osteomyelitis Flashcards
spread of infection to bone in children
hematogenous
spread of infection to bone in adults
continuous spread or direct innoculation
Sequestrum
necrotic bone that is separated (sequestered) from viablebone by granulation tissue.
Involucrum
living bone surrounding necrotic bone.
Cloaca
opening on the involucrum
Sinus tract
opening from the infection to the skin surface
Brodie abscess
subacute osteomyelitis characterized by central lucency and peripheral sclerosis.
Ddx for a Brodie absess
osteoid osteoma
What part of the bone is typically involved in osteo in kids?
metaphyses due to sluggish flow in metaphyses which facilitates bacterial invasion
Up to what age can osteo involve the epiphysis?
Infants up to 12 mo due to presence of bridging vessels that cross the physis
What lab test should be run prior to bone biopsy?
blood culture. if positive, no need to biopsy as hematogenous spread is usually due to a single organism.
Exuberant periostitis is seen in children or adults?
children. Secondary involvement of the cortex occurs as bacteria spread through Haversian and Volkmann canals into the periosteum and subsequently the soft tissues. In infants and children, the periosteum is loosely adherent to the bone, causing prominent lifting of the periosteum by infection. This manifests radiographically as exuberant periostitis.
Chronic drainage of a sinus tract predisposes pts to:
SCC of the sinus tract
differential diagnosis for diabetic foot ulcer
neuropathic joint
osteomyelitis of Garre
sclerosis and thickening of bone
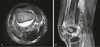
subperiosteal abscess.
happens in peds, Periosteum is loose in pediatrics and bone infection decompresses in the subperiosteal space


