Pelvic Viscera Flashcards
Pelvis Organs
Urinary
- pelvic ureter
- urinary bladder
- urethra
Genital
- ductus deferens
- seminal vesicles
- prostate gland
- ovaries
- uterine tubes
- uterus
- vagina
Digestive
- pelvic colon
- rectum
- anal canal
Bladder

One way flap valve where ureters pass.
Ureteric orifices & internal urethral orifice are at angles to trigone
Ureteric orifices have detrusor m. around them
Neck of bladder prevents retrograde ejaculation of semen into bladder
Apex= attach by median umbilical lig
Base= seminal vesicles & rectum; uterus & vagina. Receives ureters.
Bladder Blood Supply
Superior vesicle a.- apex & sup bladder (internal iliac)
Inf vesical a. - fundus & neck in males
Vaginal a. - fundus & neck in females (uterine a. branches)
Obturator a.- arterial twigs (internal iliac a.)
Seminal Glands
B/t fundus of ladder & rectum
Don’t store sperm
Duct joins ductus deferens to form ejaculatory duct
Sup= periotenum
Inf= separated from rectum by rectovesical septum
Prostate
Largest
Surrounds prostatic urethra
2/3 glandular
1/3 fibrom.
5 lobes & 3 zones
True & False fibrous capsule
Bulbourethral Glands
Cowper
pea sized in external urethral sphincter
Posterolateral to intermed part of urethra open into spongy urethra

Prostate Lobes and Zones
Ant
R & L lobes
Median lobe
post lob
Zones: central, periph (cancer), transition (BPH)

Prostate Lobes
Ant lobe- only fibrom.
median lobe- cone shpaed b/t 2 ejaculatory ducts and urethra
lateral lobes- main mass, separated by prostatic urethra
post lobe- can be palpated during DRE

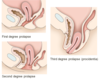
BPH
enlarged prostate in median lobe & transition lobe which obstructs urethra
Can use transurethral resection of prostate
Prostate Carcinoma
most common in >50
70% in periph zone
Blood test for PSA levesl & DRE
Female Internal

Uterus
- hollow & muscular organ
- pear shpaed
- in lesser perlivs
- perimetrium, myometirum & endometrium
Ovaries
- almond shaped female endocrine glands
- suspended by mesovarium
- covered w/ tunica albuginea not w/ peritoneum
- oocyte released into peritoneal cavity
Uterine Tubes
- lie in narrow mesentery- mesosalpinx
- has 4 parts: infundibulum; ampulla; isthmus; intramural
Vagina
- sup end surrounds cervix
- canal
Uterus
Body upper 2/3
has fundus & isthmus (just above cervix, constricted)
Cervix
Mesometrium (part of broad lig)
Hysterosalpingography
Inject H2O radioapque solution or CO2 into uterus to determine its patency
Other Procedures
hysteroscopy- examine interior of tubes via endoscopic instrument
Salpingitis- inflammed uterine tube
pyosalpinx- pus in uterine tube
female sterilize- tubal ligation (prefer clip now)
Female Pelvic Viscera

Broad Ligament

Ovarian a. & ovarin br. of uterine anastomosis

Rectouterine Pouch
Lowest part of peritoneal cavity- ascites, tumor, endometriosis & pus
B/t rectum & back wall of uterus in female human body.
Also called Douglas Space
Uterus & Vagina Angles

Procedures of Vagina
culdoscopy- inserted through vagina post to examine ovaries/uterine tubes
Couldocentesis- to remove pelvic abscess, fluid or blood in retrouterine pouch
Pelvic Ligaments

Pelvis Ligaments
Broad lig- double layer of peritoneaum extends from sides of uterus to lat walls
- mesovarium (ovary)
- messalpinx (covers uterine tube)
- mesometrium (part of broad lig)
Ovarian lig- medial pole of ovary to uterus
Transverse cervical- pelvic fascia from cervix & vagina to pelvic walls. Mackenrodt’s
Also suspensory lig & round lig!
Important Uteral structures
- lig teres- attach to uterus & below fallopian tube
- plica rectouterina- fold of peritoneaum w/ rectouterine m. pass from sacrum to base of broad ligament!
- Parametrium- of cervis to braod ligaments. Contains uterine a. & ovarian lig.
Dispositon of Uterus

Uterine Prolapse