Congenital Disorders Flashcards
_______ are a group of disorders with abnormal bone/cartilage formation & remodeling
Skeletal dysplasias (aka osteochondrodysplasias)
Abnormal enchondralbone development =
Achondroplasia
Abnormal intramembranous bone development =
Cleidocranial dysplasia
Abnormal collagen formation =
Marfan’s syndrome
Osteogenesis imperfecta
- Osteopoikilosis
- Osteopathia striata
- Osteopetrosis
- Melorheostosis
These are examples of _____
Sclerosing bone dysplasias
Disorder of histogenesis =
Neurofibromatosis
- Autosomal dominant disturbance in growth and maturity of cartilage basedbone
- Mutation in the fibroblast growth factor receptor-3 gene
Achondroplasia
Achondroplasia is associated with _____ limb shortening
Rhizomelic
(Proximal limb shortening)
Clinical presentation of ____ includes:
- Recognizable from birth
- Upper extremity more severely affected
- “Large” cranium with prominent forehead and flat nasal bridge
- Waddling gait
- Protuberant abdomen and buttocks
- Neurologic signs and symptoms due to foramen magnum and canal stenosis
Achondroplasia
Radiographic findings associated with _____ include:
- Small foramen magnum
- Hydrocephalus
- “Bullet vertebra” common at thorcolumbar junction
- Acute kyphosis
- Posterior vertebral body scalloping
- Increase lumbar lordosis
- Horizontal sacrum
Achondroplasia
What is this MRI study demonstrating?

Achondroplasia (Small foramen magnum, canal stenosis)

What imaging modality and condition is demonstrated here?

Head CT (Sagittal on left, Coronal on right)
Achondroplasia (Small foramen magnum, hydrocephalus, prominent ventricles)

What condition is likely the cause of these findings?

Achondroplasia - Bullet Vertebra

What condition is likely the cause of these findings?

Achondroplasia - horizontal sacrum

What condition is likely the cause of these findings?

Achondroplasia - Posterior Vertebral body scalloping

What condition is likely the cause of these findings?

Achondroplasia - decreasing interpediculate distance

What condition is likely the cause of these findings?

Achondroplasia - Champagne Glass
(Squared off ileum, acetabular angle is flat, short thick femoral neck)

Middle limb shortening in achondroplasia (tibia/fibula and radius/ulna) =
Mesomelic
Shortening of the end of the limb in achondroplasia (hands & feet) =
Acromelic
Shortening of the entire limb in achondroplasia =
Micromelic
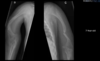
This is an example of _____ limb shortening in achondroplasia

Rhizomelic
This is an example of _____ in achondroplasia

Trident hand (3 digits in middle are same length)
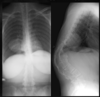
Clinical presentations of _____ includes:
- Most often affects skull, clavicle, axial skeleton
- Typically large head and small face
- Shoulders can be approximated
- Drooping shoulders
- Gait abnormalities
- Dentition abnormalities
- Short stature
Cleidocranial Dysplasia
Radiographic findings of ____ include:
- Multiple wormian bones
- Delayed closure of fontanelles
- Delayed/Defective dentition (too many or few teeth)
- Midlnie spinal defects (spina bifida occulta)
- Wide symphysis due to delayed ossifcation
- Narrow thorax
Cleidocranial Dysplasia