Phyisiology L2R Flashcards
what is the function of epithelium cells and main characteristics?
Epithelium: consists of sheets of cells that cover the external surface of the body.
- line the internal cavities and organs
- form various organs and glands and line their ducts
Functions:
- Protection( skin)
- Absorption (small and large intestines)
- Transport of material at the surface ( mediated by cilia) ,
- Secretion (glands) ,
- Excretion (tubules of the kidneys) ,
- Gas exchange (lung alveolus)
- Gliding between surfaces (mesothelium) .
Main Characteristics of Epithelia
-Line and cover all body surfaces except the articular cartilage, the enamel of the tooth and the anterior surface of iris.
- Most epithelial cells renew continuously by mitosis.
- Epithelia are avascular, recieve nutrients by diffusion.
- •Epithelia are highly cellular , have almost no or little matrix .
- •Epithelia have a basal membrane (basement membrane ).
what are the epithelia structural and functional polarity?

Epithelia have structural and functional polarity
1 Apical domain: has structures important for protection and absorption microvilli, Cilia and stereo cilia
2. Basolateral domain: have structures needed to anchor cells to basement membrane e.g. cell to extracellular matrix junctions and basal cell membrane infoldings
- Lateral Domain: have structures needed to anchor epithelial cells to each other e.g. Occluding Junctions, Desmosomes, and Cell-Cell attachment.
Functions of the 2 apical structures and the diseases.
In the apical cell surface there are:
-
Microvilli: increase the surface area for absorption/secretion and are found in cells lining stomach and intestines.
- small intestines, the microvilli are densely packed and have a uniform height –brush border or striated border.
- Celiac disease or Gluten sensitive enteropathy, is a disorder of the small intestines in which one of the first pathologic changes is loss of microvilli brush border of the absorptive* *cells .
2.Cilia transport matter along the cell surface and are found on columnar cells lining the oviduct, bronchi.
Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia, which involves Kartageners syndrome: chronic respiration infections (lack of cleansing action of cilia, infertility and immotile spermatozoa)
describe Tight Junctions.
Cell to cell attachments :Tight Junction
-Tight junctions are specialized proteins in the plasma membranes of adjacent cells.
- They “stitch together” adjacent cells to form a tight cellular connection
- They are designed to restrict the movement of material between the cells they link.
*Helicobacter pylori disrupt zonula occludens ( tight Junctions )of stomach epithelial cells .

in a cell to cell attachment what is a Desmosome?
Cell to cell attachments: Desmosome

- Desmosomes are specialized connection protein complexes in cells that “rivet” cells together. They are attached to the intermediate fibers of adjacent cells.
- The anchoring proteins can also be used to communicate between cells.
In a Cell to cell attachments what are Gap junctions?
Cell to cell attachments: Gap junctions
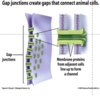
-Gap junctions are holes lined with specialized proteins that create cytoplasmic communication bridges between cells allowing for chemical and electrical signals to be passed rapidly.
*JUNCTIONAL COMPLEXES AS A TARGET OF PATHOGENIC AGENTS, many agents such as cytomegalovirus and cholera toxin cause junctional complexes to become permieable.