Reproduction Tutorial Flashcards
What are the branches of the internal iliac artery?
- Umbilical artery (and superior vesical branches) 2. Obturator artery 3. Uterine (and vaginal branch) or inferior vesical (and prostatic branch) 4. Middle rectal artery (only present in 60% of people 5. Internal pudendal artery 6. Inferior and superior gluteal arteries
Describe the course of the internal pudendal artery
Leaves pelvis via greater sciatic foramen inferior to piriformis and loops round sacrotuberous ligament, enters perineum via lesser sciatic foramen
Describe course of inferior gluteal artery
Leaves pelvis via greater sciatic foramen inferior to piriformis to supply gluteal area
Describe course of superior gluteal artery
Leaves pelvis via greater sciatic foramen superior to piriformis to supply gluteal area
What structure runs in the lateral umbilical fold?
Inferior epigastric artery
What structure runs in the median umbilical fold?
Urachus (remnant of allantois)
What structure runs in the medial umbilical fold?
Obliterated umbilical artery
What is the angle between the cervix and the vagina?
Vagina angled slightly posterior towards sacrum and cervix projects slightly anteriorly Angle –> anteversion
What is the angle between the uterus and the cervix?
Angle of anteflexion
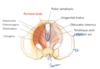
What is the perineal body?
Fibromuscular mass on which levator ani, muscles of UG diaphragm and external anal sphincter muscles converge
What does the pelvic diaphragm consist of?
Levator ani (puborectalis, pubococcygeus, iliococcygeus) and coccygeus
What separates the UG triangle and anal triange?
Imaginary line between ischial tuberosities
What are the boundaries of the UG triangle?
Pubic symphysis, ischiopubic rami laterally all the way to the ischiotuberosities, imaginary line between ishiotuberosities
Where is the perineal membrane found?
UG triangle only
What are the boundaries of the anal triangle?
Imaginary line between ischiotuberosities, laterally by sacrotuberous ligaments, posteriorly by coccyx
What are the boundaries of the ischioanal fossa?
Medial –> external anal sphincter and levator ani Lateral –> obturator internus Inferiorly –> subcutaneous tissue
What is purpose of ischioanal fossa?
Expansion during defecation
What does perineal membrane separate the UG triangle into?
Superficial and deep pouch
What is found between the perineal membrane and the pelvic floor?
Urogenital diaphragm (don’t confuse with pelvic diaphragm!) –> found in deep perineal pouch
What space is found between the UG diaphragm and the pelvic floor?
Anterior extension of ischioanal fossa (found in deep perineal pouch)
What can the UG diaphragm be divided into?
- Superior layer of loose connective tissue (superiorly) 2. Layer of striated muscle
What does the layer of striated muscle of the UG diaphragm contain?
External urethral spincter and sphincter of vagina (in females)
What is found lateral to urethral and vaginal sphincters?
Deep transverse perineal muscle (same course as perineal membrane but sits slightly deeper)
Describe layers of UG triangle
Deep pouch: 1. Anterior extension of ischioanal fossa 2. Superior layer of loose connective tissue 3. UG diaphragm (layer of striated muscle) Perineal membrane (thick layer of fascia) Superficial pouch
How does pudendal nerve enter superficial pouch?
Penetrate perineal membrane
Contents of deep perineal pouch?
- External urethral sphincter 2. Bulbourethral gland within deep transverse fascia (only in males) 3. Vaginal sphincter 4. Deep transverse perineal muscle
What does the superficial perineal pouch contain?
External genitalia
Describe the corpus cavernosum in males/females
Chamber of erectile tissue either side of corpus spongiosum Come together anteriorly to form body of penis (or body of clitoris in females)
What does corpus cavernosum attach to?
Ischiopubic ramus This forms the crus of the penis / clitoris
What muscle are corpora cavernosa covered by?
Ischiocavernosus muscles (helps keep blood within erectile chambers)
Describe corpus spongiosum in males
Erectile chamber in midline forms bulb of penis
Describe corpus spongiosum in females
Erectile chambers either side of vaginal opening (don’t fuse) forms bulb of vestibule (either side) This is just deep to labia majora
What muscle covers bulb of penis / bulb of vestibule?
Bulbospongiosus To keep blood within erectile chambers
Where are greater vestibular glands located?
Superficial pouch
What is the bulbourethral gland?
Either of two pea-shaped glands in the male, located beneath the prostate gland at the beginning of the internal portion of the penis; they add fluids to semen during the process of ejaculation Neutralises acidity of urine that may be present in urethra before ejaculation (protects sperm)
What is found in deep perineal pouch in males?
External urethral sphincter Bulbourethral glands
What is the female equivalent of the bulbourethral gland?
Greater vestibular gland
Where are the greater vestibular glands located?
SUPERFICIAL perineal pouch
What is function of greater vestibular gland?
Lubrication of vagina or urethra through mucus secretion
What are the paraurethral / Skene glands?
Glands in female that are important in lubrication of vagina (during sexual activity)
What are greater vestibular glands sometimes called?
Bartholin glands
Angle of cervix uterus and vagina diagram

Pelvic floor diagram