Gut and Peritoneum Embryology Flashcards
Define a mesentery. What do they contain?
Double layer of peritoneum that suspends the gut from the posterior body wall.
Contains: fat, arteries, veins, lymphatics, nerves (parsympathetic, sympathetic, visceral afferents)
Define intraperitoneal, retroperitoneal, and secondarily retroperitoneal organs.
Intraperitoneal organs are in the peritoneal cavity and have a mesentery.
Retroperitoneal organs developed behind the peritoneum and never had a mesentery.
Secondarily retroperitoneal organs had a mesentery during development, but lost it after they became anchored to the posterior abdominal wall.
Which organs are intraperitoneal organs?
Stomach
1st, 4th parts of duodenum and the rest of the small intestine
Cecum
Appendix
Transverse colon
Sigmoid colon
Which organs are abdominal retroperitoneal organs?
Kidneys, adrenal glands
Which organs are secondarily retroperitoneal?
2nd, 3rd parts of the duodenum
Most of the pancreas (except the tail)
Ascending colon
Descending colon
Rectum
Which arteries supply blood to the…
foregut
midgut
hindgut
?
Celiac trunk supplies foregut
SMA supplies the midgut
IMA supplies the hindgut
Which organs are part of the foregut?
Everything (including accessory organs) from the abdominal esophagus through the proximal half of the duodenum.
Aside from organs in the foregut, which other organ receives its blood supply from the celiac trunk?
The spleen
Which organs are considered part of the midgut?
Everything between the distal half of the duodenum through 2/3 of the way down the transverse colon
Which organs are considered part of the hindgut?
Everything distal to 2/3 of the way down the transverse colon.
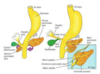
Dorsal and ventral pancreatic buds grow off of the ______ to become the _______ and _______ parts of the pancreas, respectively.
buds off the foregut to become the body & tail (dorsal bud) and head (ventral bud), respectively
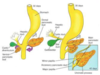
What is the part of the bile duct called where the common bile duct meets the pancreatic duct?
ampulla of Vater
Into what section of the duodenum does the ampulla of Vater empty?
The 2nd part, at the major duodenal papilla
The dorsal mesentery of the stomach goes on to form the _______ _______, which hangs from the ________ ________ of the stomach.
greater omentum, which hangs off the greater curvature of the stomach
In the case of midgut malrotation, where are some possible places where the cecum and appendix could end up (which quadrant)?
Could be in the upper right, or upper left if no midgut rotation occurred.
Meckel’s diverticulum is a remnant of the _______ _______.
Describe the “rule of 2s” for this condition.
vitelline duct
2% of population
2 yo at presentation
2x more likely in males
2 feet from the iliocecal junction
2 kinds of ectopic tissue (gastric or pancreatic)
The cloaca is divided by the ______ ______. After division, the ventral part will give rise to the ________ ________ and the dorsal part will give rise to the _______ _______.
Urogenital sinus divides the cloaca into the ventral and dorsal parts
Ventral part becomes the urogenital sinus –> bladder, urethra
Dorsal part becomes the anorectal canal
The pancreas forms from two pancreatic _____. The uncinate process and main pancreatic duct develop from the _______ ______.
pancreatic buds
uncinate process and main pancreatic duct develop from the ventral bud