Phys 3 Cardiac cycle Flashcards
(34 cards)


relate these events with the EKG
Does ventricular volume reach 0?


Aortic pressure highs and lows?
ventricular pressure?
Ventricular volume?
Atrial Pressure?
Atrial pressure - within 10-15 for systolic prob single digit for diastolic

what happens with the p wave?
p wave is atria depolarizing which causes the contraction of the atria
(lines are pressure increases)

PR interval
what happens?

QRS complex
This increases the pressure in the ventricles

How does the graph of atrial and ventricular pressure look after during ventricular contraction?

Why is atrial pressure increasing during ventricular systole?

Lowest and highest pressures in the ventricle?
ST phase is flat why?
what causes ventricle pressure to drop to its lowest?
what does this correspond with on the EKG?
Relaxation of the ventricles begins, causing a decrease in the ventricular pressure
(T waves is relax (repolarization phase 3))

During atrial contraction what happens to aortic pressure?
What happens to ventricular volume?
What are two things to note about aortic pressure?

After the atria contract and begin to relax, the ventricles start to contract… What does this do to Atria and ventricular pressure?
During this what happens to aortic pressure and ventricular volume?
Almost immediately, the ventricular pressure exceeds the atrial pressure, causing the AV valves to close, preventing blood from flowing back into the atria.

What is happening between the black lines?
what is this period called?

Contraction of the ventricles continues, building pressure in ventricles blood won’t be ejected until ventricular pressure exceeds pressure in pulmonary and aorta
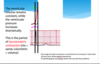

C. 68
Need to be at lease diastolic pressure in order open the valves (aortic in the situation).
What pressure does the L and R ventricle have to reach before their respective valve opens?

What will the graph look like once Ventricular pressure exceeds the aortic pressure?
what is happening to aortic pressure and ventricular volume?
Aortic pressure (green) now starts to increase as blood is ejected into the aorta.
Ventricular volume (magenta) decreases rapidly as blood is ejected

Why is there a drop in aortic pressure while blood is still being pumped out of ventricle?
what’s happening to ventricular volume during this?

whats happening here?

When the pressure in the ventricle drops below the arterial pressure, the aortic and pulmonary valves close

What is the a wave?
where is it located?

What is the c wave?
where is it located?

what is the v wave?
where is it located?

what is this graph showing us?


what is this area called?
what is happening here?


What happens once the AV node transmits action potential to the ventricles?
(what does it transfer to next)
what depolarizes 1st? 2nd?

What is happening here?














