Biochemistry L2 Flashcards
(11 cards)
List the 21 proteinogenic amino acids in the human body.
hydrophobic (van der walls):
G.A.V.L.I.P
F.Y.W.
M.
POLAR ( HYDROGEN BONDS)
S.T.
N.Q.
C.(CYSTEINE): stab. protien by disulfide bridges (covalent )
U.( SELENOCYSTINE)
CHARGED AMINO ACIDS
D.E.
H.K.R
Categorize amino acids based on their chemical properties.
-Hydrophobic amino acids 1 * non polar, non aromatic: Glycine, Alanine, Proline,Valine,Leucine, Isoleucine 2 * Aromatic, non polar -Phenylalanine * Aromatic more polar - Tyrosine, Tryptophan 3* Nonpolar sulfur : Methionine _Polar, Uncharged amino acid_ A. Asparagine, Glutamine, Serine, Threonine B. Polar, Uncharged Sulfer- or Selenium containing: Cysteine, Selenocysteine __charged amino acids ____ 1a.Negative ( acid ) :Aspartate , Glutamate 2b. Positive ( Basic ): Arginine, Lysine, Histidine.
Predict the molecular interactions amino acids participate in.
- Hydrophobic amino acids
- Charged amino acids
- Polar amino acids
Explain how amino acids form proteins.
- linkage of amino acids through peptide bonds form proteins.
- peptide bonds are formed between the Alpha-amino and Alpha Carboxyl groups of adjacent amino acids.

Provide examples for protein variabilities during embryonic development and in tissue specific expression.
certain Hemoglobin levels change
- in the Alpha globin from high z-chain to High alpha after birth.
- in the Beta globin, the Epsilon is high in the embryonic stage and then gamma chain months before birth increases and decreases after birth. Then after birth beta increases
- Proteins produced in different tissues.
- differ somewhat in their primary structures but have the same function.
- Can be used in medical diagnostics to asses the damage of a certain tissue/organ
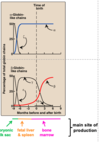
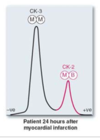
Explain how tissues specific expression of creatine kinase can be used in clinical diagnosis.
Creatine Kinase (CK or CPK )
has 2 subunits B&M.
CK has 3 Isoforms ( Isoenzymes ) we look at MB ( heart ).
When the test comes back you see if the MB is greater than 5% of total CK in the blood.
if it is patient has had an infarction. we can check 3 days after the infarction to see if the MB is elevated.
-Now we use Troponin : it stay longer in the blood and we can detect it in the blood, because it is release when the heart tissue is dead.
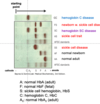
Identify hemoglobins with abnormal amino acid composition using electrophoresis.
In Electophoresis we can Identify certain Hemoglobin by the charges they have. the one that are neg. will go towards the anode (+) HbA strong negative charge, HBs is neutral and HBc is positive charge does to the Cathode.
Associate posttranslational modifications with cellular and physiological functions of proteins
- Glycosylation: Glycosylation increases the solubility of the protein
- Glycation:-Hemoglobin can be glycated by blood glucose. -This modification does not require an enzyme. -The amount of glycated hemoglobin is proportional to the blood glucose level.
3.Lipid addition: Lipid addition enables the protein to be inserted in the plasma membrane without having a transmembrane region.
4.Phosphorylation: can change the activity of enzymes
- Acetylation: of histones can change histone-DNA interactions and alter gene transcription
- ADP-ribosylation: Used by bacteria as bacterial toxins to change host cells. ( Cholera, pertusis and diptheria toxins)
- Hydroxyproline: abundant in collagens, stabilizes the triple helix of collagens
- Hydroxylysine: abundant in collagens.serves as glycosylation and crosslinking site in collagens. produced by the action of lysine hydroxylase.
- γ-Carboxyglutamate:: abundant in blood coagulation proteins. required for calcium binding and coagulation. produced by the action of γ-glutamyl carboxylase
Associate posttranslational modifications with their clinical significance.
clinical relevance:
- Glycosylation:Glycosylated proteins (and lipids) on the red blood cell surface determine ABO blood type.
- Glycation:Glycated hemoglobin (particularly Hb A1c) is used to assess compliance of diabetic patients with insulin injections. Formed by glycation of many protiens, if accumulated ( uncontrolled diabetes)
- Lipid addition 4.Phosphorylation 5.Acetylation 6.ADP-ribosylation 7.Hydroxyproline 8.Hydroxylysine 9.γ-Carboxyglutamate
Explain how changes in a protein sequence through protein engineering can provide better patient management
Changing the position of 2 amino groups in insulin can have a better absorption and faster action. - its not immunogenic
Explain how a single amino acid change in hemoglobin leads to the clinical consequences of sickle cell disease.

The change happens in the 6th position on the Hemoglobin Beta chain where Gluamate is changed to Valine.
-switching the charge form a negative charge (normal) to a neutral charge (sickle cell disease)



