Sensory Vision Flashcards
What muscles do CN 3,4,6 control?
Extraocular muscles
What does the oculomotor nerve provide a pathway for?
-parasympathetic nerves to control the ciliary muscle of the lens and the constrictor of the pupil
What does the facial nerve provide a pathway for?
-parasympathetic nerves to control secretion of tears from the lacrimal gland
Which cranial nerves supply sensory information from the eye?
-optic and trigeminal
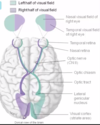
What does the optic nerve do?
-relays visual information from the retina to the lateral geniculate nucleus of the thalamus and the superior colliculus
What does the opthalmic division of the trigeminal nerve do?
-carries sensory information from the cornea (density of sensory receptors in cornea is 500x greater than skin which is why it is so sensitive to touch and pain)
What are the two elements of vision?
- Refractive media: refract the light to focus the image of the eye on the retina 2. Neural detection and transmission to the brain: detect the light and transmit the visual information to the brain
What is the vitreous humor?
-occupies the posterior segment of the eye behind the lens -consists of 99% water 1% protein -has high refractive index -slowly replaced over time with turnover of about 7 months -attached to retina at back of eye -shrinkage of eye during aging/change of composition can pull on retina and lead to a retinal detachment
Where does light first enter the eye? What is the difference in refractive index like here?
-light first enters eye through tear film at surface of cornea -this is where difference in refractive index of the air and tissues of the eye is the greatest -this means that most of bending of light occurs at this location
Where does light pass through after the cornea?
-through the anterior chamber of the eye, the lens, then vitreous humour before being focused on the retina at the back of the eye
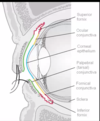
What makes up the outer fibrous coat of the eye? What does this provide?
-cornea and sclera -structural support
What does the vascular coat consist of?
-choroid which is posterior -ciliary body near front -iris
What is the choroid?
-highly vascularized and pigmented layer -supplies nutrients and oxygen to outer layers of retina and makes eye opaque to light coming from the side
What is the ciliary body?
-contains a muscle at the front of the eye that changes the shape of the lens -contains blood vessels that produce the aqueous humour immediately behind the cornea -continuous with the iris at the front of the eye
What is the iris?
-contains variable amount of pigment that blocks light from entering the eye except through the pupil -size of pupil opening in the iris is regulated by contraction of pupilary sphincter muscles at tip of iris and contraction of dilator muscles which open size of pupil that run radially to its base
What is the innermost coat of the eye? What does it do?
-neural coat -aka retina -contains rod and cone photoreceptors that transduce photons into a neural signal -also contains two layers of inhibitory neurons that process the image; allow image to be processed in both dim and bright light, sharpens image, and extracts features of texture, colour, and edges to be sent to the brain through the optic nerve
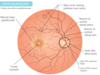
What is the fovea centralis?
- area of retina with highest visual acuity
- only small cones are located here
- cones synapse with retinal neurons located in parafoveal retina
- since blue light is scattered more than other wavelengths, retina around the fovea has deposits of yellow pigment that absorb blue light (macula lutea)
- blue light also has potential to damage photoreceptors so the macula lutea protects foveal photoreceptors
What is the function of the ganglion cells of retina?
-have axons that transmit visual info from retina to lateral geniculate nucleus of thalamus and superior colliculus of midbrain
What is the lateral geniculate pathway for from the retina? Superior colliculus pathway?
-conscious vision -unconscious vision
What are included in the connections of the superior colliculus?
-the nuclei that regulate pupil size and cerebellum that coordinates muscle movement

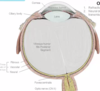
Where does bending of light occur in the eye?
- where there is greatest difference in density or refractive index
- refractory power: this is at the air/water cornea interface (80% occurs here)
- accomodation: lens is denser than the aqueous and vitreous humour and contributes 20% of refraction occurs here
How are the cornea and the lens different in terms of refraction?
- the lens is able to change its shape
- refraction that occurs when the lens is used to view close objects is higher than when the lens is used to view far objects
- accomodation: ability to increase refractive power of the lens when viewing close objects
What determines where the sharp point of focus of light from the lens and cornea will land?
-shape of fibrous coat
What is the shape of the eyeball largely determined by?
-genetic factors
What is hyperopia?
- eyeball is flattened so that the focal point lands behind the eye
- objects that are far away are sharp but objects that are close are out of focus
- 60% of the population
- can be corrected with convex (positive diopter lens) placed in front of the cornea
How does positive diopter lens work?
- lens is the same shape as the lens of the eye
- even though incidence is high, most people at a young age can get away with using their own lens but it can become a problem as you get older when the lens becomes less pliable
What is myopia?
- 25% of population
- eyeball is elongated
- focal point falls in front of retina
- objects that are near are sharp, objects that are far are not
- can be corrected with concave (negative diopter lens) in front of cornea
- younger people wearing glasses generally have this because the lens doesn’t have the intrinsic ability to change the shape in a negative way
What is astigmatism?
- eyeball can be mishapen along meridian plane
- causes blur in axis of error
- 30-60% are affected depending on ethnicity
- corrected by adding appropriate positive or negative diopters in the axis where the error occurs
Describe the cornea?
- makes up the anterior transparent part of the fibrous coat
- it’s composed of layers of collagen secreted by fibroblasts
- cornea has an epithelial layer (unlike sclera) which is bathed by tear film
- endothelium is bathed by the aqueous humour
- epithelium gets its nutrients from surrounding fluids because blood vessels would block vision