S6) The ECG Flashcards
(55 cards)
What is the ECG?
- The ECG is a device used to measure the electrical activity of the heart by using electrodes placed on the skin
- This is an extracellular recording of the combined spread of electrical activity across the whole heart
- change in volts over time

Which structures compose the specialised conducting system of the heart?
- SAN (sinus rhythm)
- AV node
- Bundle of His
- Right and Left bundle branches
- Fibres of the Purkinje system

In 9 steps, outline how action potentials spread over the heart in a precise pattern

Which different complexes can form for depolarisation waves?

Repolarisation of the ventricles happens in the reverse order.
Thus, which different complexes can form from repolarisation waves?

What determines the nature of the signal?
The nature of the signal depends upon the direction of spread of the electric field relative to the position of the recording electrode
How can the nature of the signal be predicted in terms of repolarisation and depolarisation?
- Depolarisation towards a positive recording electrode → upward deflection
- Depolarisation away from a positive recording electrode → downward deflection
- Repolarisation towards a positive recording electrode → downward deflection
- Repolarisation away from a positive recording electrode → upward deflection
Which factors affect the amplitude of the deflection?
- Size and speed of muscle changing potential
- Direction of wave of activity towards the electrode (directly, obliquely, perpendicular)
Describe the electrical activity in this 5 individual diagrams and the depolarisation complexes they form


What is the mechanism behind the P wave?

P wave: atrial depolarisation (contraction) spreads along both atrial fibres & internodal pathways towards the AV node

What is the mechanism behind the Q segment?

Q segment: the initial downward deflection after the P wave as the muscle in the interventricular septum depolarises from left to right

What is the mechanism behind the QRS segment?

QRS segment: ventricular depolarisation

What is the mechanism behind the R segment?

R segment: initial upward deflection after p wave (large as there is greater muscle mass i.e. more electrical activity)

What is the mechanism behind the S segment?

S segment: downward deflection after the R as depolarisation finally spreads upwards to the base of the ventricles

What is the mechanism behind the T segment?

T segment: ventricular repolarisation (epicardial surface → endocardium) produces medium upward deflection

What is the R-R interval in the ECG and what is its significance?
- Where to measure: from peak to peak of R-waves
- What does this indicate: shorter interval = faster heart rate

What is the QRS complex in the ECG and what is its significance?
- Where to measure: start of the Q-wave to the end of the S-wave
- What does this indicate: wider QRS complexes are associated with abnormal ventricular depolarisations

What is the P-R interval in the ECG and what is its significance?
- Where to measure: start of the P-wave to start of the Q-wave
- What does this indicate: longer P-R intervals indicate slow conduction from the atria to the ventricle (first degree heart block)
time between depolaristion of atria and ventricles

What is the ST segment in the ECG and what is its significance?
- Where to measure: end of S-wave to start of T-wave
- What does this indicate: the ST segment should be isoelectric (myocardial infarction/ischaemia if raised/depressed)
when ventricle is depolarised but hasnt started repolarising
will be raised when someone is having a heart attack

What is the Q-T interval in the ECG and what is its significance?
- Where to measure: start of Q-wave to end of T-wave
- What does this indicate: a prolonged Q-T interval suggests prolonged repolarisation of the ventricles, lead to arrhythmias

Explain the relationship of the Q-T interval with the heart rate, and how this can be adjusted for
- The faster the heart rate, the shorter the R-R and Q-T interval
- This can be adjusted to improve the detection of patients with increased risk of ventricular arrhythmia (QTc)
time it takes for the ventricle to depolarise and repolarise - prolonged QT = prolonged repolarisation
should be less than 0.04s and half RR interval
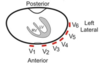
How many electrodes are used to record the ECG and where are they placed?
- Limbs: 4 electrodes (A) better to put them on 4 corners of your chest and lower abdomen
- Chest: 6 electrodes (B)
= 12 views via 12 leads

What are the colours of the different limb electrodes?
Mnemonic: Ride Your Green Bike

What are the colours of the different chest electrodes?
Mnemonic: Ride Your Great Big Brown Pony