Clin 1 Normal ECG Flashcards
(26 cards)
P wave
represents what?
upright when?
inverted when?
variable when?

P-R interval
spans what?
represents what?
what kind of timing?

QRS complex
represents what?
Duration?
Q waves width?
Q waves normal size and where its normal?

ST segment
observe what?
Normally?
ST depression?
ST elevation?

T wave
represents what?
upright when?
inverted when?
variable when?
Shape?
Height?

QT
its duration is what?
shows what diseases?
T wave inverted shows what?
ST elevation?
Q wave deep and wide not small?



EKG features to be examined
order?

What happens with a large T wave in a healthy person?
can be a normal variant look at whole patient not just paper

in A compare Lead 1 and 3
in B compare lead 1 to the rest
in C what is there?


What is off here?
Know some causes?


QRS complexes
how we label Q R S
what if multiple?

compare C ST to A
D what is happned?


compare T waves


What do these findings show?

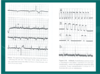
Rhythm
type of rhythm?
what other things can you look for for rhythm?
best leads for p-waves?




Rate
heart rate ranges?
dark line how many sec?
smaller box?
Method for quick rate calc?

The quicker way to estimate HR?

HR using 3 second time markers?
6?
what can a saw jagged tooth EKG be?

Practice figuring HR

L: 300, 150, 100 then not quite 75 inbetween 75-100 approx 87
R: 300, 150, 100, 75, then almost 50
approx 57
Rhythm
P wave preceeds?
P:QRS =?
normal rhythm?
other rhythms?

what if P wave follows QRS?
No P waves?

bipolar and augmented limb leads and their position compared to + and -
recreate the graph
all six limb leads meet to form six intersecting leads that lie in a flat “frontal” plane on the patient’s chest





