S2) Control of Cardiac Output Flashcards
(48 cards)
What are the 7 phases of the cardiac cycle?
- Atrial contraction
- Isovolumetric contraction
- Rapid ejection
- Reduced ejection
- Isovolumetric relaxation
- Rapid filling
- Reduced filling
How can the cardiac cycle be split into 2 phases?
- Systole: isovolumetric contraction, rapid ejection, reduced ejection
- Diastole: isovolumetric relaxation, rapid filling, reduced filling, atrial contraction
What happens to systole and diastole when the HR increases?
When the heart rate increases, systole stays the same but diastole gets shorter
In terms of left atrial pressure, left ventricular volume, and the ECG, explain the changes occuring in Phase 1: Atrial Contraction
At the end of Phase 1, ventricular volumes are maximal: termed the End-Diastolic Volume (EDV) typically ~120 ml

What is End Diastolic volume?
End-Diastolic Volume is the maximal ventricular volume and occurs at the end of atrial contraction (~120 ml)
In terms of left ventricular pressure, left atrial pressure, left ventricular volume, the ECG and the phonocardiogram, explain the changes occuring in Phase 2: Isovolumetric Contraction

In terms of aortic pressure, left atrial pressure and left ventricular volume, explain the changes occuring in Phase 3: Rapid Ejection
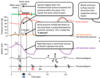
In terms of left ventricular pressure, left atrial pressure and the ECG, explain the changes occuring in Phase 4: Reduced Ejection

In terms of aortic pressure, left ventricular pressure, left ventricular volume and the phonocardiogram, explain the changes occuring in Phase 5: Isovolumetric Relaxation

In terms of left atrial pressure and left ventricular pressure, explain the changes occuring in Phase 6: Rapid Filling

In terms of left ventricular volume, explain the changes occuring in Phase 7: Reduced Filling

What is cardiac output?
Cardiac output is the volume of blood pumped per minute by the left side of the heart
CO = HR x SV
Explain how end diastolic volume is determined by the filling of the heart
- During diastole, the ventricles fill as the venous pressure drives blood into them
- The passive stretch of the ventricular wall causes intra ventricular pressure to rise, until it matches venous pressure, when no more filling will occur
How is stroke volume determined?
- Stroke volume is determined by how much the ventricle contracts during systole
- All myocardial cells normally contract, so active tension is changed by factors which act directly upon individual myocardial cells
Define the terms preload and afterload
- Afterload is the load the heart must eject blood against (~equivalent to aortic pressure)
- Preload is the amount the ventricles are stretched in diastole (related to the EDV or cVP)
Define the term total peripheral resistance
Total peripheral resistance (aka systemic vascular resistance) is the resistance to blood flow offered by all the systemic vasculature
What are the effects of changing total peripheral resistance?
- If TPR decreases and CO is unchanged:
I. Arterial pressure will decreases
II. Venous pressure will increase (will still be lower than arterial)
- If TPR increases and CO is unchanged:
I. Arterial pressure will increase
II. Venous pressure will decrease
What are the effects of changing cardiac output?
- If CO increases and TPR is unchanged:
I. Arterial pressure will increase
II. Venous pressure will decrease
- If CO decreases and TPR is unchanged:
I. Arterial pressure will decrease
II. Venous pressure will increase
Explain how the heart responds to an increased demand for blood
- Arterioles and precapillary sphincters dilate
- Total peripheral resistance falls
- Heart pumps more blood so aBP does not fall and cVP doesn’t rise
Referring to the profile of pressure changes in the internal jugular vein, identify the following component areas:


What is the Frank-Starling Law of the Heart?
Frank – Starling law of the heart: the more the heart fills, the harder it contracts (up to a limit) the bigger the stroke volume

How does the Frank Starling Law of the heart explain the relationship between the stroke volume and central venous pressure?
- Increased venous pressure causes the heart to fill more
- Increased force of contractions increases the stroke volume

Explain how the Starling Law of the heart ensures that both sides are balanced
The increased stroke volume with increased filling of the heart ensures that both sides of the heart maintain the same output as the pulmonary and systemic circulations operate in series
The relationship between left ventricular pressure and volume is illustrated in the Ventricular Compliance Curve.
Outline this
- In diastole, ventricle fills until the walls stretch enough to produce an intraventricular pressure equal to the venous pressure.
- The higher the venous pressure, the more the heart fills