Skin Flashcards
Cause of pustules
Leukocyte infiltrate
Characteristics of equine melanomas
Grey horses - lesions are usually progressive and mulicentric
Chemical Burns
Caused by body or wound secreations, application of drugs, exposure to acids, alkalies, soaps, detergents, or irritant plants
Type IV Hypersensitivity
Cell-Mediated Hypersensitivity
Manifestation = contact dermatitis, tubercular leasion and graft rejections
Melanoma
Dog, Horse, Angora Goat
Usually dark brown
Location, size, mitotic index, and cell morphology may help predict behavior
Suppurative/Pustular/Exudative/Neutrophilic lesions are associated with what types of disease
Bacterial
Auto-Immune
Disease and cause

Sarcoptic Mange
Sarcoptes scabiei
Histologic characteristics of allergic skin disease
Lymphocyte and eosinophillic dermatitis
Scale
Gross appearance of Discoid Lupus Erythematosis
Depigmentation
Erythema
Scaling
Erosion
Ulceration
Crusting
Pathological processes that could cause scale
Inflammation and Repair
Disorders of growth
MDx

Ulcerative/Exudative dermatitis
MDx

Neutrophilic dermatitis/folliculitis
Pathogenesis of sarcoptic mange
- Burrow into stratum corneum
- Intesnse pruritis through hypersensitivity mechanism
- Self trauma, chronic irritation
- Hyperkeratosis, lichenification, alopecia
Histological appearance of acral lick dermatitis
Not really a granuloma!
Epidermal hyperplasia
Granulation tissue
Fibrosis
Disease

Collagen Dysplasia
Gross appearance of insect bite hypersensitivity
Often includes papules
Disease

Zinc Responsive Dermatosis
Vesicle / Bulla
Palpable elevation filled with clear fluid
Vesicle - < 1cm
Bulla - > 1cm
Histological appearance of callus
Epidermal hyperplasia
Calcificaion of skin
Most common forms observed int he skin are both classified as dystrophic calcification
Chalky white, gritty to hard texture
Calcinosis cutis vs Calcinosis circumscripta
Disease

Hemangioma / Hemangiosarcoma
Hemangioma - Hemangiosarcoma
Young adult dogs
Due to solar radiation
Pox Virus Infections
Have gene product similar to epidermal growth factor → epidermal hyperplasia
Many cutaneous lesions only, some systemic and fatal

Plaque
Sarcoptic Mange
Highly contagious and zoonotic
Chronic dermatitis
Gross lesion progression from solar injury
Erythema → Blistering/Vesicles → Sloughing of necrotic skin
MDx

Neutrophilic / exucative dermatitis/folliculitis
Disease

Histiocytoma
Congential Hypopigmentation
Inherited lack of melanocytes
Piebalism
Albinism
Pathogenesis of Erythema Multifome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis
Thought to involve type IV hypersensitivity towards antigens or the surface of keratinocytes inducing apoptosis
Disease

Sebacious Adenoma
Canine Leproid Granuloma
Mycobacterial Dermatitis
Transmission = fly bites?
Nodules involving dorsal pinna, less commonly other distal extremities
Short coated breeds - boxer
Self limiting
Ulcer
Loss of epidermis with exposure of dermis
Mdx
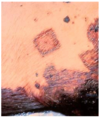
Cutaneous Infarcts
Dermatophytosis
Contagious - acquired by contact with scales shed from infected animals
Colonize keratin, do not need to invade tissue to cause disease
Self limiting in healthy animals, can become chronic/generalized in immunocompromised animals
Predisposing factors to dermatophytosis
Young or immunocompromised
Hot/humid environments
Melanin synthesis
- Tyrosine → dihydroxyphenylalanine by Tyrosinase
- Dihydroxyphenylalanine → melanin
- Melanin packaged into melanosomes
- Melanosomes transferred to epithelial cells or melanophages
Disease

