Nose and Nasal Cavity Flashcards
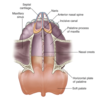
Anterolateral view of nasal cavities

Structures within nasal cavities

What are the anterior apertures called
Nares - open onto inferior surface of the nose
What are the posterior apertures called
Choanae, which open into the nasopharynx
How are the nasal cavities separated
From each other by a midline nasal septum
From the oral cavity below by the hard palate
From the cranial cavity above by parts of the frontal, ethmoid and sphenoid bones
What do the conchae do
Increase SA of contact between tissues of the lateral wall and respired air
Openings into nasal cavity

Regions of the nasal cavity
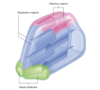
What is the nasal vestibule
A small dilated space just internal to the naris that is lined by skin and contains hair follicles
RESP REGION
- Neurovascular supply
- Lined with…
- Composed of
- Rich neurovascular supply
- Lined by respiratory epithelium
- Composed mainly of ciliated and mucous cells
OLFACTORY REGION
- Lined with
- What does it contain
- Lined by olfactory epithelium
- Contains the olfactory receptors
Other than housing receptors for smell (olfaction), name 2 other functions of nasal cavities
- Adjust temperature and humidity of respired air by the action of a rich blood supply
- trap and remove particulate matter from the airway by filtering the air through hair in the vestibule and by capturing foreign material in abundant mucus (which is then moved posteriorly by cilia on epithelial cells in the nasal cavities and is swallowed)
General sensation of the nasal cavities
Trigeminal nerve (V)
Innervation of anterior region
Ophthalmic nerve (V1)
Innervation of posterior region
Maxillary nerve (V2)
What are all glands innervated by
Parasympathetic fibres in the facial nerve (VII), which join branches of the maxillary nerve (V2) in the pterygopalatine fossa
Where are the sympathetic fibres of the nasal cavities derived from
T1 spinal cord level
Where do the sympathetic fibres of the nasal cavities synapse
Mainly in the superior cervical sympathetic ganglion
How do postganglionic fibres reach the nasal cavities
Along blood vessels or by joining branches of the maxillary nerve (V2) in the pterygopalatine fossa
Blood supply to the nasal cavities
- Terminal branches of the maxillary and facial arteries, originating from the external carotid artery
- Ethmoidal branches of the ophthalmic artery, originating from the internal carotid artery
Ethmoid bone

What does the crista galli anchor
A fold of dura mater, falx cerebri, in the cranial cavity
What does the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone articulate with
- POSTERIORLY - Sphenoidal crest on the body of the sphenoid bone and vomer
- ANTERIORLY - nasal spine on frontal bone and with the site of articulation at the midline between the 2 nasal bones
- INFERIORLY AND ANTERIORLY - septal cartilage
External nose