Joints of the hip complex Flashcards
Is all of the acetabulum articular?
No
Lunate surface is weight bearing
Acetabular notch and fossa are non-articular
Describe the shape of the epiphysis in the acetabulum until puberty?
Y shaped

What crosses the actebular notch?
Ligament

What fills in the space in the acetabulum?
Potential space filled with fat pad
Describe the location of the fat pads within the hip joint?
Intra-articular
Extra-synovial
What is the anatomical neck of the femur?
Line of growth plate

Where is the fovea in the femur?
Head

Where can traction epiphyses occur in the femur?
Greater and lesser trochanters
Where is the intertrochanteric line/crest?
What is its significance?
Between greater and lesser trochanter
Line is anterior, crest is posterior
Ligament attaches here

Where do blood vessels that supply the head of the femur enter the bone?
Enter growth plate just below anatomical neck
What is the significance of pressure and traction epiphyses in the femur?
Pressure epiphyses are weight bearing
Traction epiphyses can form where ligaments or muscles attach
Describe the orientation of the head of the femur?
What is the significance of this for the joint?
Directed upwards, medially and forwards
So, anterior part of head lies outside socket
How is the anterior part of the head of femur that lies outside the acetabulum protected?
Psoas bursa

What is the function of the psoas bursa?
Protects head of femur that lies outside acetabulum and tendon

What in the acetabulum does the head of the femur articulate with?
Why?
Roof of acetabulum
Thickest cartilage here

List the intra-articular structures in the hip joint?
Describe the function of each?
Labrum: deepens cup and increases SA
Ligament of head of femur: directs artery to femoral head

Describe the bony architecture of the femur?
Two trabecular systems that intersect: superior (vertical and arcuate) and inferior (medial and lateral)

Compare the functions of the vertical and arcuate bundles in the bony structure of the femur?
Arcuate bundle: resist bending forces on neck of femur
Vertical bundle: for weight bearing in stance
Where is the site of weakness in the bony architecture of the femur?
Why?
Arcuate bundles
Degenerate with ageing

Where does the line of gravity lie in relation to the hip joint?
Behind centre of joint

Describe the position of greatest stability in the hip joint?
Why?
Extension
Abduction
Medial rotation
This is the close packed position where the ligaments are most taught
Describe the ligamentous supports of the hip joint?
Iliofemoral ligament (strong, anterior)
Ischiofemoral ligament, Pubofemoral ligament (weaker, posterior)

Describe the attachment of the ligaments of the hip joints?
Iliofemoral: ileum to femur (2 attachments)
Ischiofemoral: from ischeum, blends with capsule (no attachment to femur)
Pubofemoral: from pubis, blends with capsule (no attachment to femur)

Describe the shape and function of the iliofemoral ligament?
Inverted V shape
Tighten and spiral medially when joint is in extension
Resist extension, prevent us from falling backwards

What are the retinacular fibres in the hip joint?
What is their function?
Reflections of fibrous tissue from capsule to femoral neck
Contain vessels which supply head of femur
Describe the movements that occur at the hip joint?
Flexion/extension
Abduction/adduction
Medial/lateral rotation
Describe the rotation that occurs at the hip joint during locomotion?
Medial rotation in stance
Lateral rotation in swing
Which muscles stabilise the head of femur in the acetabulum?
Cuff of fixator muscles
Dynamic support
Describe the actions of gluteus medius and minimus?
Maintain position of pelvis in coronal plane (stop pelvis from falling to unsupported side)
Abduct hip

Describe the effect of injury to the gluteus medius and minimus?
Trendellenberg gait
Which muscles are associated with the development of osteitis pubis?
Adductor muscles
Describe the nerve supply to the hip joint?
Innervated by articular branches of femoral and obturator nerve
Hilton’s law: joint receives pain and proprioceptive fibres from branches to muscles that move the joint (also pass to overlying skin)
Where does pain referred to the hip originate from?
Lumbar spine and SIJ
Describe the blood supply to the hip joint?
Via anastamoses between branches of medial and lateral femoral circumflex arteries (normally from profunda femoris)

Describe the structures that lie posterior to the hip joint that may be damaged in dislocation?
Sciatic nerve

Describe traumatic dislocations of the hip joint?
Head of femur slips out back of joint
Usually associated with fractured posterior lip of acetabulum
Why is re-artculation important in traumatic dislocations of the hip joint?
To maintain blood supply
Must be within 5-6 hours
Describe the appearance of a leg with a fractured neck of femur?
Why?
Muscle spasm causes external rotation and shortening of limb

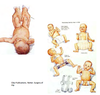
How can congenital dislocation of the hip joint be identified and treated?
Test in adduction
Treat by putting hip into abducted posture > adductor magnus pulls along line of femur and pulls head back into socket
Which fracture leaves the hip joint particularly susceptible to disruption of blood supply?
Fractured neck of femur