Actinomycete Mycetomas
Wheal
Elevated, irregular shaped area of cutaneous edema, solid, transient
Insect Bite Hypersensitivity
Type I and or Type IV Hypersensitivity Reaction
React to saliva of insect
Distribution depend on areas favored by insect - can become generalized
MDx
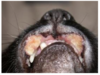
Ulcerative dermatitis/ cheilitis
Disease

Pyotraumatic Dermatitis
Eosinophilic Granuloma Complex
Cats
Not a disease - Pattern of lesions
Indolent ulcer
Eosinophillic plaque
Eosinophilic granuloma
MDx

Chronic locally extensive cutaneous ulcer
Disease

Cutaneous Habronemiasis - Summer Sores
Actinomycete Mycetomas
Bacteria introduced by traumatic injury
Form large clumps - grossly evident as “sulfur granules”
Nodules, ulceration, draining sinuses, involvement of unerlying bone
Canine Superficial Spreading Pyoderma
Usually secondary condition
Bacterial infection of superficial follicles and adjacent skin
What secondary condition is commonly associated with flea bite hypersensitivity
Pyotraumatic dermatitis - secondary to self trauma associated with pyoderma

Ulcer

Vesicle / Bulla
Disease and Cause

Purpura hemorrhagica
Streptococcus equi
Disease

Equine Sarcoid
Scale
Accumulation of loose keratinized cells
Granulomatous lesions are associated with what type of diseases
“Higher” Bacteria
Mycobacteria
Fungal
Foreign Substance
Nodules
Palpable, solid elevated mass > 1 cm and deeper than papules
Conditions grossly indistinguishable from Canine Superficial Spreading Pyoderma
Demodicosis
Dermatophytosis
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Verrucous and ulcerated
Poorly pigmented, sparsley haired, sun exposed areas
Causative agent of what disease

Dermatophilosis
____________________
Dermatophilus congolensis
Cause of Canine Leproid Granuloma
Saprophytic mycobacteria
Lichenification
Thickening and hardening of the skin
Localized Hyperpigmentation
Chronic inflammation or physical irritation
Congenital
Superficial Pyoderma Diseases
Canine Superficial Spreading Pyoderma - Bacterial Folliculitis
Impetigo - Superficial Pustular Dermatitis
Greasy Pig Disease
Dermatophilosis

Nodule
Histiologic changes that can lead to the formation of vesicle/bulla
Intercellular edema - “spongiosis”
Intracellular edema - “hydropic degeneration”
Disruption of intercellular junctions - “acantholysis”
T/F: Degenerative/Necrotic lesions are the only pathological processes that cause ulceration
False
Eosinophilic Granulomas
Grossly similar to non-eosinophilic granulomas
Often see collagenolysis due to proteolytic enzymes of eosinophil granules
Disease

Discoid Lupus Erythematosis
Disease

Primary Idiopathic Seborrhea
Cause of dermatophytosis
Epidermophyton microsporum
and
Trichophyton spp
Pathogenesis of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Solar radiatoin, chronic injury commonly involved
Calcinosis circumscripta
Young, rapidly growing, large breed dogs
Single hard subcutaneous nodule, usually over pressure points or at previous site of trauma/injection
Disease

Allergic Skin Disease - Atopy
MDx

Exudative dermatitis
Mucinosis
Mucin is normally in the dermis - protein bound to hyaluronic acid
Thickened / puffy gelatinous skin
If severe can exude viscous fluid when pricked with needle
Prone to injury
Pathological processes that cause crust
Degeneration / Necrosis
Inflammation and Repair
Disorder of Growth
Crust
Dried exudate, serum, blood and scale that is adhered to the skin surface
Primary ____________ often lead to degeneration/necrosis
Circulatory disorders
Causes of Vesicles/ Bulla
Auto-Immune Dermatoses
Viral Infections
Chemical Irritants
Burns
Eosinophillic Granuloma
Nodules - may be ulcerated - on thighs, face or mouth
Mdx

