coronary sinus
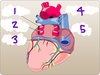
What structure is labeled by A?

Body of the sternum

Which structure is lableled by #5?

Anterior interventricular artery
(Left anterior descending artery)

Which chamber is labeled by #1?

Left atrium

What structure is labeled by #3?

Left Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve

What structure is labeled by #5?

Diaphragm

What structure is labeled by #6?

Intercostal Muscles

What structure is labeled by #2?

Superior Vena Cava

Which structure is lableled by #1?

Left auricle

What structure is labeled by #9?

Greater Splanchnic Nerve

What structure is labeled by #1?

Serous Parietal Pericardium

What structure is labeled by #13?

Right Vagus Nerve

Which structure is labeled by #6?

Muscular interventricular septum

Wich structure is supplied by #8?

Sinoatrial node

Which structure is labeled by #1?

Right auricle

What structure is labeled by #14?

Right Subclavian Vein

What structure is labeled by #3?

Left Common Carotid Artery

List the layers of the pericardium from outermost to innermost
From outermost to innermost:
- Fibrous parietal pericardium
- Serous parietal pericardium
- Visceral pericardium (aka epicardium)

Which structure is labeled by #4?

Right ventricle

What is the function of the coronary sinus?
Drains blood from most of the heart to the right atrium
What structure is labeled by #6?

Superior Vena Cava

What structure is labeled by #11?

Splanchnic Nerves

Which structure is labeled by #10?

Chordae tendineae

Which structure is labeled by #4

Left pulmonary artery

Which structure is labeled by #3?

Pectinate muscles

What structure is labeled by #4?

Pericardial Sac
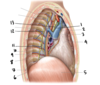
What structure is labeled by #6?

Ligamentum Arteriosum

In a posterior-anterior x-ray, pneumonia in which lung lobe would obscure the right margin of the heart?
Which structure of the heart would be ill-defined?
Middle right lobe
This would make it difficult to define the right atrium
Which structure is labeled by #6?

Trabeculae carneae
(muscle columns)

Which structure is labeled by #8?

Interatrial septum

Which structure is labeled by #6

Left pumonary veins

Where is the Bicuspid Valve??
Where do you place your stethoscope to listen?
Valve: Between the left atrium and the left ventricle
Stethoscope: Left 5th intercostal space near the mid clavicular line
(Circled M)

What structure is labeled by #4?

Left Vagus Nerve

Which structure is labeled by #1?

Right pulmonary artery

Which structure is labeled by #4?

Left cusp of the aortic semi-lunar valve

Which structure is lableled by #3?

Circumflex artery

Which structure is labeled by #3?

Chordae tendineae

What structure is labeled by #2?

Ligamentum Arteriosum

List the structures of the heart supplied by the left coronary artery
Anterior of the heart
- Left atrium and ventricle
- Anterior part of the right ventricle (adj. to IV septum)
- AV bundle branches in the IV septum
What structure is labeled by #10?

Left Atrium

What structure is labeled by #9?

Pulmonary Trunk

Which structure is labeled by #15?

Left pulmonary artery

What structure is labeled by #14?

Superior Vena Cava

What structure is labeled by A?

Thymus

Describe the composition of each layer of pericaridum
Parietal pericardium
- Fibrous parietal pericardium = outermost layer
- Dense connective tissue
- Protects the serous parietal pericardium
- Serous parietal pericardium
- Fused to the fibrous parietal pericardium
- Interfaces with the visceral pericardium
- Simple cuboidal epithelium
Visceral pericardium aka epicardium
- Attached to the heart
- Simple cuboidal epithelium
What structure is labeled by C?

Right brachiocephalic vein

Which structure is labeled by #5

Inferior vena cava

Which structure is labeled by #2?

Left auricle

Which structure is labeled by #7?

Posterior interventricular branch of the right* coronary artery
*Usually the right coronary artery suppolies the posterior interventricular artery = right dominance
If the left coronary artery supplies, it is called left dominance

What structure is labeled by #6?

Left Brachiocephalic Vein

Which part of the heart is cut open in this image?

Right ventricle

Describe the pathway of parasympathetic innervation to the heart
- Pre synaptic neuron
- Vagus nerve
- Synapse
- Plexus on the bifurcation of the trachea
- Post synaptic neuron
- Begins after synapse (very short neuron)
An atherosclerotic occlusion in which artery will affect the function of the AV bundle branches?
The anterior interventricular branch of the left coronary artery
What structure is labeled by #12?

Sympathetic Trunk aka Sympathetic Chain
(specifically a ganglion)

Which structure is labeled by #2?

