Renal Replacement Therapy 2 (Transplantation) Flashcards
where is the transplanted kidney placed and what vessels is it connected to?
Transplanted kidney is placed into the iliac fossa and anastomosed to the iliac vessels
Are the old kidneys removed in a kidney transplant?
Native kidneys usually remain in situ

What are some indicstions to remove the original kidneys?
Indications for native nephrectomy include size (polycystic kidneys) and infection (chronic pyelonephritis)
how is preservation of doner kidney done?
Cold storage solutions
Minimize oedema
Preserve integrity of tissues
Buffer free radicals
what are some transplant surgical complications?
Vascular complications:
- Bleeding: Usually anastomotic sites, Perirenal haematoma can be arterial or venous
- Areterial thrombosis
- Venous thrombosis
- Lymphocele (a collection of lymphatic fluid within the body not bordered by epithelial lining)
Ureteric - Urine leak
Infections
Why is immunosuppression needed in a kidney transplant?
As the body of the person receiving the kidney will reject it and the persons body cells will attack it
Can interfere with these 3 signals is how you do immune suppression

what are examples of immunosuppressive agents? and what are osme of their side effects?
Corticosteroids
Calcineurin inhibitors - Tacrolimus, Cyclosporine
Anti-proliefratives - Mycophenolate mofetil, Azathioprine
mTOR inhibitors - Sirolimus
Costimulatory signal blockers - Belatacept
Depleting agents - Basiliximab ( anti-CD25), Anti-thymocyte globulin (ATG), Rituximab (anti-CD20)

What is the immunesuppression protocol?
Induction: Basiliximab
Maintenance: Tacrolimus + Mycophenolate + steroids - tripple agent
Steroid free is possible
Others: CNI-free using Belatacept
what are the different type of donors?
Deceased Donors
Living Donors
what are the types of Deceased Donors?
Donation after brain death/DBD - standard / extended criteria
Donation after cardiac death/DCD - standard / extended criteria
what are the types of living donors?
Living Related Donor
Living Unrelated Donors:
- spousal
- altruistic
- paired/pooled
what is the brain death criteria?
(bulk of donations are from these people)
Coma, unresponsive to stimuli
Apnoea off ventilator (with oxygenation) despite build up of CO2
Absence of cephalic reflexes:
▪ pupillary
▪ oculocephalic
▪ oculovestibular (caloric)
▪ corneal
▪ gag
▪ purely spinal reflexes may be present
Body temperature above 34 C
Absence of drug intoxication
What is SCD and ECD?
Standard criteria, not ECD
Extended criteria (ECD):
- Donor aged > 60y
- Donor aged 50-59 + history of hypertension, death from cerbrovascular accident or terminal creatinine of >132µmol/L
Go for standard criteria as it is a better kidney but you can still take the risk and take the extended criteria donor kidney
is there a gap between demand and donation?

WHat type of transplant has the best survival rates?
All better survival if you have a living kidney donation

What is the Frequency of donor type-Scotland 1960-2013?

What is the post-listing outcome of transplant like?
If on transplant list should have a long chance of survival of around 5 years
Some do die while waiting
Some removed if they become more ill

what is the waiting time for a transplant?

what tends to be the gae of transplantation?
Dialysis is a treatment that filters and purifies the blood using a machine. This helps keep your fluids and electrolytes in balance when the kidneys can’t do their job
In medicine, dialysis is the process of removing excess water, solutes, and toxins from the blood in people whose kidneys can no longer perform these functions naturally. This is referred to as renal replacement therapy

living kidney donation may be done by who?
Live related donor
Live unrelated donor (eg spousal)
Live unrelated donor – altruistic, non-directed
Paired / pooled
ABO incompatible / HLA incompatible
What is pooled donation?
Create a chain and the number of transplants you did is much greater and utilise the altruistic to start the chain

