Hematologic Diseases Flashcards
Clinical findings of ___ include:
- Doesnt manifest until after 6 months of age
- Weakness, pallor, jaundice
- Abdominal crisis of bowel infarctions
- Organomegaly
- Hand-foot syndrome (children under 2 years)
Sickle Cell Anemia
Bony changes in sickle cell anemia are primarily due to _____
ischemia/osteonecrosis
Imaging findings of ____ include:
- Fish vertebrae
- “H” vertebrae (Reynolds)
- Hair-on-end skull (uncommon)
- Osteopenia/osteosclerosis
Sickle cell anemia
What condition is likely the cause of these findings?
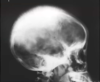
Sickle cell anemia - Hair-on-end
(differential = thalassemia should be first thought)
What condition is likely the cause of these findings?

Sickle cell anemia - H vertebra
(differential = thalassemia should be 2nd thought)

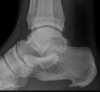
What condition is likely the cause of these findings?

Sickle cell anemia - H vertebra & fish shaped
What condition is likely the cause of these findings?

Sickle cell anemia - osteosclerosis
(differential = osteopetrosis, padgetts, blastometaphysis)
Erlenmeyer flask deformity is associated with osteopetrosis & _____
Sickle cell anemia
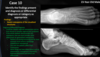
What condition is likely the cause of these findings?

Sickle cell anemia - hand-foot syndrome

What condition is likely the cause of these findings?

Sickle cell anemia - osteomyelitis
(aggressive lesion)

What condition is likely the cause of these findings?

Sickle cell anemia - Erlenmeyer flask

What condition is likely the cause of these findings?

Sickle cell anemia - multiple bone infarcts

The following are soft tissue imaging findings associated with ____:
- Gallstones (up to 65%)
- Bowel infarction
- Organomegal
- Auto splenectomy (secondary to infarction and fibrosis)
- Extramedullary hematopoiesis (uncommon)
Sickle cell anemia
What condition is likely the cause of these findings?


Clinical findings of ____ include:
- Pallor, lethargy, retarded growth
- Organomegaly
- Rodent facies
- Repeated transfusions → hemochromatosis → cardiac failure/death
B-Thhalessemia major
What condition is likely the cause of these findings?

B-Thalassemia Major - hair-on-end (most commly occurs in this tradition)

What condition is likely the cause of these findings?

B-Thalassemia - hair-on-end
CT

What condition is likely the cause of these findings?
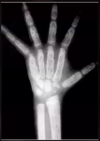
B-Thalassemia Major - Honeycomb trabecular pattern
What condition is likely the cause of these findings?

B-Thalassemia - Honeycomb trabecular pattern
What condition is likely the cause of these findings?

B-Thalassemia Major - Extramedullary hematopoiesis

What condition is likely the cause of these findings?

B-Thalassemia Extramedullary Hematopoiesis

H-shaped vertebral bodies most common w/ ___ but can be seen with (just less common)
Sickle cell anemia
Thalassemia
Most common childhood malignancy (peak age 2-5 years)
Acute childhood leukemia (acute lymphocytic)
Imaging findings of ____ include:
- Osteopenia
- Lucent metaphyseal bands
- Periostitis
- Lytic bone lesions
- Splenomegaly
- Chloroma a soft tissue tumor of myeloid tissue (rare)
Acute childhood leukemia