Left subclavian artery

Which cardiac chamber has the greatest muscle mass?
Left ventricle
Which structure is labeled by #3?

Sepatal papillary muscle

What structure is labeled by #5?

Fibrous Pericardium

What structure is labeled by #10?

Esophagus

What is the AV node?
What does it do?
A secondary conduction site for electrical signals through the heart
Normally, signal goes from SA node -> AV node -> rest of heat
If the SA node isn’t working, the AV node and purkinje fibers together can generate a beat, but it is slower.
Which structure is labeled by #2?

Lunule of the posterior cusp of the aortic semi-lunar valve

Which structure is labeled by #5?

Right atrioventricular valve + orifice

What is the azygous vein?
Where is it located?
A vein located on the right side of the body that delivers blood to the superior vena cava
Where in the body is the crista terminalis found?
Right atrium of the heart
What is the SA node?
The pacemaker that initiates heartbeat without any other stimulation
(Sympathetic and parasympathetic influence can alter the heart beat)
What is #14 called in the left ventricle?

The aortic vestibule

What structure is labeled by H?

Trachea

A tumor near the root of the left lung would compress which major vessel in the mediastinum?
The arch of the aorta
Describe the structure and function of the semi-lunar valves
-
Structure
- Each valve has 3 half-moon shaped cusps
- Blood-filled sinuses between the valve cusps and arterial walls prevent sticking
- Aortic semi-lunar valve
- Cusps: Left, Right, Posterior (non-coronary)
- Left and Right = origins of left and right coronary arteries respectively
- Pulmonary semi-lunar valve
- Cusps: Left, Right, Anterior
-
Function
- Prevent backflow from artery to ventricle after systole
What does the septomarginal trabecula (moderator band) do?
Carries part of the right bundle branch to the anterior papillary muscles. This is important for electrical conduction throught the heart
What structure is labeled by J?

Thoracic Duct

What structure is labeled by F?

Left common carotic artery

Which structure is labeled by #9?

Anterior cusp of the mitral valve

What structure is labeled by #1?

Trachea

Which structure is labeled by #6?

Inferior vena cava

Which structure is labeled by #4?

Left atrium
(Interarterial septum separates left and right atrium)

Heart muscle ischemia near which structure will impair the initiation of a normal heartbeat?
Superior vena cava
Which structure is labeled by #4?

Left coronary artery

What structure is labeled by #5?

Aortic Arch

What is the stellate ganglion?
Where is it?
Sympathetic trunk
A large, star-shaped ganglion that supplies the heart and lungs
Which organs do not have anastomosis?
Why is this significant?
End organs have no anastomosis
Ex: Renal arteries, central artery to retina of the eye
If the arteries reaching these organs are occluded, blood flow will stop; there is no backup
Which structure is labeled by #9?

Interatrial septum

What structures are supplied by the right coronary artery?
Right atrium
Right ventricle
Bottom portion of the left ventricle (near the apex)
Back of the Interventricular septum
Which structure is the green arrow pointing to?

Superior Vena Cava

What structure is labeled by #2?

Mediastinal Pleura

Which structure is labeled by #12?

Anterior papillary muscles

What structure is labeled by F?

Arch of the Aorta

What structure is labeled by #7?

Neurovascular Bundle
(contains intercostal vein, intercostal artery, intercostal nerve)

Which structure is labeled by #12?

Right atrium

Which structure is labeled by #14?

Pulmonary trunk

Which structure is the blue arrow pointing to?

Aorta

What structure is labeled by E?

Brachiocephalic trunk

Which structure is labeled by #8

Coronary sinus

Failure of which valve will cause pooling in the left atrium?
The bicuspid (mitral) valve
What physiological feature provides collateral circulation if one artery is occluded?
Anastomosis
Which structure is labeled by #5?

Posterior cusp of the aortic semi-lunar valve

Where is the Pulmonary Semi-Lunar Valve?
Where do you place your stethoscope to listen?
Valve: Between the right ventricle and the pulmonary trunk
Stethoscope: In the second intercostal space to the left of the patient’s sternum
(Circled P)

What structure is labeled by #2?

Brachiocephalic Trunk

What is anastamosis?
What is its significance?
End to end joining of the branches of 2 distinct vessels
It allows blood to reach an area even if one of the vessels is occluded
Which structure is labeled by #1

Left common carotid artery

Which structure is labeled by #2?

Right coronary artery

What structure is labeled by #8?

Left Pulmonary Artery

Which structure is labeled by #15?

Right posterior interventricular artery