what things need to be thought about in relation to kidney donation saftey?
Is it safe to donate a kidney?
What are short and long-term risks?
Is there a risk of end stage kidney disease?
How does GFR and urinary albumin excretion change after donation?
Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR) and Urinary Albumin Excretion According to Time since Donation

what are the risks of kidney donation?
Similar patient survival to general population
Lower rate of ESRD compared to general population reduced
Compensatory increase in GFR of remaining kidney to 70% of pre-donation values
Compensatory increase greater in younger donors
Older age and high BMI were associated with GFR of <60
Relatively short follow up time (12 years)
what are the different types of complications that may happen after renal transplant?
rejection
infective - Infection increases when you offer immunosuppression to deal with rejection
cardiovascular
malignancy
what are types of rejection complications after a renal transplant?
Cell mediated
Humoral (Ab mediated)
what are types of infective complications after a renal transplant?
Bacterial
Viral
Fungal
what are types of cardiovascular complications after a renal transplant?
Underlying renal disease
CRF
Hypertension
Hyperlipidaemia
PT Diabetes
what are types of malignancy complications after a renal transplant?
Skin
Lymphoma
Solid Cancers
what are the types of acute rejection?
Hyperacute rejection (pre-existing alloreactivity to donor)
Acute rejection:
- T cell mediated rejection (TCMR)
Tubulointerstitial (Banff I) - Banff 1 not as bad as Banff 3
Arteritis/endothelialitis (Banff II)
Areterial fibrinoid necrosis (Banff III)
- Acute antibody mediated rejection (ABMR)
ATN-like (Banff I)
Capillaries and or glomerular inflammation (Banff II)
Arterial inflammation (Banff III)
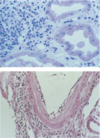
What are the types of T cell mediated rejections?
top picture:
Lymphocytic infiltrate
Tubulitis (inflammation of a tubule)
bottom picture:
Endarteritis (inflammation of the inner lining of an artery)
Endothelialitis (inflammation of the endothelium)
What are the 3 ways to check for antibody mediated rejection?
Microvascular inflammation:
- Neutrophil infiltration
- Glomeruli
- Peritubular capillaries
Donor specific antibodies
Positive C4d
- peritubular capillaries
What may someone dveelop after transplantation?
New onset diabetes mellitus after transplantation
Diabetes risk high in the first year then comes down

Infection after renal transplantation
What is the most important transplant-related infection?

Cytomegalovirus
Affects around 8% of trasnplant recipients, despite prophylaxis therapy
High mortality and morbidity if untreated
Recipient affected via:
- Transmission from donor tissue
- Reactivation of latent virus
CMV viremia is said to be a tissue _________ disease
Tissue invasive disease
- Pneumonitis
- Hepatitis
- Retinitis
- Gastroenteritis
- Colitis
- Nephritis

Does prophylaxis help CMV
Avoid it by prophylaxis in the first place

What are the clinical manifestations of the BK virus?
Can have it in other transplants and settings

How do you check to see if someone has BK virus?
Urine and Allograft-Biopsy Specimens from a Patient with BK Virus Nephropathy
Check it in blood to see if someone has it

Higher immunosuppression then higher risk of __
BK
WHat are the outcomes and management of BKAN?
Outcome:
- Allograft dysfunction
- Loss of graft in 45-80%
Treatment:
- Reduce immunosuppression
- Antiviral therapy (Antiviral therapy doesn’t really work) - cidofovir +/- IVIG, leflunomide
what is the risk of different malignancies after transplant?
When tumour occurs you are forced to come down on immunosuppression as that is the priority

Summary:
Kidney Transplantation is the best way to treat _____
Demand is much higher than ______
Expanding living and cadaveric donor pool is possible
Transplantation is not right for everyone and is not ____ free
Summary:
Kidney Transplantation is the best way to treat ESRD
Demand is much higher than supply
Expanding living and cadaveric donor pool is possible
Transplantation is not right for everyone and is not risk free


