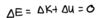Physics formulas Flashcards
(64 cards)
What is the linear motion equation without displacement?
vf = v0 + at
What is the linear motion formula without final velocity?
x = v0t + ½at2
What is the linear motion formula without time?
v2 = v02 + 2ax
What is the formula for average velocity when given displacement and time?

What is the formula for average velocity when given initial and final velocity?

What is the formula for acceleration?

What is the definition of a vector?
Physical quantities with both magnitude and direction, such as force and velocity
What is the definition of a scalar?
Physical quantities that have magnitude but no direction
What is acceleration?
The rate of change of an objects velocity
What is the formula for displacement when given average velocity and time?

What is the formula for displacement given initial velocity, final velocity, and time?

What is static friction?
The force that must be overcome to set an object in motion
What is the definition of kinetic friction?
Kinetic friction opposes the motion of objects moving relative to each other
What is the formula for kinetic friction?

Newtons first law of motion:
A body in a state of motion or at rest will remain in that state unless acted upon by a net force
What is the definition of Newtons second law of motion?
What a net force is applied to a body of mass, the body will be accelerated in the same direction as the force applied to the mass.
What is the formula for Newtons second law of motion?
F = ma
What is Newtons third law of motion?
If body A exerts a force on body B, then B will extert a force back onto A that is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction.
Definition of mass:
A scalar quantity that measures a body’s intertia
- Represented by m
- measured in kg
What is weight?
A vector quantity that measures a body’s gravitational attraction to earth
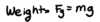
In order for an object to be in equilibrium…
The sum of opposing forces acting on the obkect must be equal to 0
What is the term and formula on a constant force acting on an object that moves a displacement?
Work

What is the formula for centripetal acceleration?

What is the formula for centripetal force?