Pleura Flashcards
What is each pleural cavity lined by
A single layer of flat cells, mesothelium, and an associated layer of supporting CT => pleura

Parietal pleura
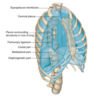
Attachments of the suprapleural membrane
- This connective tissue membrane is attached laterally to the medial margin of the first rib and behind to the transverse process of vertebra CVII
- Receives muscle fibres from some of the deep muscles in the neck (scalene muscles) that function to keep the membrane taut
Vertebral level of the root of the lung
T5 - T7
Where is the mediastinal pleura continuous with the visceral pleura
At the hilum of the lung
Innervation of the parietal pleura
- Somatic afferent fibres
Innervation of the costal pleura
Branches from IC nerves
=> pain would be felt in relation to the thoracic wall
Innervation of diaphragmatic & mediastinal pleura
Phrenic nerves (C3, C4, C5)
Where does the costal pleura reflect onto
Costal pleura reflects onto the diaphrgm above the costal margin
In the midclavicular line, where does the pleural cavity extend to
Inferiorly to approximately rib 8

Visceral and parietal pleura are continuous at
The hilum of each lung
Parietal pleural reflections and recesses

Where does the costomediastinal recess occur
On each side where costal pleura is opposed to mediastinal pleura
Largest is on the left in the region overlying the heart
- Where do the costodiaphragmatic recesses occur
- When are they deepest/shallowest
- Occur between the costal pleura and diaphragmatic pleura
- Deepest after forced expiration
- Shallowest after forced inspiration

- Inferior margin of the lung (from the MCL to the vertebral column)
- Inferior margin of the pleural cavity
- Line running between rib 6, rib 8 and vertebra T10
- PC = rib 8, rib 10 and T12
- Costodiaphragmatic recess is the region between the 2 margins


