Male & Female External Genitals Flashcards
Female External Genitilia
Mons Pubis- fatty elevation over pubic region. Skin acquires coarse hair
Labia majora- pair of skin folds contain areolar tissue, fat & terminal part of round ligament. Anterior & posterior commissure where meet at each end.
Labia minora- 2 small skin folds contain sebaceious glands. Meet at post frenulum. Ant form clitoris frenulum & prepuce.
Female External Genitilia
Clitoris- eretile body composed of 2 corpora cavernosa & glans.
Vesibule- space b/t labia minora, urethral orifice & vaginal orifice’
Hymen- thin muous mem that covers vaginal orifice (introitus). After rupture during sexual intercourse its called hymenal caruncles.
External Genitilia in Male

Erectile Bodies in Penis
Corpus spongiosum- distal expansion- gland w/ margin corona
- proximal expansion forms bulb of the penis
Corpora cavernosa- distal covered by glans.
- proximal forms crus which attach to ischiopubic ramus & covered by ischiocavernous m.
Root of the penis= bulb+ 2 crura
Erectile Bodies in Penis
Tunica albuginea- fibrous coat, covers erectile bodies but thinner around corpus spongiosum.
Deep fascia/ Buck’s- covers all 3 bodies
Skin of penis- hairless & thin & loose except over the glans.
Prepuce covers the glans (foreskin)

Internal Pudendal a. in females
I PPADD
I= inf rectal a.
P= perineal a.
P= post labial branches
A= a. of bulb of vestibule
D= dorsal a. of clitoris
D= deep a. of clitoris
Internal Pudendal a. in Males
I PPADD
I= inf rectal a.
P= perineal a.
P= post scrotal branches
A= a of bulb of penis
D= Dorsal a. of penis
D= deep a. of penis
Ligaments of Penis
Fundiform lig of penis- from linea alba to pubic symphysis, splits to surround penis & units w/ dartos fascia
Suspensory lig of penis- from ant surface of pubic symphysis. Splits to fomr sling that attaches to deep fascia at penis (around root & body)
Ligamentolysis- release fundiform ligament & suspensory ligament for penile elongation!

Urethra
Female a lot shorter than male.
M. around internal urethral orifice in female not organized into internal sphincter.

Male Urethra

- Preoprostatic- @ neck of bladder; surrounded by internal urethral sphincter
- Prostatic- ant prostate; widest
- Intermed- passes through deep perineal pouch & perineal mem; narrowest
- Spongy- corpus spongiosum; longest & most mobile bulbous+ penile
Suprapubic Cystotomy
Full bladder punctures above pubic symphysis to introduce catheters or instruments w/o opening peritoneam.
Use for urinary calculi, foreign bodies & small tumors
Urethral stricture- constrict urethra duet o penile trauma or infection
Use cystoscopy to observe bladder through urethra

Superficial Perineal Pouch

Deep Perineal Pouch
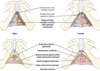
Glands of Female
The Great Vestibular glands/Bartholin- in superficial perineal pouch on either vestibule side.
- mucus secreting during sex
- Site of vulvar adenocarcinomas
The lesser vestibular glands/Skene’s
- on either vestibular side
- open into vestibule b/t urethra & introitus
- secrete mucus to moisten vestibule & labia
Bartholinitis &Bartholin cyst

Penis Innervation

Sympathetic T11-L2
Parasym S2-S4
To form cavernous n.
Pudendal n. for somatic innervation
N. Path in Erection
Parasymapthetic

Erection
Autonomic- cavernous n. regulate blood flow
Somatic- dorsla n. penile sensation.
Relax trabecular smooth m. & vasodialte arterioles, increase & blood expands sinusoidal space. Compress subtunical plexus agains tunica albuginea.
Stretching of tunica compresses emissary v. & reduces blood outflow

Flaccid
Inflow through constricted & tortuous a. is minimal so free outflow through subtunical venular plexus.

Erection
Parasym stim S2-S4
Arteriovenous anastomoses that bypass sinuses of corpora cavernosa are closed
Helicine a. straighten, enlarge their lumin & allow blood flow

Ejaculation
Sym L1-2 close internal urethral sphincter
Para sym S2-S4 contrac urethral m.
Pudendal n. S2-S4 contract bulbospongiosus

Emission
Sym L1-L2
Semen delivered to prostatic urethra after peristalsis of ductus deferens & seminal glands
Remission
Symp
COnstrict smooth m. in coiled helicine a.
Relax bulbospongiosus & ischiocavernuous allows more blood to be drained from cavernous spaces into deep dorsal v.
ED
Peyronie’s disease PD is fibrotic disorder of tunica albuginea resulting in penile defornity, pain & ED
lesion of prostatic plexus or cavernous n.
Semirigid or inflatable penile
prosthesis in refractory cases
Urethral Trauma







