Phys 8 Hemostasis Flashcards
(28 cards)
Production of platelets?
what factor helps create more?
where is this produced?

Thrombopoietin
binds where?
what type of receptor?
what type of cells?

Production of platelets
under these conditions:
High number of platelets?
Low number?

Thrombopoietin
what will it have effects on?
what are these effects?

what do platelets contain?

what do platelet cell membranes express?

SUmmary of thrombocytes?



The four steps of Hemostasis

Hemostasis Step 1 ?
what are the primary causes?

Hemostasis step 1
factors contributing to the spasm?

Hemostasis step 2?
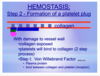
Hemostais step 2
the steps of platelets binding to collagen?
once platelet is activated what happens?
Step 1: Von Willebrand Factor
- Plasma protein
- bind between collagen and platelet
- (white line)

Hemostasis step 2
steps that happen (summary)
once platelet is activated

hemostasis step 2
is enough for what type of injuries?

Platelet plug summary

Hemostasis step 3
Coagulation
uses the coagulation cascades from the next lecture

Hemostasis How in step 3 do we get excess fluid out?

Hemostasis step 3 summary

Hemostasis step 4?
what is secreted?
by what?

Getting rid of the clot
what can do this?
where is it made?
what activates it?
released by?
activation inhibited by?

how plasminogen is activate (cascade)
what is involved?
Thrombin is binding thrombomodulin

How to prevent clotting?
1.

how does atherosclerosis increase risk for a clot?
They will occur under endothelial lining as clot grows big enough endothelial cell lining will rupture Exposing plaque and is no longer a smooth surface