Ulcerative dermatitis
Disease

Dermatophilosis
Cytology of Histocytoma
Round cells
Langerhans cell origin
Subepidermal Vesicle
Entire epidermis separates from the dermis and forms the roof
MDx
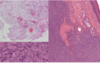
Grade II soft tissue sarcoma
Mdx

Generalized subcutaneous edema
Spongiosis
Intercellular Edema
Disease

Acral Lick Dermatitis
Feline Leprosy
Mycobacterial Dermatitis
Cats in cold, wet areas
Disease

Alopecia
Infarcts
Sharply demarcated geometrical shaped dark red to blue area
Becomes firm, dry, sunken, darkened - features of necrosis predominate
Disease
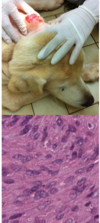
Cutaneous Soft Tissue Sarcoma
Mucinosis is seen with
Inherited in the Chinese Shar-Pei
Myxedema with Hypothyroidsim
Diagnostic tests used for Feline Leprosy
PCR
____________________
Does not grow in culture
Pathogenesis of Solar Injury
- Direct cellular injury by ionizing radiation; endothelial damage and cytokine production may cause erythema of sunburn
MDX

Chronic and exudative dermatitis
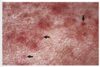
Papule
Disease
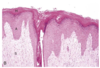
Acral Lick Dermatitis
Vesicles are associated with what type of diseases
Viral Infections
Predisposing factors for dermatophilosis
Wet weather in humid climates (“rain rot”)
Prolonged wetting of skin/hair/wool allows penetration of epidermis by zoospores
Zinc Reponsive Dermatosis
Scaling around mouth, chin, eyes, pressure points and pawpads
Arctic breeds due to inherited defect in zinc absorption
Rapidly growing large breeds due to low zinc diet
Disease
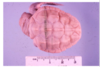
Hypopigmentation
_______________________
Albinism

Pustule
Cutaneous Lymphomas
Poor prognosis
Epithelialtropic - T cells
Nonepitheliotropic - T or B cells

Crust
Epidermal Collarette
Circular rim of scale that occurs secondary to rupture of a vesicle, pustule or papule
Solar/Actinic Keratosis results in an increased risk for
Neoplasia due to direct DNA injury and subsequent mutations
Cause Actinomycete Mycetomas
Nocardia
Actinomyces sp
Hypopigmentation - Hypomelanosis
Melanocytopenic (decreased melanocytes) vs Melanopenic (decreased melanin)
Congenital vs Acquired
MDx
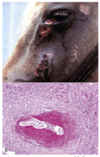
Eosinophilic and granulomatous dermatitis
Histiocytoma
Dogs - young
Head, ears, neck, distal forelimbs
Dome shaped
Benign often sponaneously regress
Later gross features of dermatitis
Scaling
Ulceration
Alopecia
Lichenification
Pigmentary change
Fibrosis/scarring
Greasy Pig Disease
Exudative Epidermitis
Fatal in neonatal pigs
Erythema → Pustule → Crust
Disease
Canine Superficial Spreading Pyoderma
Disease

Opportunistic mycobacteriosis
_______________________________
Organisms more often found extracellularly
Gross lesions associated with allergic skin disease
Lesions due to self-inflicted trauma - erythema, alopecia, excoriation
Lesions due to secondary pyoderma - papules, pustules, crusts
Lesions due to chronicity - lichenification, hyperpigmentatin, scaling
Dermatophilosis is caused by
Eosinophilic lesions are associated with what type of diseases
Allergy
Parasitic
Type I Hypersensitivity
IgE mediated hypersensitivity
Typical manifestation - systemic anaphylaxis and localized anaphylaxis
Allergy
Arabian Fading Syndrome
Horses with vitiligo
Pathogenesis of Primary Idiopathic Seborrhea
Thought to involve hyperproliferation of the epidermis, hair follicle infundibulum and sebaceous gland
Pathogenesis of Papillomas
Viral gene activate host tumor-suppressor proteins
Urticaria involves what skin layers
Superficial dermis
MDx
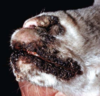
Pustular, exudative dermatitis/cheilitis
Deep Pyoderma diseases
Bacterial Furunculosis
Abscesses
MDx

