Regions of the neck Flashcards
Describe the borders of the anterior and posterior neck?
Anterior: inferior border of mandible down to manubrium
Posterior: superior nuchal line down to C7/T1 disc
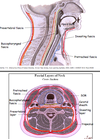
What are the four fascial layers of the neck?
Superficial fascia
Visceral fascia
Vascular fascia
Vertebral fascia

Give a general description of the fascial layers of the neck?
4 longitudinal compartments each contained within layers of cervical fascia

Describe the superificial fascial layer of the neck?
Contains a thin sheet of muscle called platysma
Blends with facial muscles and shares their nerve supply
Contains EJV

Describe the superficial veins of the neck?
Include their course and structures that they drain.
EJV and AJV
EJV begins at angle of mandible, vertical descent on sternocleidomastoid
Together, drain superifical muscles of neck

What is contained within the visceral fascial layer of the neck?
Thyroid, parathyroid and thymus glands
Also relates to trachea and oesophagus

What is contained within the vascular fascial layer?
Cartoid sheath and contents

What is contained within the vertebral fascial layer?
Cervical vertebrae and postural muscles

Where is the investing fascia located?
What does it contain?
Deep to superificial fascia
Surrounds all layers
Splits to enclose sternocleidomastoid and trapezius

Where is the prevertebral fascia loacted?
What does it contain?
Cylinder surrounding vertebral compartment
Contains vertebrae and postural muscles

Where is the pretracheal fascia located?
What does it contain?
Comprises pretracheal and buccopharyngeal fascia
Preatracheal fascia extends up to hyoid bone
Together surround visceral compartment
What is the significance of the pretracheal fascia connecting to the hyoid bone superiorly?
Hyoid bone moves up and down with swallowing > anything within pretracheal fascia will also move up and down with swallowing
What is the significance of the fascial layers of the neck in terms of communication?
Spaces between fascial layers can communicate up as well as down to medistinum
Allows unrestricted spread of infection
Describe the contents of the carotid sheath?
Common carotid artery/just afetr bifurcation
IJV
CN X

Describe the borders of the anterior triangle of the neck?
In front of sternocleidomastoid
Below inferior border of mandible
To one side of midline of neck (two anterior triangles: right and left)

Describe the borders of the posterior triangle of the neck?
Behind sternocleidomastoid
In front of trapezius
Above middle third of clavicle

Describe the contents of the anterior triangle of the neck?
Anterior vertebral muscles
Carotid system
Veins of neck
Glossopharyngeal, vagus, accessory and hypoglossal nerves
Thyroid gland
What do the anterior vertebral muscles consist of?
Suprahyoid and infrahyoid muscles
Describe the suprahyoid and infrahyoid muscles?
Suprahyoid: connect hyoid bone to skull, constitute floor of mouth, elevate hyoid and larynx
Infrahyoid: anchor hyoid bone down to sternum/clavicle/scapula, depress hyoid or larynx

In which fascial layer do the anterior verebral muscles lie?
Between investing fascia and pretracheal fascia

Describe the actions of the anterior vertebral muscles?
Steady or move hyoid bone and larynx
Suprahyoid: elevates
Infrahyoid: depresses
Describe the innervation of the anterior vertebral muscles?
Anterior rami of cervical nerves
At which level in the neck does the common carotid artery bifurcate?
C3/4 (upper border of thyroid cartilage)

Describe the braches of the internal carotid artery in the neck?
No branches in neck











