Acute Kidney Injury Flashcards
What is the current deifniton of acute kidney injury?
a sudden episode of kidney failure or kidney damage that happens within a few hours or a few days. AKI causes a build-up of waste products in your blood and makes it hard for your kidneys to keep the right balance of fluid in your body
Increase in Creatinine:
- by ≥ 26.5 μmol/l (0.3 mg/dl ) within 48 hours; or
- to ≥ 1.5 times baseline, which is known or presumed to have occurred within the prior 7 days; or
Urine volume <0.5 ml/kg/h for 6 hours

is AKI common
yes
estimated that one in five people admitted to hospital each year as an emergency has AKI
What are the immediately dangerous consequences of AKI?
Dependant on cause to an extent at least in the first few hours
- Acidosis
- Electrolyte imbalance - Hyperkalaemia can cause CARDIAC ARREST
- Intoxication TOXINS
- Overload
- Uraemic complications

What are some short-term (in-hospital) outcomes even if AKI “not that bad”?
Death, dialysis (indications AEIOU), length of stay etc
What are some intermediate/long-term (post-discharge) outcomes even if AKI “not that bad”?
Death, CKD, dialysis, CKD related CVevents etc
what is the mortality (in-hospital)
2% no AKI
8% AKIN 1
25% AKIN 2
33% AKIN 3

Even ______ rises in Creatinine bad
small

what are the outcomes at 90 days like if they survive the week?

Is death common in the long-term?
yes
Risk progression over 10 years is increased two-fold with AKI compared to no AKI (if eGFR on discharge >=60; 1.5 times (1.5 95%CI(1.1-2.0) if eGFR 45-59
12% of AKI 3 who survived to discharge will be on RRT by 1 year
If have an AKI then recovered completely then still an increase of death

Example:
- baseline creatinine of 80 μmol/L
- Rises to 120 μmol/L (may still be in “normal” range)
- Significant kidney injury
- This is the moment to act – it is too late when the creatinine reaches 400
Start doing things as soon as there is a rise and don’t wait till 400 and its too late to reverse it
what are some pre-renal causes of AKI?
(Prerenal acute kidney injury is the most common type of acute kidney injury (70%). It can be a complication of almost any disease, condition, or medicine that causes a decrease in the normal amount of blood and fluid in the body. Anything causing hypoperfusion to the kidneys)
cardiac failure
haemorrhage
sepsis
vomiting and diarrhoea
what are some post renal causes of AKI?
(Mechanical obstruction of the urinary collecting system, including the renal pelvis, ureters, bladder, or urethra. Obstruction delaying or stopping the normal flow of urine, the plumbing. Something wrong with both kidneys to get an AKI, obstruction has to be affecting both kidneys)
tumours
prostate disease
stones
what are some intrinsic causes of AKI?
(rarer)
Glomerulonephritis
Vasculitis
Radiocontrast
Myeloma (a type of cancer that develops from cells in the bone marrow called plasma cells)
Rhabdomyolysis (breakdown of damaged skeletal muscle)
Drugs (NSAIDs, Gentamicin)
Can a indivual be multifactor for AKI?
yes
__________ is better than treatment of AKI
prevention

What are ways to pre-empt AKI developing?
Who is at risk of developing it?
- Post-surgery
- Volume deplete
- Rhabdomyolysis
- Radiocontrast
- Septic patients
- Acutely unwell (MI)
- Comorbid (DM)

Much of AKI is avoidable so how can it be prevented?
- Avoid dehydration
- Avoid nephrotoxic drugs
- Review clinical status in those at risk… and act on findings
- ? hold medication
- ? Give fluids
- Treat sepsis

IN th emanagement of a patient with a AKI, whta re th emain things to focus on?
Focus on optimising BP and volume and reassess the response afterwards
Pictures explaining medicine sick day rules?

Suggest to stop these tablets in order to get better and back to eating and drinking

Responding to AKI
Grampian guidance for AKI diagnosis and immediate management

What investigations and what things are assessed for AKI?
- History
- Examination - Fluid status etc
- Drugs
- Insults
- Renal function etc
- Urine dipstick
- FBC
- USS
- Blood gas
- Fancy blood tests for specifics if indicated
what things may be asked in a history?
Past medical history / systemic diseases (new rash, nose bleeds, sore eyes, joint pains)
Family history / social
Drug exposure (what / when)
Pre/post renal factors
Uraemic symptoms
Timing of symptoms – shortness of breath / urine output / vomiting etc…
what things may be checked on examination?
Vital signs (BP, pulse etc.,)
Volume status
Systemic illness (rash, joints, eyes etc.,)
Obstruction
what are some investigations that could be done?
blood tests
U&Es, Bicarb, LFTs, bone
FBC
Clotting
Blood gas?
? ANCA / Ig / C3 C4 dsDNA
urine tests
Urine dip
?blood?protein
?Urine PCR or ACR
??Urine Bence Jones Proteim
histology - renal biopsy?
radiology
Reviewing someone with AKI
picture showing grampian guidance on AKI review and follow up
Most important thing if you see someone with an AKI is to document why you think they have an AKI and how bad it was
Helps to write they have had an AKI so the GP knowns and also have a follow up plan for patients and this differs for every patient

