SA Otitis Flashcards
(29 cards)
Label this schematic of the ear.

THINK!
Describe the characteristics of the different parts of the tympanic membrane.

Pars flaccida
Stria mallearis - Insertion of auditory ossicles
Pars tensa - Translucent
Thick hairs lie proximal to membrane
Why is it difficult to flush a cats eat when compared with a dog?
A bony shelf separates two parts of the inner ear (little communication between each compartment) making flushing difficult
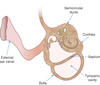
What cleaning mechanisms exist within the external and middle ear?
External canal - cerumen - antimicrobials, barrier, IgA. Epithelium carry cerumen out of the canal
Middle ear - Eustachian tube - drains fluid from the middle ear
3 P’s of otitis pathogenesis
Primary factor - initiates
Predisposing factor - continues
Perpetuating factor - makes worse
PAIN FREE
Primary factors mneumonic.
- P - parasitic
- A - allergic
- I - inflammatory
- N - neoplastic/ polyps
- F - foreign body
- R - rare/ misc
- E - epithelialisation
- E - endocrinopathies
Parasitic causes of otitis.
Otodectes cyanotis
Demodex - cornei, canis

Otodectes cynotis - hypersensitivity reactions cause otitis

Demodex canis - long tail

Demodex cornei/ gatoi - short tail
What types of hypersensitivity cause allergic skin disease?
Type 1 - IgE
Type 4 - delayed
Due to food or environmental allergens
What type of hypersensitivities cause immune-mediated otitis?
Generalised disease
Type 2 - Cell mediated antibody production
Type 3 - immune-complexes
Why do neoplastic or polypoid growths lead to otitis?
They disrupt the cleaning process/ expulsion of cerumen
Differentials for unilateral otitis..
Neoplasia
Foreign body - grass seed
Primary secretory otitis media
Plug of mucus within the middle ear - causes progrssive hearing loss, air scratching
Eustachian tube dysfunction
How do endocrinopathies lead to otitis?
Changes in epithelial turnover
Outline some predisposing factors which can lead to otitis.
- Conformation - large, pendulous ears, narrow ear canals, waxy ears
- Environment/ behaviour - lots of swimming, high humidity
- Iatrogenic - overcleaning/ inappropriate cleaning agents
Outline some perpetuating factors which lead to progressive otitis.
- Secondary bacterial infection - overgrowth of commensal bacteria
- Malassezia, Pseudomonas, staph pseudointermedius
- Progressive pathological change - calcification, stenosis, osteomyelitis
- Otitis media - ascending infection/ rupture of tympanic membrane

Peanut shaped malassezia found on cytology

Cocci - staphs/ streps
You perform an otic exam and find reduced flexibility on palpation. What could this be suggestive of?
Calcification of the ear canal
Differentials for pruritis on otic palpation
- Acute otitis
- Otodectes
- Malassezia
Differentials for pain on otic palpation
Chronic otitis
Epithelial ulceration/ hyperplasia (inflammatory)
Gram -ve bacterial infection (Pseudomonas/ proteus)
Modified wright-giemsa stain
Diff-quik


