Osteoarthritis and Principles of Management Flashcards
Who manages osteoarthritis?
Nurses
Patients
GPs
Physicians
Dieticians
Occupational therapists
Orthopaedic surgeons
Physiotherapists
What are the characteristic features of osteoarthritis?
Osteo- arthritis is characterised by focal loss of articular cartilage, subchondral osteosclerosis, osteophyte formation at the joint margin, and remodelling of joint contour with enlargement of affected joints. There is also loss of space in the joint cavity. Also subchondral cysts. Inflammation can occur but is not a prominent feature
What are the joints most commonly affected in OA?
Joint involvement in OA follows a characteristic distribution, mainly tar- geting the hips, knees, PIP and DIP joints of the hands, neck and lumbar spine
What are the risk factors for OA?
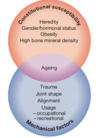
What is the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis?
- Trauma & mechanical imbalance
- Inflammation & pain
- Repair processes around the joint

What are the biomechanical factors associated with osteoarthritis?
- Abnormal anatomy (DDH)
- Intra-articular fracture
- Ligament rupture
- Meniscal injury
(The medial meniscusof the knee is a thickened crescent-shaped cartilage pad between the two joints formed by the femur (the thigh bone) and the tibia (the shin bone).)
•Occupation – farmers, football players
Persistent heavy physical activity
Elite running
Obesity
What are the inflammatory signs on OA?
- Synovial hypertrophy
- Subchondral changes
- Joint effusion
What are the biochemical mediators?
•IL-1𝝱, TNF 𝜶, MMPs…
Higher levels of these are associated with arthritis
Patient perspective of OA
Patients suffer from – pain on movement, hip arthritis can causes pain in the groin – can radiate down the leg to the knee
Knee arthritis tends to go to the front of the knee
Stiffness (when they get out of bed in the morning – after a few minutes it wears away and they loosen up)
Rheumatoid arthritis causes prolonged early morning stiffness
Hip osteoarthritis – complain that they can’t reach down to put on their shoes or socks - maybe can’t cut their nails or toenails
Unlikely that a patient who is 10 years old will have osteoarthritis – tends to appear in 45’s and upwards
What is the diagnosis of OA?
- 45 years +
- Activity-related joint pain plus
- has either no morning joint-related stiffness or morning stiffness that lasts no longer than 30 minutes
When should you pay special attention to the diagnosis - may be something else
- Trauma
- Prolonged morning-related stiffness
- Rapid deterioration of symptoms
- Hot, swollen joint
What is the differential diagnosis for osteoarthritis?
Gout
Other inflammatory arthritides
Septic arthritis
Malignancy
Here is the nice guidelines for OA
and also some discussion from the lecture
Firstly – conservative management and self care – anaelgesics (NSAIDS – gastric side effects – can exacerbate asthma symptoms)
Paracetamol often has synergistic effect
Morphine based pain killers often have undesirable side effects
Activity modification and weight loss

What are non-pharmacological treatments for OA?
- Thermotherapy
- Electrotherapy
- Aids and devices
- Manual therapy
- NICE do not recommend: acupuncture, nutraceuticals (glucosamine, chondroitin)
TEAM
Aids – walking sticks, crutches and support bandages
Walking sticks are held in the opposite hand
Manual therapy is physiotherapy
Physiotherapy – improving strength of the muscle around the joint. Improving the quad strength can improve the knee pain
What are pharmacological treatments for OA?
- Oral analgesia:paracetamol, NSAIDs
- Topical treatments: NSAIDs, capsaicin (knee, hand)
From Davidson’s:
‘Addition of a topical NSAID, and then capsaicin, for knee and hand OA can also be helpful. Oral NSAID should be consid- ered in patients who remain symptomatic. These drugs are significantly more effective than paracetamol and can be successfully combined with paracetamol or compound analgesics such as co-codamol if the pain is severe. Opiates may occasionally be required. For temporary benefit of moderate to severe pain, intra-articular injection of corticosteroids can be helpful’
When is surgical referral indicated?
- Substantial impact on quality of life
- Refractory to non-surgical treatment
- Referral letter
Referral letter should list the things that you’ve tried already, also include the time frame of the condition. The patients quality of life should also be included. Include the patients BMI – if the patient is over 40 then surgery would probably be avoided just because of the risks assocaited.
X- ray is the only investigation that is needed – MRI is not necessary. Blood tests may be used to exclude rheumatoid arthritis.
Davidsons: ‘Osteotomy can prolong the life of malaligned joints and relieve pain by reducing intra- osseous pressure, but is performed infrequently. Total joint replacement surgery is by far the most common surgical procedure for patients with OA. It can trans- form the quality of life for people with severe knee or hip OA and is indicated when there is significant structural damage on X-ray, and pain and functional impairment are limiting quality of life despite the use of medical therapy’
What is the only reason to perform a hip replacement in OA?
PAIN
Why is obesity a risk factor for osteoarthritis?
Obesity is another strong risk factor. Although this is likely to be due in part to increased mechanical loading of the joints, it has been speculated that cytokines released from adipose tissue may also play a role
What is the hereditability of OA?
Genetic factors play a key role in the pathogenesis of OA, and family-based studies have estimated that the heritability of OA ranges between about 43% at the knee to between 60% and 65% at the hip and hand, respectively
What is the pain like in OA?
Insidious onset over months or years
Variable or intermittent over time (‘good days, bad days’)
Mainly related to movement and weight-bearing, relieved by rest
Only brief (< 15 mins) morning stiffness and brief (< 5 mins)
‘gelling’ after rest
Usually only one or a few joints painful
What are the clinical signs of OA?
Restricted movement due to capsular thickening, or blocking by osteophyte
Palpable, sometimes audible, coarse crepitus due to rough articular surfaces
Bony swelling around joint margins
Deformity, usually without instability
Joint-line or periarticular tenderness
Muscle weakness and wasting
Synovitis mild or absent
From Davidsons clinical medicine book
“Quadriceps strengthening exercises are particularly beneficial in knee OA. Weight loss can have a substantial beneficial effect on symptoms if the patient is obese and is probably one of the most effective treatments for reducing pain, particularly in OA of the lower limbs. Shock-absorbing footwear, pacing of activities, use of a walking stick for painful knee or hip OA, or provision of built-up shoes to equalise leg lengths can all improve symptoms.”


