Circulatory Disturbances Flashcards
Ground substance of ECM consists of
Glycoproteins (Fibronectin and Laminin), Glycosaminoglycans, Proteoglycans, etc
Edema can be classified as
Inflammatory
Non-Inflammatory
Water distribution between plasma and interstitium is primarily determined by
Hydrostatic and Osmotic pressure differences between the two compartments
Thrombosis
Clot (thrombus) forms within a vessel which is not injured or only mildly injured
Endothelin released from vascular endothelium has what effect
Vasoconstriction
Coagulation Factors
Plasma proteins produced by the liver
Interstitial fluid accounts for ________% of total water weight
15%
Starling Equation
Illustrates the role of hydrostatic and osmotic forces in the movement of fluid across capillary membranes
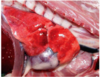
Common name for this disease

“Mulberry Heart Disease”
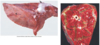
Nutmeg Liver
Appearance of the parenchyma with animal suffering from chronic hepatic congestion
Coagulation Cascade
Amplifying series of enzymatic conversions; each step proteolytically cleaves an inactive proenzyme into an activated enzyme, culminating in thrombin formation
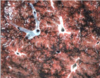
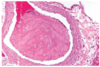
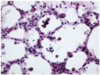
Histological appearance of what circulatory disorder

Edema
Interstitium is composed of
Extracellular Matrix (ECM)
Supporting Cells
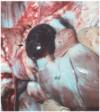
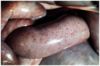
Condition

Submandibular edema
_______________________
“Bottle Jaw”
Fat Embolsim can be the result of
long bone fractures
Pericardial Effusion
“Mulberry Heart Disease”
Inflammatory edema
Fibrin strands and cloudy appearance of pericardial fluid
Cardinal signs of inflammation
Reddening - Rubor
Edema - Tumor
Heat - Calor
Pain
Loss of Function
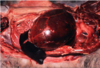
Example of what circulatory disturbance
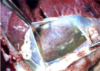
Edema
________________
Inflammatory Edema
Pathogenesis of septic shock
- Endotoxin - producing gram negative bacilli
- LPS and other microbial substances induce injury and activation of the vascular endothelium
- Stimulate WBCs to release cytokines
- Vasodilation and prothrombotic diathesis
Describe what happens during the primary hemostasis step of normal hemostasis
- Endothelial injury exposes highly thrombogenic subendothelial ECM allowing platetlets to adhere and be activated
- Activation of platelets results in a dramatic shape change and release of secretory granules lead to further platelet aggregation to form the primary hemostatic plug
- Secreted products recruit additional platelets
Hemostasis
Arrest bleeding by physiological properties of vasoconstriction and coagulation or by surgical means
Anti-coagulation factors secreted by endothelium
Prostacylin
Nitric Oxide
Tissue Plasminogen Activator (tPA)
Thrombomodulin
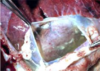
Condition

Hydrothorax
Gingivitis and blood shot eyes are an example of what circulatory disturbance
Hyperemia
Pro-coagulation factors secreted by endothelium
Thromboplastin
Platelet Activation Factor (PAF)
Von Willebrand Factor
Describe what happens during the secondary hemostasis step of normal hemostasis
- Tissue factor is exposed at the site of injury
- Thrombin cleaves circulating fibrinogen into soluble fibrin creating a fibrin meshwork deposition
- Thrombin also induces further platelet recruitment and granule release
Venous Infarcts
Intensely hemorrhagic as blood backs up into the affected tissue behind the obstruction
In which direction does hydrostatic pressure move fluid?
Moves fluid out of vasculature
Classification of hemorrhage

Paintbrush hemorrhage
Describe the basic mechanism of normal hemostasis
- Vasoconstriction
- Primary hemostasis
- Secondary hemostasis
- Thrombus and antithrombotic events
Example of what circulatory distrubance
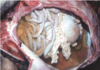
Edema
Hemothorax
Blood in the thoracic cavity
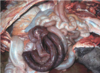
Condition

