Imaging of spine Flashcards
(34 cards)
When should imaging be employed when patients present with back pain?
Most back pain patients don’t require imaging
Need to select patients that have potential for serious instability or neurological damage
When is plain film useful for spinal imaging?
Alignment
Fractures
When is MRI useful for spinal imaging?
Looking at soft tissue structures
When is CT useful for spinal imaging?
Fractures
Discs
Describe the curvatures of the spine?
Cervical and lumbar: lordosis
Thoracic and sacral: kyphosis

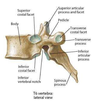
Describe the orientation of the facets in the lumbar spine?
Oblique

Describe the shape of vertebral bodies in the lumbar spine?
Concavity in lateral, anterior and posterior margins

Describe what is seen when viewing an X-ray of the anterior lumbar spine?
Thicker cortical bone
Concavity of body
Ring of shadows of cortex of pedicle
Spinal canal between pedicles

Describe why two lines of cortical bine are sometimes seen in imaging of the spine?
When cortical margin in oblique to X-ray beam

Describe what can be seen in an X-ray image of the lateral spine?
Thick and broad spinous process
Thicker cortical bone

Describe what can be seen in an oblique X-ray of the spine?
Scotty dog appearance

Where is a common fracture site of the spine in young people?
How does it appear on imaging?
Lamina - stress fractures
Neck of Scotty dog

Label the features of these X-rays?


How can intervertebral discs be visualised?
CT (T2 weighted)
MRI
Describe the appearance of the intervertebral discs in a T2 weighted C2 image?
Centre of discs appeasr bright
Strong signal due to water content of nucleus

Describe the arrangement of structures exiting the IV foramen?
Nerves superiorly
Small artery
Small nerve
Veins inferiorly
Surrounded by epidural fat

Describe the way in which spinal nerves exit the spinal cord?
Cervical: nerve goes out above pedicle of same name
C8 below C7 and above T1
Rest beneath pedicle

Which level has this axial image been taken at?

Below L1/L2 (cauda equina visible)
Which spinal nerve is affected due to lateral protusion of L4/5 disc? Why?
Which spinal nerve is affected due to lateral protusion of L5/S1 disc? Why?
L4/5: Affects L5 spinal nerve, as L4 nerve root has already exited above
L5/S1: affects S1 spinal nerve, as L5 nerve root has already exited above

Between which structures does the ligamentum flavum run?
Between laminae

Locate the ALL, PLL and ligamentum flavum in the following images?


Which ligaments are visible in axial spinal images?
Don’t see ALL and PLL well
Can see ligamentum flavum

Why is MRI used for spinal imaging?
Discs
Spinal cord
Contents of canal
Nerve roots
How are the spinous processes of the thoracic spine different to that of the lumbar spine?
Longer and more inferior direction