Chest Disorders Flashcards
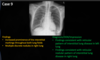
Identify the structures shown here

1 - Aortic Arch (should be ~4 cm)
2 - Pulmonary Trunk
3 - Left ventricle
What is demonstrated by the yellow lines?

What structures are represented by the blue & purple markings?

Blue
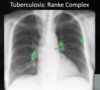
What condition is likely the cause of these findings?

Pneumonia/Tuberculosis
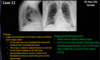
Identify the structure shown here

Horizontal fissure

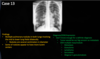
What pattern of pneumonia is shown here?

- Bilateral, perihilar area, Irregular
- Bronchopneumonia
- Pink circle = cavitation •associated w/ Infection ie. TB & Tumor)

This appearance is associated with what condition

Interstitial/Nodular
“Milliary pattern”
Associated with TB or fungal infection
(Differential = metastasis/tumor)
- Opacities frequently desribed as ill-defined, hazy or fluffy
- Margins of opacities are poorly defined & indistinct
- May demonstrate air bronchograms & silhouette signs
Air space disease (aka consolidation)
In air space disease, air is replaced with what 4 things
Blood (pulmonary hemorrage)
Pus (exudate assoc. w/ infection)
Water (aspiration)
Cells (tumor)
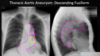
What findings are demonstrated here?


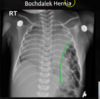
What findings are shown here?


____ pattern in interstitial disease that appears as lines
Reticular
____ pattern in interstitial disease that appears as small numerous discrete opacities separated from one another by normal lung
Nodular
_____ pattern in interstitial disease that is a combo of lines & opacities
Reticulonodular
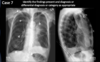
What findings are shown here?


What findings are shown here?


What findings are shown here?


When two similar radiographic densities are in anatomical contact with one another, the visible border between the two structures is lost
Silhouette sign
Involvement of RUL → what structure silhouetted
Ascending aorta
Involvement of RML → what structure silhouetted
Right heart border
Involvement of RLL → what structure silhouetted
Right hemidiaphragm
Involvement of LUL → what structures silhouetted
Aortic knob
Pulmonary trunk
Left heart border
Involvement of LLL → what structures silhouetted
Descending aorta
Left hemidiaphragm
What findings are shown here?

Silhouette Sign - Increased density in RML which obscures right heart border