Metabolic & Endocrine Disorders Flashcards
Normal bone quality, decreased bone quantity =
Osteoporosis
Females are affected by osteoporosis __:__ over males
4:1
(After 80, females = males)
Secondary causes of ____ include metastasis, multiple meyloma, alcoholism, endocrine disorders, etc.
OSteoporosis
Clinical presentation of ____ include:
- Clinically silent
- Increased kyphosis as disease progresses
- Symptoms become apparent when there are fractures
Osteoporosis
Radiographs are ____ (good/not good) are grading osteoporosis
Not good
Radiographic findings of ____ include:
- Osteopenia (on radiographs this is a descriptive term ie. less dense, DEXA scan it is diagnosis)
- Loss of 2° stress trabeculae, accentuation of 1° trabeculae
- Vertical striations in VBs (pseudohemangiomas)
- Pencil thin cortices
- Compression fractures (anterior wedge, fish vertebra)
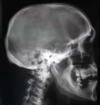
Generalized Osteoporosis
What are is the likely cause of these findings?
(Normal on left)
Generalized Osteoporosis - CT w/ Fish Verterbra

What is the likely cause of these findings?

Generalized Osteoporosis - Accentuated Vertical Striations (pseudohamangiomas)
What is the likely cause of these findings?

Generalized Osteoporosis - Accentuated Vertical Striations, anterior wedging, and gas bubble

What is the likely cause of these findings?

Generalized Osteoporosis - Anterior compression fracture as a result of hyperkyphosis

What is the likely cause of these findings?

Generalized Osteoporosis - Ward’s Triangle

What is the likely cause of these findings?

Generalized Osteoporosis - Pencil thin cortices

What is the likely cause of these findings?

Generalized Osteoporosis - Insufficiency Fracture

____ is gold standard for osteoporosis diagnosis, ____ is most accurate but expensive
DEXA scan
Quantitative CT
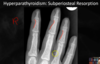
____ is the most common cause of regional osteoporosis
Other causes are ___ & ____
Disuse (common following immobilization)
Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS) & Transient osteoporosis of hip (TROH)
Regional osteopenia can be seen within _____ in disuse regional osteoporosis, _____ following CRPS
7-10 days
3-4 months
What is the most likely cause of these findings?

Regional Osteoporosis - Disuse
- Relatively normal bone quantity, poor bone quality
- Results in soft bones
Imaging findings include:
- Generalized osteopenia
- Trabecular coarsening & indistinctness
- Fracture deformites (fish vertebrae, Triradiate pelvis, kyphoscoliosis, etc.)
- Pseudofractures (insufficiency fractures in unusual locations)
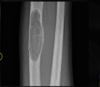
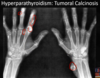
Osteomalacia
What is the most likely cause of these findings?

Osteomalacia - but NOT associated specifically, can be seen in any condition with decreased bone density (quantity, quality or both)

What is the most likely cause of these findings?

Osteomalacia - Pseudofractures
(Can also be seen in Padgets or Fibrous dysplasia)

- Vitamin D related
- Primarily a disease of growth plates (seen w/ osteomalacia)
- Clinically, may see bowing deformities, overgrowth of cartilage near joints, “rachitic rosary”
Rickets
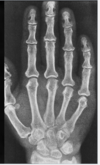
Image findings of ____ include:
- “Paint brush” metaphysis
- Splayed/cupping of metaphysis
- Non-calcified zone of provisional calcification → widened growth plate
Rickets
What is the most likely cause of these findings?

Rickets - Non-calcific zone of provisional calcification & cupped appearance

What is the most likely cause of these findings?

Rickets - Paint brush metaphysis