Colonic Torsion
Increased blood hydrostatic pressure can be the result of
Generalized - Right sided CHF
Localized - Tightly bandaged limb resulting in venous occlusion
Role of vascular endothelium in hemostasis
- Anti-thrombotic and pro-fibrinolytic in normal state
- Pro-thrombotic and anti-fibrinolytic during injury
Hemorrhage by Rhexis
Due to a substantial rent or tear in the vascular wall (or heart)
Example of what circulatory disturbance?
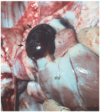
Hemorrhage
Iron (Perl’s) Stain
Highlights hemosiderin - laden macrophages within alveoli
_____________________
Stains blue
Pathological hyperemia is usually caused by
Inflammation
Substances released from vascular endothelium that modulate perfusion
NO
Endothelin
Types of hyperemia
Physiological
Pathological
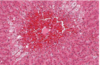
Condition - Fibrin thrombi within glomerular capillaries

Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC)
Describe the histologic appearance of edema
- Clear or pale eosinophilic staining
- Dependent on inflammatory vs non-inflammatory
- Spaces distended
- Blood vessels filled with RBC
- Lymphatics dilated
- Collagen bundles separated
Difference betwen hemorrhage and hyperemia/congestion
Hemorrhage the blood is outside the vessel wall
Hyperemia/Congestion the blood is within the blood vessels
Tissue Factor - Factor III-Thromboplastin
Membrane bound procoagulant glycoprotein synthesized by endothelium. Acts in conjunction with Factor VII as the major in vivo pathway to activate the coagulation cascade, eventually culminating in thrombin
Nitric Oxide when released from vascular endothelium has what effect
Relaxation and vasodilation
Hemoptysis
Coughing up of blood or blood-stained sputum from the lungs or airways
End results of shock
Hypotension
Impaired tissue perfusion
Cellular hypoxia
DIC and multi-organ system failure
Thrombosis
Formation or presence of a solid mass within the cardiovascular system
Secretory granules secreted during primary hemostasis
ADP and TXA2
Thrombomodulin
Has anticoagulent activity
Structural molecules of the ECM include
Collagen, Reticulin and Elastic Fibers
Edema
Abnormal accumulation of excess extracellular water in interstitial spaces or in body cavities
_____________________
Fluid is outside both vascular fluid compartment and cellular fluid compartment
Thromboplastin
Promotes blood coagulation
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC)
Systemic reaction in which there is generalized activation of the blood coagulation system
Etiology
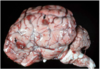
Histophilus somni infection
Pathological form of hemostasis is
Thrombosis
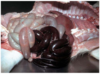
Example of what circulatory disturbance

Thrombosis
___________________
Saddle Thrombosis
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)
Sudden, diffuse and direct - increase in vascular permeability.
High fatality rate
Pneumonia if animal survives
Clinical significance of hemorrhage is determined by
location and severity
Hydrothorax
Fluid in the thoracic cavity
Condition

Chronic Hepatic Congestion
_______________________
Nutmeg Liver
Example of what circulatory disturbance

Congestion
_________________
Pulmonary congestion
Tissue Plasminogen Activator (tPA)
Regulates fibrinolysis
Describe what happens during the vasoconstriction step of normal hemostasis
- Brief period of arteriolar vasoconstriction occurs mostly as a result of reflex neurogenic mechanism
- Augmented by local secretions of factors such as endothelin
Example of circulatory disturbence

Edema
___________________
Pitting Edema
Example of what circulatory disturbance
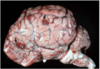
Thrombosis
Condition

Pulmonary Edema
Extracellular Matrix is composed of
Structural molecules
Ground substance
Decreased plasma colloid osmotic pressure can be the result of
- Proteins not absorbed from diet
- Proteins not produced
- Protein loss
Congestion
Passive venous engorgement - blood is not oxygenated