Oral Cavity and Salivary Glands Flashcards
What are the componenents of the GI Tract?
- oral cavity: teeth, tongue, salivary glands
- Pharynx
- Oesophagus
- Stomach
- Small intestine: duodenum, jejunum and ileum
- Large intestine: caecum, veriform, appendix, accessory colon, transverse colon, descending colon and sigmoid colon
- Rectum and anal canal
What are the main accessory organs of the digestive system?
- gall bladder
- liver
- pancreas
What is the main function of the digestive system?
preparation of food of cellulcar ultilisation
What are the 8 main processes that occur in the digestive system?
- ingestion
- masticuation
- deglutition (swallowing)
- propulsion; peristalsis and segmentation
- Mechanical digestion
- chemical digestion
- absoprtion
- defecation
What is the oral cavity?
space between the lips and cheeks and palatoglossal folds
Alternative names for palatoglossal folds
palatoglossal arches
anterior pillars of the fauces
Where is the oral cavity proper located?
internal to the teeth
Where does the vestibule lie?
between the lips and the cheeks externally and the gums and teeth internally
What is the boundary between the oral cavity and the pharynx?
palatoglossal folds
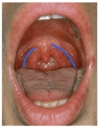
blue = palatoglossal folds
What forms the lateral wall of the oral vestibule?
cheek (buccae)
What is the cheek made up by?
- skin
- buccinator muscle
- buccopharyngeal fascia
- buccal glands
- buccal fat pad
- mucous membrane
What is the function of the buccal fact pad?
enhance the sucking capability of an infant by creating negative pressure
What is the function of the buccinator muscle?
mastication/chewing
creates continuity between the oral cavity and the pharynx
What is the buccinator muscle attached to?
maxilla, mandible and pterygomandibular raphe, where it fuses with the pharyngeal constrictor
Where do the fibres of buccinator terminate and what muscle do they contribute to?
fibres terminate in both lips and contribute to orbicularis oris muscle
What is the point of cross over of the buccinator muscle fibres called?
modiolus
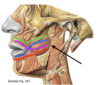
black = pyterygomandibular raphe
What constitutes the anterior wall of the oral cavity?
lips
What are the lips internally and externally lined by?
internally = oral mucosa
externally = skin
What is between the skin and the mucous membrane of the lips? Describe this zone
vermilion (red) zone of the lips
- poorly keratinised
- rich in blood vessels
What connects the lips to the adjacent gum?
median labial frenulum
Where are the small labial glands located?
between the muscle tissue and the oral mucosa and open into the oral vestibule
What forms the roof od the oral cavity and separates it from the nasal cavity?
hard and soft palate
What forms the anterior 2/3 of the palate?
hard palate
- palatine process of maxilla
- horizontal plate of palatine bone
What travels in the incisive foramen?
nasopalatine nerve
What travels in the greater palatine foramen?
greater palatine nerve

red = incisive foramen
green = greter palatine foramen
Where is the soft palate attached to and what is it composed of?
- attached to posterior border of the hard palate
- composed of aponeurosis (perisoteum and tendon of tensor veli palatini), mucous glands and mucous membrane
What is the soft palate continous with at the sides?
latera; wall of the pharynx
What does the soft palate form?
superior and lateral margins of isthmus faucium
What is the projection in the midline of the posterior margin of the soft palate called?
uvula
What are Epstein’s pearls and who are they common in?
clusters of white spots in the midline at the junction of hard and soft palates
Common in neonates

red = uvula
What two arches extend from the uvula to the lateral walls? And what forms between the two arches?
- anteriorly = palatoglossal arch
- posteriorly = palatopharyngeal arch
- Tonsillar fossa is formed beyween the arches and houses the palatine tonsils
What muscles attaches to the palatiglossal arch (anterior pillar)
palatoglossus muscle
What muscles attaches to the palatopharyngeal arch (posterior pillar)
palatopharyngeus muscle

red = palatoglossal arch
blue = palatopharyngeal arch

red = palatoglossus arch
blue = palatopharyngeal arch
green = palatine tonsils
What are the muscles of the soft palate?
- palatoglossus
- palatophayngeus
- levator veli palatini
- tensor veli palatini
What muscles of the soft palate are supplied by the vagus nerve?
- palatoglossus
- palatophayngeus
- levator veli palatini
What nerve supplies tensor veli palatini?
trigeminal (V) nerve
What is the only muscle of mastication that opens the mouth?
lateral ptyergoid
What nerve supplies the muscle of mastication?
mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve

red = medial pterygoid
blue = lateral pterygoid
green = masseter
black = temporalis
What forms the floor of the mouth and what is its function?
muscular diaphragm composed mainly of the mylohyoid muscle extending between the mandible and the hyoid bone
It forms a support for the tongue
What is the tongue?
A ‘bag’ of striated muscles, covered with mucous membrane
What are the main functions of the tongue?
- mastication
- deglutition
- taste
- speech
Why does the tongue have a ‘fury’ appearance? And what is the function of this?
presence of papillae
- grip food
- house taste buds
What are the main papillae of the tongue? And what are their specific functions?
- vallate (circumvallate) papillae, foliate papillae, fungiform papillae = taste
- filiform papillae = grip food
What are the two groups of muscles of the tongue
extrinsic and intrinsic
What is the function of the extrinsic muscles of the tongue?
attach the tongue to the styloid process and the soft palate above and to the mandible and hyoid bone
Alter position of (move) the tongue
What are the extrinsic muscles of the tongue innervated by?
hypoglossal nerve
*except palatoglossus (pharyngeal plexus, CN-X)
What is the function of the intrinsic muscles of the tongue?
confined to the tongue and are not attached to bone
alter the shape of the tongue
What nerve innervates the intrinsic muscles of the tongue?
hypoglossal nerve (CN-XII)
What is the action of palatoglossus and styloglossus?
draw the tongue upwards and backwards
What is the action of the hyoglossus muscle?
draw the sides of the tongue down
What is the most importsnt muscle of the tongue? and why?
genio-glossus
prevents sufocation when unconcious
What separates the root (posterior 1/3) of the tongue from the body (naterior 2/3) of the tongue?
v-shaped sulcus terminalis
What are the palatine and lingual tonsils?
collections of lymphoid tissue in the mucosa of the pharynx
What are pockets or folds that occur naturally in the tonsils called?
crypt
What tonsil bed is highly vascular and can cause difficulty during surgical removal?
palatine tonsils (tonsillar fossa)
bleeding comes from tonsillar branches of the palatine artery
What is Waldeyer’s ring?
tonsils form a lymphatic ring around the openings of the respiratory and gastro-intestinal tracts
Draw Waldeyer’s ring

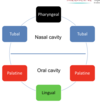
What are the main functions of salivary glands?
secrete water, mucus, electrolytes and enzymes
- lubrication and binding for masticated food
- solubisation of dry food
- digestion of carbohydrates (α-amylase)
- Oral hygiene (lysozyme)
What is the primary stimulus for salivary glands?
parasympathetic - secretomotor fibres from the facial (CN-VII) and glossopharyngeal (CN-IX) nerves
Desrcibe the parotid gland
a erous gland enclosed within a tough, unyielding capsule
Where is the parotid gland located?
lies in retromandibular fossa (below the external acoustic meatus, behind the ramus of mandible)
Describe the course of the parotid duct (Stensen’s duct)
crosses masseter superifically, pierces buccinator and opens into the oral vestibule
Terminal branching of what artery and nerve occurs in the parotid gland?
external carotid artery and facial nerve

red = parotid gland
green = Parotid (Stensen’s) Duct
Where exactly does Stensen’s duct open?
opposite the secondary maxillary molar tooth in the oral vestibule
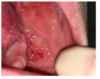
Multiple white spots around the orifice = Koplik spots
Unqiue sign for measles
What type of gland is the sublingual gland and where are they located?
mucous glands
lies above mylohyoid muscle, beneath the mucous membrane of the floor of the mouth
How do the sublingual glands open?
open by 8-20 separate ducts into the floor of the mouth, along the sublingual fold

green = sublingual fold
Describe the submandibular glands and their location
mixed mucous and serous gland
lies beneath the lower border of the body of the mandible
Where does the submandibular gland empty into?
oral cavity at sublingual papilla
What is the most common site for sialoithiasis?
submandibular duct

submandibular gland
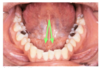
sublingual papilla
What are the 4 regions of teeth in adults?
- left/right
- maxillary/mandibular
What does each region of teeth have in adults?
- 2 incisors
- 1 canine
- 2 premolars
- 3 molar
What are the arrangement of decidous teeth?
2 incisiors, 1 canine, 2 molars


