PHY 6 Fluids and Solids Flashcards
(41 cards)
How would you calculate the density of an object ?
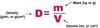
How would you calculate specific gravity at a given temperature ?

What are the two key properties of fluids ?
- Density
- Pressure
What is the relationship between density and specific gravity ?
They are usually the same, as the density of water is usually 1g/ml at unit temperature.
What are the dimensions of specific gravity and density ?
Density is mass per unit volume, specific gravity is dimensionless.
How would you calculate pressure ?

What is the SI unit for pressure ?
The Pascal
(1 Pa = 1N/m2)
Describe 5 non-SI units that can be used to represent pressure ?
1.01 x 10 5 Pa =
- 1.00 atm
- 1.01 bar
- 760 mmHg
- 760 torr
- 14.7 lb/in2
How would you calculate the change in pressure at a depth below the surface of water ?
Change in pressure =
density x gravity x height change
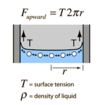
Describe the first 3 key rules of incompressible fluids that are not moving
- In a fluid confined by solid boundaries, the surface (normal) force acts perpendicular to the boundary
- An any particular depth, the pressure of the fluid is the same in all directions
- The fluid or hydrostatic pressure depends on the density and depth of the fluid
What does the hydrostatic paradox imply ?
The size or shape of the container does not influence the pressure
What is Pascal’s principle ?
If an external pressure is applied to a confined fluid, the pressure at every point within the fluid increases by that amount.

How do you calculate the force exerted by an object at rest ?
E.g. a wooden block sitting on a table
Force = mass x gravity
What is Archimedes principle ?
An object which is completely or partially submerged in a fluid experiences an upward force equal to the weight of the fluid displaced

What is the equation used to calculate bouyant force (Archimedes principle) ?

How would you predict the fraction of the height of a bouyant object below the surface of a fluid ?
Specific gravity is equal to the height of the object immersed
E.g. If SG = 0.9, the object is 90% immersed
What is atmospheric pressure ?
The force per unit area exerted against a surface by the weight of the air above that surface.
What is barometric pressure ?
Atmospheric pressure is measured using a barometer, and is sometimes referred to as barometric pressure
What is atmospheric pressure in mmHg at sea level ?
760 mmHg
Describe the relationship between pressure and elevation ?
When the altitude or elevation increases, we get closer to “outer space” so there is less overlying atmospheric mass from gases.
Therefore, pressure decreases with increasing elevation
What is gauge pressure ?
E.g. Tyre gauge pressure is the pressure difference between the tyre and the outside.
What is the absolute pressure ?
The pressure of a fluid relative to the pressure in a vacuum.
Pabs = Patm + Pgauge
What are the two equations that describe fluids in motion ?
- The continuity equation
- Bernoulli’s principle
Describe Laminar flow
Fluids are assumed to have streamline (laminar) flow which means that the motion of every particle in the fluid follows the same path as the particle that preceeds it.