Neutrophilic dermatitis/folliculitis with intrafollicular mites and bacteria
Disease

Fungal dermatitis
Acanthosis
Increased thickness of stratums basale and spinosum
Second most common autoimmune skin disease
Discoid lupus erythematosis
Disease
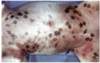
Solar/Actinic Keratosis
Examples of benign skin disorders of growth
Nodular Hyperplasia
Hamartoma
Cysts
Dry from (seborrhea sica)
Dry skin and white to grey scales that exfoliate
Disease
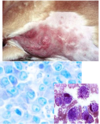
Mast Cell Tumor
Type III Hypersensitivity
Immune complex mediated hypersensitivity
Manifestation - localized arthus reaction and generalized reactions such as serum sickness, necrotizing vasculitis and glomrulonephritis
Pustules and Crust are indicative of what pathological process
Inflammation and Repair
Mdx

Cutaneous hyperpigmentation
_______________________
D/t Hyperadrenocorticism (Cushing’s Disease)
Calcinosis cutis
Associated with hyperadrenocorticism
Erythematous to white gritty plaques and nodules
MDx
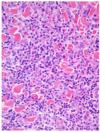
Eosinophillic and granulomatous dermatitis
Vitiligo
Idiopathic acquired melanocytopenic hypomelanosis (depigmentation)
Gradual expanding pale macules - symmetical
Genetic inheritance
Types of Cutaneous Soft Tissue Sarcomas
Fibrosarcoma
Nerve Sheath Tumor
Malignant Firbous Histiocytoma
Liposarcoma
Myxosarcoma
Mdx

Chronic dermatitis and cutaneous hyperpigmentation
______________
D/t chronic flea allergy dermatitis
Characteristics of canine melanomas
Oral, mucocutaneous, subungual lesions are typically malignant
Lesions on haired skin are often benign
Demodicosis
Lesions vary by host/mite species
Distribution on the body
Neutrophilic to granulomatous
In dogs - localized vs generalized form
Piebaldism
Foci of lack of melanocytes
Tissue Pigment

Melanin
Pathogenesis of pyotraumatic dermatitis
Self trauma → Bacterial infection
OR Underlying pruruits (Flea Allergy Dermatitis)
Acquried Hypopigmentation
Copper deficiency
Destruction of melanocytes or melanin containing keratinocytes
Disease

Photosensitization
MDx

Multifocal exudative dermatitis
Pathogenesis of Frost Bite
- Formation of ice crystals which physically disrupt cells
- Vasoconstriction and endothelial damage
- Reduced blood flow
- Thrombosis
- Infarction
Plaques
Coalesced papules
Histological appearance of squamous cell carcinoma
Keratinizing squamous cells gone wild
Stain used to detect fungal dermatitis

GMS Stain
Pathogenesis of Intertrigo
- Closely apposed skin surfaces
- Frictional trauma
- Moisture
- Opportunistic bacterial infections
MDx

Papular, pustular dermatitis
Disease

Canine Leproid Granuloma
Causes of scale
Disorders of keratinization
Chronic dermatitis
Greasy Form (Seborrhea oleosa)
Excessive brown to yellow lipids
Disease

Actinomycete Mycetomas
Deep Pyoderma
Involes the deep dermis
Causes of lichenification
Chronic irritation/inflammation
Collagen Dysplasia
Cutaneous Astehenia, Dermatosparaxis, Ehlers-Danlos
Skin is hyperextensible
Disase

Lipoma
Mdx
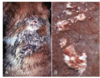
Cutaneous calcification
MDx

Multifocal granulomatous dermatitis
Equine Sarcoid
Common in young adult horses
Frequently involve sites of previous wounds
Invasive, high rate of recurrance, but do not metastasize
Variable range from nodular to plaque like to wart like
Subcorneal Vesicle
Stratum corneum forms the roof of the vesicle
Disease

