Anatomy L8R Flashcards
Thoracolumbar fascia funtion?
-Covers the deep muscles of the back and contributes to the overall organization and integrity of the region
-
- Superiorly : passes posteriorly to serratus anteriorly muscle and is continuous with the deep fascia of the neck .
- In the thoracic region , covers the deep muscles and separates them from the muscles in the superficial and intermediate layers.
- Medially : attaches to the spinous processes of the thoracic vertebrae and laterally to the angles of the ribs.
- The medial attachments of latissimus dorsi and serratus posterior inferior blend with the thoracolumbar fascia
Thoracolumbar fascia


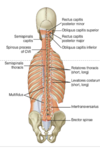
Deep ( intrinsic ) Back Muscles
•Consist of groups of muscles
arranged in 3layers. From superficial
to deep, they are:
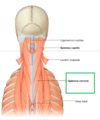
- A- Splenius muscles. Also called (spinotransversales), mainly in the neck
- B- Erector spinae: vertically oriented
- C- Transversospinalis: in general run superomedially, associated with vertebral column throughout back
- Segmental muscles - more of proprioception than movement of vertebral column
- Segmentally innervated by posterior rami of spinal nerves

-Ascends laterally across the back of the neck, covering the
deeper.
FORMED BY THE :(spinotransversales)
SPLENIUS CAPITIS which is attached to the skull
SPLENIUS CERVICIS attaching to the transverse process of the cervical vertebrae.
ACTION:
- Extensors and rotators of the head and neck
- Acting unilaterally, laterally bends &
- rotates the head to the ipsilateral side;
- acting bilaterally extends the head and neck


Splenius Capitis:
ORIGIN
INSERTION
INNERVATION
ACTION

•Origin : lower half of ligamentum nuchae , spinous processes of CV7 – TV4
- Insertion : mastoid process , skull below lateral third of superior nuchal line
- Innervation : posterior rami of middle cervical nerves
- Action : bilaterally draw head backward , extending the neck. Unilaterally draw and rotate the head to the same side
(turn face to the same side )
Splenius Cervicis:
Origin:
Insertion:
Innervation:
Actions:
- Origin : spinous processes of TV3 –TV6
- Insertion : transverse processes of CV1 –CV3
- Innervation : posterior rami of lower cervical nerves .
- Actions : together extend the neck . Individually draw and rotate the head to same side
( turn face to same side )
•
Erector spinae (second layer)
Erector spinae (Sacrospinalis)
- Consists of 3 muscle columns:
- Iliocostalis, laterally
- Longissimus, intermediate
- Spinalis, medially
- Arises from a broad thick tendon attached to the sacrum, spinous processes of lumbar and lower thoracic vertebrae, and iliac crest
- Primary extensors of vertebral column and head
- Acting unilaterally, bends (flexes) the vertebral column to the ipsilateral side; acting bilaterally, extends the vertebral column and head

Iliocostalis Cervicis, Thoracis , Lumborum
ORIGIN:
INSERTION:
NERVES:
ACTION:
BLOOD SUPPLY:
- Mostlateral
- Origin: 3rd-12th ribs and sacrum and medial iliac crest
- Insertion: transverse processes of Cv4-Cv6, angles of 1st-12th ribs
- Nerves: dorsal primary rami of
cervical, thoracic and lumbar spinal nerves
•Action: extends and laterally
flexes vertebral column
•Blood supply – posterior
intercostal arteries
Longissimus capitis, cervicis, thoracis
ORIGIN:
INSERTION:
ACTION:
BLOOD SUPPLY:
•Origin: transverse process of
Cv5-Cv7, Tv1-Tv5 and lumbar
vertebrae
- Insertion: mastoid process, transverse process of C2-C6 and thoracic vertebrae and 3rd-12th ribs
- Action:capitis muscle extends and rotates the head; cervicis and
thoracis muscles extend and laterally flex the vertebral column
•Blood supply: posteriorintercostal
arteries
•

Spinalis (capitis), cervicis, thoracis
Origin
Insertion
Nerve
Action
Blood supply
- Origin: ligamentum nuchae, spinous processes of C7, spinous processes of lumbar and thoracic vertebrae
- Insertion:spinousprocesse of C2 and spinous processes of T1-8 vertebrae
- Spinalis capitis muscle usually blends with semispinaliscapitis muscle
•Nerve: dorsal primary rami of cervical and thoracic spinal
nerves
- Action: extends vertebral column
- Blood supply: posterior intercostal arteries

C- Transversospinalis (third layer):
- run from transverse processes to spinousprocesses (superomedially)
- acting unilaterally, rotate the vertebral column and head toward the contralateral side; acting bilaterally, extend the vertebral column and head

- consists of three layers from superficial to deep:
- Semispinalis(in the upper half of the vertebral column) span 4-6 segments
- Multifidusspan 2-4 segments
- Rotatoresspan 1-2 segments
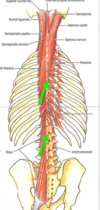
Semispinalis capitis, cervicis, thoracis
- Origin: Cv4-Cv7 and Tv1-Tv6 and transverse processes of Tv7-Tv12
- Insertion: occipital bone, spinous processes of C2-C5 and T1-T4 vertebrae
- Nerve supply: dorsal rami of cervical, thoracic and lumbar spinal nerve
- Action:extends vertebral column; rotate head and vertebral column to contralateral side
- Blood supply: post. intercostal arteries
- Semispinalis capitis, due to attachment to skull, has unique action. Bilaterally, pulls head posteriorly; unilaterally, pulls head
posteriorly and turns it, causing chin to move superiorly and turn to ipsilateral side
(similar to erector spinae m.)

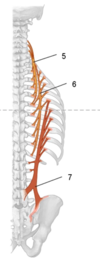
2.Multifidus:
Origin
Insertion
Nerve
Action
Blood supply
Origin:Arises from posterior sacrum, posterior superior iliac spine, aponeurosis of erector spinae, sacroiliac ligaments , mammillary processes of lumbar vertebrae, transverse processes of T1-T3 and articular processes of C4-C7.
Insertion:Inserts along the entire length of spinous processes 2-4 spinal segments
*It is best developed in lumbar region
Action:
Acting bilaterally it extends the vertebral column
Acting unilaterally it rotates the trunk to the opposite side
Rotatores:
Origin
insertion
action
Origin:The deepest layer of transverso-spinal muscles and arise from the transverse process of vertebrae
_Insertion:_attach to the transverse process of vertebrae.
*Shortest as they span 1-2 spinal segments. Extends from sacrum to Cv2.
*Most developed in the thoracic region
Segmental muscles:more of proprioception than movement of vertebral column

Segmental muscles
- •The 2 groups of segmental muscles are deeply placed in the back and innervated by posterior rami of spinal nerves.
- •The first group of segmental muscles are the levatores costarum muscles. They have an oblique lateral and downward direction
- The second group consists of true segmental muscles ___ the i_nterspinales and the intertransversarii_