Quiz 2- Lec 11-12 Flashcards
(66 cards)
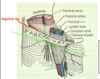
anterior hip muscles:
list
- psoas minor (absent in 40-50% of cases)
- iliacus
- psoas major (iliacus + psoas major = iliopsoas)

which anterior hip muscle is absent 40-50% of the time?
psoas minor

psoas major: origin & insertion
- o:
- ventral fibers from IV discs and vertebral bodies (T12-L5);
- dorsal fibers from inferior edges of transverse processes of L1-L5
- ins: all fibers converge into single muscle belly and thru combined tendon w/ iliacus into LESSER TROCHANTER

psoas major: innervation
L1-L3
(twigs from ventral rami)

psoas major: action
- *major hip flexor
- side-bending
- pelvic stabilization during gait;
- other actions are considered (lat. rotation of flexed hip & active during sit-ups & leg raises – hip flexion component)

iliacus: origin and insertion
- o: iliac fossa, internal lip of iliac crest, lateral part of pelvic surface of sacrum, ventral sacroiliac and iliolumbar ligaments
- i: thru combined tendon w/ psoas major into lesser trochanter and femoral shaft distal to lesser trochanter

iliacus: innervation
- *L2-L3
(fibers/twigs from ventral rami); diff’t from psoas major
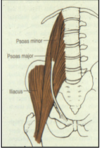
iliacus: action
- *major hip flexor
- pelvic stabilization during gait;
- other actions are considered (lat. rotation of flexed hip & active during sit-ups & leg raises – hip flexion component)
*NOT side-bending (but psoas major incl. this)

psoas minor: origin & insertion
- o: (anterior to major) from T12 & L1 vertebral bodies and disc
- i: iliopubic eminence (where pubis and ilium meet)

psoas minor: innervation
L1
(twig from ventral ramus)

psoas minor: action
- weak trunk flexion (controversial)
- & NO ACTION AT HIP; does not cross hip joint!

which muscles provide stability to hip joint anteriorly?
psoas major and iliacus muscles

identify:
- hip joint capsule
- iliopectineal bursa


identify where the following movements occur:
- trunk flexion
- hip flexion
- external (lateral) rotation


describe the blood supply to the lower limb?

- aorta
- common iliac
- external iliac
- femoral (after crossing deep to inguinal)
- internal iliac artery and branches
- superficial circumflex iliac
- deep circumflex iliac
- inguinal ligament
- femoral artery

where does SUPERIOR GLUTEAL ARTERY leave the pelvis?
through L4/5 and S1
*L4/L5 is lumbosacral trunk

where does INFERIOR GLUTEAL ARTERY leave the pelvis?
through S3/S4

where does OBTURATOR ARTERY leave the pelvis?
- originates from anterior division of internal iliac artery
- travels along the obturator fascia of the pelvic sidewall, between the obturator nerve and vein, to reach the obturator foramen
- leaves pelvis through OBTURATOR CANAL

contents of obturator canal
- connects the pelvis to the thigh
- contents: obturator artery, obturator vein, and obturator nerve all travel through the canal.
*internal pudendal artery: course
- exits the pelvic cavity through the greater sciatic foramen, inferior to the piriformis muscle, to enter the gluteal region.
- It then curves around the sacrospinous ligament to enter the perineum through the lesser sciatic foramen.

4 gateways to lower extremity from abdomiopelvic cavity
“LOGS”
- Lesser sciatic foramen
- Obturator canal
- Greater sciatic foramen
- Subinguinal space

identify the following:


subinguinal space: contents
- femoral vessels & nerve, lymphatics,
- Iliopsoas & pectineus muscles

obturator canal: contents
obturator vessels (artery and vein) and obturator nerve