Opportunistic Mycobacteriosis
Pyotraumatic Dermatitis
Hot Spots
Very common in dogs
Moist, alopecic, slighly raised red well circumscribed lesions that lead to ulceration and crusting
Degernateive/Necrotic lesion become ____________ over time as normal response to injury.
Inflammation and Repair
Early gross features of dermatitis
Edema
Erythema
+/- pustules, crust vesicles
Special stain used to disagnose what disease

Zn Stain
Canine Leproid Granuloma
______________________________
Stain shows acid fast bacilli within macrophages
Eosinophillic Plaque
Discrete red to ulcerated plaques on abdomen or medial thigh
Diagnostic technique used for opportunistic mycobacteriosis
Culture and Sensitvity
Causes of eosinophilic granulomas
Parasite infection
Insect bite hypersensitivity
Foreign body reaction
Most degeneration and necrosis skin cases have what features
Bacterial infection
Epidermal necrosis/ulceration
Leukocyte infiltrate
Thrombosis
Pemphigus Foliaceious
Group of autoimmune diseases involving type II hypersensitivity against cell adhesion proteins (desmosomes)
Most common and milder form of pemphigus
Involves the face, ears, footpads and clawbeds
Vesicles, pustules, crusts, ulcers
Can be spontaneous, drug induced or associated with allergic skin disease
Hydropic Degeneration
Intracellular Edema
Disease
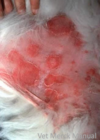
Canine Superficial Spreading Pyoderma
Cause of demodicosis
Demodex spp mite
Histologic findings of puppy strangles
Pyogranulomatous dermatitis
Panniculitis
+/- lymphadenitis
Papule
Palpable, solid, elevated mass < 1 cm diameter
Pyoderma
Clinical term encompassing several diseases
“Pus in the skin”
Usually bacterial infection involved
MDx

Pustular to exudative dermatitis
Generalized Hyperpigmentation
Endcrine dermatosis - change in [tyrosinase]
Acanthosis nigricans - genetically determinded disease
Characteristics of 3rd degree thermal burns
Full thickness epidermis and dermis +/- subcutis
Sloughing of necrotic tissue, followed by granulation tissue
Scar; life threatening - fluid/protein loss and portal for sepsis
Disease

Pox Virus
Disease and Cause

Hypotrichosis - Singy Calf
In utero BVD Infection
MDx

Neutrophilic dermatitis
_____________________________
Seen with intertrigo
Mdx

Multifocal cutaneous ecchymotic hemorrhages
Miliary Dermatitis
Cats
Not a disease - Pattern of lesions
Small crusty erythematous papules
Associated with allergic skin disease
Disease

Frost bite
Pathological processes that could cause ulcers
Degeneration/Necrosis
Inflammation and Repair
Circulatory Disorders
Disorders of Growth
Fungal Dermatitis
“Swamp Cancer”
Uncommon
Clinically resembles neoplasia… invasive lesions, involvement of regional lymph nodes
Suprabasal vesicle
Portion of the epidermis forms the roof
Depigmentation are characteristically what type of lesions
Immune mediated inflammatory lesions
Proliferative lesions are associated with what type of disease
Viral

Callus
Disease

Epitheliogenesis Imperfecta
Disease
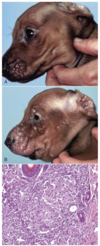
Puppy Strangles
Pathogenesis of purpura hemorrhagica
Type III hypersensitivity immune mediated vasculitis
Causes of Infarcts
Vascultitis
Frost Bite
Toxins causing extreme vasconstriction (ergot)
Mdx
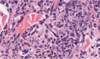
Eosinophillic dermatitis with epidermal hyperplasia
_____________________________
Consistent with allergic skin disease
Disease

