Quiz 3- Lec 15-16 Flashcards
(57 cards)
list the medial thigh muscles
- pectineus
- adductor brevis
- a. longus
- a. magnus
- gracilis
- obturator externus

where does the saphenous nerve leave the adductor canal?
between sartorius and gracilis;
just above the knee on the medial side
contents of the adductor canal
saphenous nerve
femoral artery
femoral vein
pectineus:
origin/ insertion
o: superior pubic ramus & pectin pubis
i: prox. 1/2 of pectineal line of the femur
* crosses hip; “pecten” means tooth of comb*

pectineus:
action/ innervation
- act: hip flexion and weak hip adduction
- inn: femoral nerve or obturator nerve (or both)

adductor brevis:
origin, insertion
o: body and anterior/ventral surface of inferior pubic ramus
ins: distal part of pectineal line of femur & prox. 1/3 of medial lip of linea aspera
* crosses hip*

adductor brevis:
action, innervation
act: ADDUCTion of hip, and flexion
inn: obturator nerve (anterior, posterior divisons, or both)

adductor longus:
origin, insertion
o: ventral surface of body of pubic, adjacent to pubic tubercle
ins: middle 1/3 of medial lip of linea aspera

adductor longus:
action, innervation
act: ADDUCTION of hip, flexion of hip joint
inn: anterior branch of obturator nerve

gracilis
origin, insertion
o: ventral surface of body of pubis & inferior pubic ramus
ins: tibia (pes anserinus) - posterior to sartorius & superior to semitendinosus

gracilis:
action, innervation
act: ADDUCTS hip, flexes the knee, medially rotates the leg while knee is flexed
inn: anterior division of obturator nerve
adductor magnus:
origin, insertion
- o:
- hamstring part: inferolateral part of ischial tuberosity
- adductor part: ventral surface of ischiopubic ramus
- ins:
- gluteal tuberosity & proximal ¼ of medial lip of linea aspera (minimus part of magnus) &
- distal ¾ of medial lip of linea aspera (adductor part) adductor tubercle via tendon &
- part of medial supracondylar ridge(hamstring part)

adductor magnus:
action, innervation
- act: ADDUCTION of hip, flexion of hip, (adductor part)
- extension of hip w/ hamstrings (hamstring part)
- inn:
- hamstring: tibial nerve
- adductor part: posterior branch of obturator nerve

CC: groin pull
an injury to the muscle tendon unit that produces pain on palpation of the adductor tendons or its insertion on the pubic bone with or without pain during resisted adduction
CC: riders’ bones
localized ossification sometimes seen on the inner aspect of the lower end of the tendon of the adductor muscle of the thigh in horseback riders.
which adductor group muscles are found in the:
anterior layer
- pectineus
- adductor longus

which adductor group muscles are found in:
middle layer
- adductor brevis
- gracilis

which adductor group muscles are found in:
posterior layer
adductor magnus

which adductor muscles are found in the
anterior, middle, and posterior layers
- ANTERIOR
- a. Longus
- Pectineus
- MIDDLE
- a. Brevis
- Gracilis
- POSTERIOR
- a. Magnus
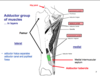
cc: which of the adductor muscles can be transplanted?
gracilis (part of all w/ neurovascular supply) can be transplanted to replace hand muscles &
to replace external anal sphincter muscle (free up distal attachment)
which part of the adductor magnus is the “hamstring part”?
the ischiocondylar part

identify the anterior and posterior divisions of the obturator nerve

- anterior division
- posterior division

course of the internal iliac artery leaving pelvis
leaves pelvis through obturator canal;
terminates by dividing to anterior and posterior branches
anterior branch of internal iliac artery supplies:
medial thigh muscles (adductor group)

