what are potential indications for RRT (renal replacement therapy)?
Dependant on cause to an extent at least in the first few hours
- Acidosis
- Electrolyte imbalance
- Intoxication TOXINS
- Overload
- Uraemic complications
If patient has any one of these complications and have tried to fix and still has one of these problems then may end up needing dialysis
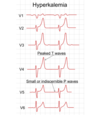
ECG changes hyperkalaemia:
what changes in T waves are seen?
Peaked T waves (usually the earliest sign of hyperkalaemia) Tall tented T waves

ECG changes hyperkalaemia:
what changes happen to P waves?
- P wave widens and flattens
- PR segment lengthens
- P waves eventually disappear
(should be a red circle, check slide 38)

ECG changes hyperkalaemia:
what other changes may be seen?
- Prolonged QRS interval with bizarre QRS morphology
- High-grade AV block with slow junctional and ventricular escape rhythms
- Any kind of conduction block (bundle branch blocks, fascicular blocks)
- Sinus bradycardia or slow AF
- Development of a sine wave appearance (a pre-terminal rhythm)

ECG changes hyperkalaemia:
what serious and life threatening condition may be seen?
CARDIAC ARREST!!!!!
Asystole
Ventricular fibrillation
PEA with bizarre, wide complex rhythm

what is the treatment of hyperkalaemia?
- Stabilise (myocardium) - First and most important is to try and stabilise the myocardium - Calcium Gluconate
- Shift (K+ intracellularly) - Want to try and push the potassium back into the cells
- Salbutamol
- Insulin-Dextrose
• Remove
- Diuresis - Give patient fluid which help lower potassium as it will have a dilute effect and perfuse the kidneys and get them to pee out the potassium
- Dialysis
- Anion exchange resins
Summary:
- AKI is _______
- AKI is source of much ________ and _______
- Early recognition of at ___ people should ___ AKI happening
- Early recognition and management of people with AKI should allow ________ outcomes
Summary:
- AKI is common
- AKI is source of much mortality and morbidity
- Early recognition of at risk people should stop AKI happening
- Early recognition and management of people with AKI should allow improved outcomes
Case A:
- E/a via GP 74 year old lady
- PC: Unwell and SOB
- Background: DM (on tablets); high BP; eczema; OA Rknee
- HPC: coughing last 5/7, slight CP with cough; inc SOB; cough green gunk 2/7; shivers and shakes come and go; feeling yeuk not eat and drink well; S/B GP for admission
- DH: aspirin 75mg cocodamol 30/500 2 tabs qds/prn; ramipril 10mg od, metformin 500mg bd; amlodipine 10mg od; bisoprolol 5mg od
- SH: lives with husband and dog, non-smoker and housewife
- FH: hypertension
- ROS: no GI symptoms
- Exam: temp 38.5oC, HS 1 and 2 nil else, p130 90/40; crackles++ L lung base, Abdo slight tenderness LUQ on deep pressure, soft, BS normal,
- What are the symtoms of concern?
- What are the signs of concern?
- What are your differential diagnoses?
- What investigations do you do?
- What risk factors for AKI does the patient have?
- Does this patient have AKI?
- Creatinine 120 was 90 last time checked
- What treatments might you start (or stop) and why?
Case B:
- E/a via GP 62 year old lady
- PC: Creat increased with GP
- Background: high BP; RhA
- HPC: Longstanding arthritis. Been feeling less well recently. Joint pains worse than usual, red spots on legs, went to GP. Creatinine blood test 160 (was 60 last time done)
- DH: aspirin 75mg; bisoprolol 2.5mg od
- SH: lives with husband
- Exam: temp 36.7oC, HS 1 and 2 nil else, p100 120/80; crackles++ L lung base, Abdo slight tenderness LUQ on deep pressure, soft, BS normal, joints slighlty swollen, rash on feet and legs
- What are the symtoms of concern?
- What are the signs of concern?
- Does this patient have AKI?
- What are the likely causes of AKI (pre/renal/post)?
- What investigations do you do?
- Should you write up all the drugs?