Insect bite hypersensitivity
Opportunistic Mycobacteriosis
Mycobacterial Dermatitis
Cause atypical mycobacteria
Facultative saprophytes - inhabitants of soil, water and decomposing vegetation
Rapid vs Slow Growing
Infection occur via wound contamination or traumatic implantation
Interface lesions are associated with what type of diseases
Auto Immune
Purpura hemorrhagica
Red or purple macules or patches (hemorrhage or infarct) in the skin or mucous membranes
Cause of ulcers
Secondary to:
Epidermial necrosis
Inflammation
Infarction
Neoplasia
Histological appearance of insect bite hypersensitvity
May have eosinophilic pustules, folliculitis or granulomas
Disease and cause

Pseudo-lumpy Skin Disease
BHV-2
MDx

Epidermal hyperplasia, dermal fibrosis and elastosis
Disease

Papilloma
Disease

Demodicosis
Pattern

Milliary Dermatitis
Disease

Intertrigo
MDx

Pustular Dermatitis
Pustule
Palpable elevation filled with pus
Discoid Lupus Erythematosis
Induction/ exacerbation by UV light
Dorsal nose and nasal planum, pinnae, lips, periocular resion, oral mucosa
Puppy Strangles - Juvenile Sterile Granulomatous Dermatitis
Pups < 4 months old
One or mre in litter
Pathogenesis unknown
Pustules, nodules, swelling of face, ears, mucocutaneous junctions
Fever and joint pain
Pathogenesis of primary photosensitization
- UV Light absorbed by photodynamic chemicals in the skin
- Free radical damage
- Epidermal necrosis of lightly pigmented or sparsely haired skin
Causes of papules
Infiltrate of inflammatory cells
Infiltrate of neoplastic cells
Epidermal hyperplasia
Depostis of mineral
Pathogenesis of Urticaria
Type I and III hypersensitivity ; mast cell degranulation causes focal edema, congestion and pruritis
Mast Cell Tumor
Dogs - behavior vaires with grade but all considered potentially malignant
Cats and Horses - benign
Can look like anything
Often resembles inflammtion
What special stain is used and what is it used to diagnose?
GMS or Grocott -Silver Stains
Diagnose Canine Leproid Granuloma
Histopathology
PCR- if needed
____________________________
Difficult to culture
Disease

Feline Leprosy
Causes of crust
Severe disorders of keratinization
Severe pustular dermatitis
Secondary to ulcers
Callus
Raised, irregular patch of thickened skin developing from chronic friction, usually over pressure points
Idiopathic Sterile Granuloma and Pyogranuloma Syndrome
Rare
Cause unknown
Diagnosis of exclusion
Solar Injury
Acute UV light exposure leads to sunburn
Skin infections typically involve what bacterial species
Staphylococcus sp
__________________________
Exception - opportunistic gram negatives, and cases of dermatophilosis
Disease

Arabian Fading Syndrome
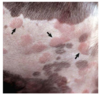
Wheal
Atopy
Type I hypersensitivity to environmental allergens
Distribution on ventrum, face and distal extremities
Alopecia can be due to
Endocrine disorders
Hair cycle abnormalities
Excessive grooming
Self trauma
Autoimmune
General poor nutrition
Hyperkeratosis
Cicatricial alopecia
Contact Dermatitis
Type IV hypersensitivity reaction - exposure via direct contact
Low molecular weight haptens present in chemicals require binding to cell associated proteins prior to being recognized by CD8+ T Lymphocytes
Distribution depends on site of contact - often poorly haired areas
Disease

Greasy Pig Disease
Diagnosis of Atopy
Intradermal Skin Testing
Mdx
Proliferative dermatitis with “ballooning degeneration” and intracytoplasmic inclusion bodies
______________________
Consistant with swine pox infection
Disease and Cause

“Diamond Skin Disease”
E. rhusiopathiae
Histological appearance of equine sarcoid
Composed of both epithelial and dermal components - need biopsy that is not ulcerated to diagnose
Papillomas
Benign, spontaneously regress
Horny cauliflower like mass
Caused by papilloma virus
Histologic feature of solar/actinic keratosis
Dermal fibrosis and comedones
Allergic skin disease can be due to
Atopy
Food Allergy
Contact Hypersensitivity
Insect Bite Hypersensitivity
Disease and Cause

