Skull Osteology, Muscles of Mastication, Infratemporal Fossa Flashcards

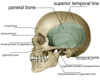
Name the holes and what goes through each (in red).

- Foramen rotundum (V2)
- Foramen ovale (V3)
- Foramen spinosum (middle meningeal artery)

9 (not in answer photo) is the mylohyoid line

Name the origin, insertion, and action(s) of the masseter muscle.
Origin: zygomatic arch
Insertion: ramus of the mandible
Action: elevates mandible (closes jaw)

Name the origin, insertion, and action(s) of the temporalis muscle.
Origin: temporal fossa
Insertion: medial aspect of the coronoid process
Actions: elevate, retract, laterally move mandible

Name the origin, insertion, and action(s) of the medial pterygoid muscle.
Origin: medial aspect of the lateral pterygoid plate
Insertion: medial aspect of the mandibular angle
Action: elevate mandible (close jaw)

Name the origin, insertion, and action(s) of the lateral pterygoid muscle.
Origin: lateral aspect of the lateral pterygoid plate.
Insertion: anterior aspect of the condylar process.
Action: protrude mandible.

Name the origin, insertion, and action(s) of the anterior belly of the digastric.
Origin: digastric fossa of the mandible
Insertion: intermediate tendon/fascial sling on the hyoid
Action: elevate hyoid, depress mandible

Name the origin, insertion, and action(s) of the posterior belly of the digastric.
Origin: mastoid notch
Insertion: intermediate tendon/fascial sling on the hyoid
Action: elevate hyoid, depress mandible (open jaw)

Name the origin, insertion, and action(s) of the stylohyoid muscle.
Origin: styloid process of the temporal bone
Insertion: body of the hyoid
Action: elevate hyoid bone

Name the origin, insertion, and action(s) of the mylohyoid muscle.
Origin: mylohyoid line on mandible
Insertion: hyoid bone
Action: elevate floor of the oral cavity

Name the origin, insertion, and action(s) of the geniohyoid
Origin: inferior genial spine of the mandible
Insertion: hyoid bone
Actions: open jaw, protrude hyoid

What is the action of the buccinator muscle?
Contracts during chewing to keep food in the oral cavity.
What is the motor nerve for the muscles of mastication?
CN V3
Describe the pathway an infectious agent could take from the upper teeth –> brain.
Upper tooth –> pterygoid plexus of veins –> emissary vein superiorly –> cavernous sinus

Name the hole/fissure/foramen that provide a route of communication between the pterygopalatine fossa and the…
- Infratemporal fossa
- Middle cranial fossa
- Nasal cavity
- Orbit
- Palate
- Infratemporal fossa: Pterygomaxillary fissure
- Middle cranial fossa: Foramen rotundum
- Nasal cavity: Sphenopalatine foramen
- Orbit: Inferior orbital fissure
- Palate: Palatine canal (greater and lesser palatine foramen)

After V3 exits foramen _______, it divides into four large, grossly visible nerves that can be found in the infratemporal fossa. Name them. What are the spatial relationships between these nerves and the lateral pterygoid muscle?
Foramen ovale
Splits into the [long] buccal nerve, lingual nerve, inferior alveolar nerve, and auriculotemporal nerve.
Long buccal nerve (sensory branch of V3) exits between the two heads of the lateral pterygoid, while the inferior alveolar and lingual nerves exit below the inferior head of the lateral pterygoid muscle.



