Skeletal Trauma Flashcards
Nondisplaced fracture only visualized on ___ view
Oblique
The following is what imaging modality

CT
____ is the preferred modality for traumatically induced internal drangment of joints & soft tissues (including spinal cord & nerves)
MRI
Entire circumference of the bone is disrupted = ____ fracture
Complete
Involves only part of the cortex (seen MC in children or in smaller bones such as distal radius or ulna) = ____ fracture
Incomplete
This is an example of a ____ (complete/incomplete) fracture

Complete
This is an example of what kind of fracture

Incomplete - Greenstick (generally only occure in skeletally immature population)
This is an example of what kind of fracture?

Incomplete - Torus (aka buckle, generally occurs in skeletally immature)
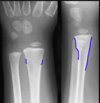
This is an example of what kind of frature?

Incomplete - Stress

____ fractures are a result of tension and/or angular forces
Transverse

This is an example of a ____ fracture

Transverse

____ fractures are a result of compressive forces
Oblique
This is an example of ____ fracture

Oblique
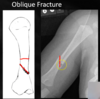
____ fractures are a result of rotational forces
Spiral
The following is an example of ____ fracture

Spiral

More than two fragments = ____
Only two fracture fragments = ____
Comminuted
Non-comminuted
This is an example of ____ (comminuted/non-communited) fracture
Non-communited

This is an example of ____ (comminuted/non-communited) fracture

Communited

The degree of contact at the fracture site between the fragments = ____
Apposition
Describe the apposition of the following image

Good

Describe the apposition of the following image

No (poor) apposition - Distraction

Describe the apposition of the following image

No apposition - Bayonet

Describe the angulation of the following image

Posterior angulation of the distal aspect of distal fragment

Describe the angulation of the following image

Lateral angulation of the distal aspect of the distal segment

















