Impetigo - Superficial Pyoderma
Bacterial infection secondary to immunosuppression/debilitation
Mdx

Dermal fibrosis and epidermal hyperplasia
Greasey Pig Disease is caused by
Staphylococcus hyicus
Indolent Ulcer
Ulcers on upper lips
Acral Lick Dermatitis
Lick Granuloma
Common in dogs
Extremities - circumscribed, hairless, and ulcerated
Thermal Burns
Caused by exposure to excessive heat - hot liquids, flames, friction, electricity, heating pads, blow dryers, drying cages, and lightning
Disease
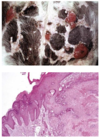
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
MDx

Chronic Dermatitis
Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis
More severe than Erythema Multiforme
Sheets of apoptotic/necrotic cells resembling a burn
Cause of purpura hemorrhagica
Streptococcus equi infection
Pattern

Eosinophilic granuloma complex
Pathological process that cuases pustules
Inflammation and Repair
Mdx

Deep pyoderma with bacterial furunculosis
Chin acne
Erythema Multiforme
Milder than Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis
Single cell apoptosis +/- lymphocyte satellitosis
Mdx

Multifocal cutaneous edema and congestion
Portals for bacterial infection of skin
Pores - Follicular Openings
Hematogenous Spread
Direct entry through damaged skin
Superficial Pyoderma
Epidermis and hair follicles
Lipoma
Benign Growth of Dogs > Cats
Looks and feels like fat, only forming a nodule
MDx

Eosinophilic pustular dermatitis with intralesional acantholytic keratinocytes
_______________________
Pemphigus folliaceious
Mdx

Granulomatous dermatitis
Disease

Ichthyosis
Disease

Acute Solar Injury
Two forms of epidermal hyperplasia
Acanthosis
Hyperkeratosis
Cause of Sarcoptic Mange
Sarcoptes scabiei
Cause of acral lick dermatitis
Persistant chewing or licking
Type III (Hepatogenous) photosensitization can be caused by
Poor hepatic clearance of phylloerythrin - product of rumenal chlorophyll transformation
Toxins causing biliary obstruction
Disease

Melanoma
Histologic appearance of discoid lupus erythematosisi
Interface dermatitis
Dermatophilosis
Lesions on back or distal extremities
Stimulate neutrophilic exocytosis
Pustule → Exudate → Matting of hair/wool → Alopecia
Mdx

Granulomatous dermatitis
Predisposing factors of bacterial infection of skin
Allergy
Disorders of keratinization - seborrhea
Immunodeficiency
Anatomic predispostion
Hyperpigmentation - Hypermelanosis
Usually increase in amount of melanin rather than number of melanocytes
Generalized vs localized
Causes of fungal dermatitis
Pythium
Lagenidium spp
Mdx

Papular dermatitis
Type I (Exogenous) Photosensitization can be caused by
Drugs or chemicals containing photosensitive chemicals
St Johns Wort, Lucerne, Perennial Ryegrass
TMS, Quinolones, Griseofulvin
Localized form of demodicosis
Lesions present on forelimbs and face
Young dogs
Self limiting
Angioedema involves what layers of the skin
Dermis and Subcutis
Pathological process that could cause lichenification
Inflammation and repair
Disease
Flea Bite Hypersensitivity
Frost bite
Lesions in cold exposed extremiteis
Caused by exposure to cold temperature
Why are bacterial skin infections common in dogs?
Thin stratum corneum
Lack of lipid seal of hair follicles
High skin pH
Mdx

