Larynx Flashcards
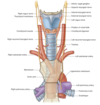
General structure of the larynx

What is the larynx suspended from and attached to
Hyoid bone above
trachea below
What happens to the larynx during swallowing
The dramatic upward and forward movements of the larynx facilitate closing the laryngeal inlet and opening the oesophagus
Motor and sensory innervation of the larynx
Vagus nerve (X)
Structure of cricoid cartilage

Attachments to the posterior surface of the cricoid cartilage
Oesophagus is attached to the ridge
Depressions are for attachment of the posterior crico-arytenoid muscles
Structure of thyroid cartilage

What is the oblique line a site of attachment for
Extrinsic muscles of the larynx
Sternothyroid
Thyrohyoid
Inferior constrictor
Structure of epiglottis

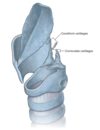
Structure of arytenoid cartilages

Cornicualte and cuneiform cartilages
Suspended in the part of the fibro-elastic membrane of the larynx that attaches the arytenoid cartilages to the lateral margin of the epiglottis
Thyrohyoid ligament

Cricothyroid ligament
When the airway is blocked above the level of the vocal folds, the median cricothyroid ligament can be perforated to establish an airway
Except for small vessels and the occasional presence of a pyramidal lobe of the thyroid gland, normally there are few structures between the median cricothyroid ligament and skin

Quadrangular membrane

Vestibular ligament and vocal ligament

What sort of joints are the cricothyroid and cricoarytenoid joints
Synovial - each is surrounded by a capsule and is re-inforced by associated ligaments
Movements of the cricothyroid joints
Because the vocal ligaments pass between the posterior aspect of the thyroid angle and the arytenoid cartilages that sit on the lamina of cricoid cartilage, forward movement and downward rotation of the thyroid cartilage on the cricoid cartilage effectively lengthens and puts tension on the vocal ligaments

Movements of the crico-arytenoid joints

Structure of the cavity of the larynx
What is the central cavity of the larynx lined with
Mucosa

LARYNGEAL CAVITY
- Anterior border
- Lateral borders
- Posterior border
- mucosa covering the superior margin of the epiglottis
- mucosal folds (aryepiglottic folds), which enclose the superior margins of the quadrangular membranes and adjacent soft tissues, and two tubercles on the more posterolateral margin of the laryngeal inlet on each side mark the positions of the underlying cuneiform and corniculate cartilages
- mucosal fold that forms a depression (interarytenoid notch) between the two corniculate tubercles

What is the inferior opening of the laryngeal cavity continuous with
The lumen of the trachea and is completely encircled by the cricoid cartilage - continuously open
What is within the walls of these laryngeal saccules
Numerous mucous glands
Mucus secreted into the saccules lubricates the vocal folds
Cricothyroid origin
cricoid cartilage

Cricothyroid insertion
Oblique part—inferior horn of the thyroid cartilage
straight part—inferior margin of thyroid cartilage