Chronic dermatitis
Albinism
Melanocytes present but defect to synthesize melanin; color dilution is a mild form
Diagnosis of fungal dermatitis
Cultrue and PCR
Sebaceous Adenoma
Benign growth of dogs
White-yellow, greasy, cauliflower-like
Histologic feature of solar/actinic keratosis
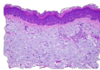
Dermal Elastosis
Characteristics of 1st degree thermal burns
Epidermis
Reddend/darkened necrotic epidermis
Complete healing
Urticaria - “Hives”
Localized areas of edema
Triggered by food, drugs, antisera, insect stings, etc
Characterisitcs of 2nd degree thermal burns
Epidermis and dermis
Vesicle formation
Some adnexa are preserved allowing epidermal regeneration with some scarring
MDx

Pyogranulomatous dermatitis
Causes of developmental anomalies
Genetic defect
In utero infection
In utero exposure to teratogen
Diagnostic techniques for Canine Superficial Speading Pyoderma
Cytology of pustule/crust
Woods Lamp
Fungal Culture
Skin Scrape
MDx

Pustular, exudative dermatitis
Acantholysis
Disruption of intercellular junctions
Pathogenesis of secondary photosensitization
- Light activates agents
- Free radical damage
- Epidermal necrosis of lightly pigmented or sparsely haired skin
What pathological process causes vesicles/bulla
Degeneration / Necrosis
OR
Inflammation and Repair
Type II (Intrinsic) Photosensitization can be caused by
Porphyria
Inherited deficiency of proporphyrinogen III cosynthetase
Defect in heme synthesis
Buildup of porphyrins
Mdx

Vesiculo-ulcerative dermatitis
Mdx

Superficial spreading pyoderma - a superficial pyoderma with bacterial folliculitis
Cause

Primary hemostasis defect - vasculitis vs thrombocytopenia
Sequence of lesion in pox viral infections
Macule → Papule → Vesicle → Umbilicated Pustule → Crust → Scar
Characteristics of skin lesions caused by circulatory disorders
Discrete reddened areas
Lesions follow a linear pattern
Lesions are in geometrical shapes
Vascular lesions result in ischemia
Equine sarcoid is caused by
Bovine Papilloma Virus
Factors that influence production of melanin
Hormones
Genes
Age
Inflammation
Primary Idiopathic Seborrhea
Inherited disorder of keratinization or cornification
Dry form Vs Greasy form
Secondary hyperkeratosis can be due to
Endocrine imbalances
Chronic dermatitis
Zinc responsive
Cause of Feline Leprosy
Mycobacterium lepraemurium
________________________
Obligate intracellular organism
Generalized form of demodicosis
Familial with young dogs
Adult onset - associated with systemic disease such as neoplasia, endocrinopathy or immunosuppresive therapy
Hypotrichosis
Less than the normal amount of hair
Hereditary most common
More susceptible to environmental extremes and infections
Type II Hypersensitivity
IgG or IgM Mediated Cytotoxic Hypersensitivity
Manifestations - blood transfusion reactions, erythroblastosis fetalis and autoimmune hemolytic anemia
Auto-Immune
Predisposing factors for Greasy Pig Disease
Other skin lesions
Poor nutriton/ husbandry
Lacerations
Disease

Mucinosis
Cutaneous Soft Tissue Sarcomas - Spindle Cell Tumors
Very common in dogs
Multiple types
Prognosis predicted by grade and margins
Locally invasive, slow to metastasize
Impetigo
Superficial Pustular Dermatitis
Nonfollicular pustules which develop into crusts
Prepubescent puppies - healthy
Adults - look for underlying cause
Solar/Actinic Keratosis is caused by
Chronic (years) of UV light exposure
Intertrigo
Skin Fold Pyoderma
Hyperkeratosis
Increased thickness of stratum corneum
Scaling “seborrhea”
Primary Vs Secondary
Cutaneous Habronemiasis - Summer Sores
Cutaneous eosinophilic granulomas caused by larval migration of Habronema or Draschia sp deposited into a wound by house or stable fly
Melanin
Pigment that imparts skin color
Histological appearance of melanomas
Characteristic junctional change in nonulcerated biopsies


