Anterior and Lateral Wall, Inguinal Region and Hernias Flashcards
What are the 2 planes that divide the adbomen into 4 quadrants
- transumbilical plane - L3/4 intervertebral disc (through umbilicus)
- Median/mid-sagittal plane - through the xiphoid process and pubic symphysis
What are the 4 quadrants of the abdomen?
- right upper quadrant
- left upper quadrant
- right lower quadrant
- left lower quadrant
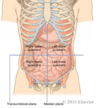
What planes split the abdomen into 9 regions?
- midclavicular line - mid point of clavicle (x2)
- Subcostal plane - L3 vertebrae, lowest point of the costal margins (10th costal cartilages)
- Trans-tubercular/intertibercular plane - L5 vertebra, iliac tuburcles
What are the 9 regions of the abdomen?
- Right hypochondrium
- Epigastric region
- Left hypochondrium
- Right lumbar region (loin, flank)
- umbilical region
- left lumbar region
- Right inguinal region (groin)
- Hypogastric region (pubic, suprapubic)
- Left inguinal region

From superificial to deep give the layers of the abdominal wall
- Skin
- Subcutaneous fascia
- subcutaneous fatty layer (Camper’s fascia)
- Deep membranous layer (Scarpa’s fascia)
- Abdominal muscles (3 layers)
- Transveralis fascia
- Extraperiotneal fat
- parietal peritoneum

Give the properties of the skin of the anterior abdominal wall
- attached to subcutaneous tissues except at umbilicus
- Natural lines of cleavage in the skin are constant running downward and forward almost horixontally around the trunk
What do Langer’s Lines correspond with?
skin creases
NB: incisions made across the lines of skin tension promote hypertrophic scarring (oblique or S-shaped incisions may be preferred)
What is the abdominal wall continous with?
perineum wall
What is camper’s fascia continous with?
Cruveilheir’s fascia (subcutaneous tissue of the perineum)
What is Scapa’s fascia continous with?
Colles’ (perineal) fascia and dartos fascia
What muscles are contained within the abdominal wall?
3 flat muscles, vertical strap-like muscles and pyramidalis
What are the main (common) functions of the abdominal wall muscles?
- support abdominal contents
- raise intra-abdominal pressure
- withstand pressure from descent of diaphragm
- respiration
- support vertebral column
- flex, laterally flex and rotate the trunk
What nerves supply the abdominal wall muscles?
- thoraco-abdominal (7th-11th intercostal nerves)
- subcostal nerve (12th intercostal)
- some branches from L1
What is the vertical strap like muscle in the abdominal wall?
rectus abdominis
What is the origin of rectus abdominis
pubic creat and pubic symphysis
What is the insertion of rectus abdominis
5th-7th costal cartilage and xiphoid process
What is the action of rectus abdominis
stabilises the pelvis during gait
What is each rectus abdominis muscle enclosed in?
rectus sheath; formed by aponeuroses of the flat muscles of the abominal wall
How many tendinous intersections are within rectus abdominis
three
Describe the power of the rectus abdominis muscle
minimal
Draw a diagram of the rectus sheath (transverse section) above the arcurate line

Where is the arcuate line?
1/3 between umbilicus and pubic symphysis
What is linea alba?
fusion of aponeurosis; tendinous structure
good place to enter the abdomen during surgery as it is bloodless
Draw a diagram of the rectus sheath below the arcuate line


green = semilunar line
red = arcuate line
blue = linea alba
What do all aponeurosis fuse as in the midline?
linea alba
What is at the inferior border of the aponeurosis of transversus abdominis
arcuate line
What enter the rectus sheath at the arcuate line?
inferior epigastric vessels, pass anterior to the arcuate line
What is the origin of external oblique muscle?
lower 8 ribs
What is the insertion of external oblique muscle?
- iliac crest
- linea alba
- xiphoid process
- pubic tubercle
- anterior superior iliac spine
How do the fibres of external oblique muscle run?
infero-medially
What muscle is the external oblique muscle similar to?
external intercostal muscle
What is the inguinal ligament?
lower border of the aponeurosis of the external oblique muscle
Where does the inguinal ligament extend between?
attached to and extends between the ASIS and pubic tubercle
What occurs at the medial end of the inguinal ligament?
fibres turn posterolaterally and attach to the pubic pectan
this is called the lacunar ligament
What border so the lacunar ligament form
medial border of the femoral canal

red = external oblique
What is the superificial inguinal
defect on the aponeurosis of the external oblqiue, just above the pubic tubercle
superificial opening of the inguinal canal
What is the femoral canal?
conical shaped potential space
opening of the canal is formed by femoral vein, inguinal ligament and lacunar ligament
Where does thoraco-lumbar fascia pass between
from iliac crest to the 12th rib in 3 layers
What occurs in the thoraco-lumbar fascia?
three layers fuse and provide the origin to the transversus abdoominis and internal oblique muscles but not external oblique
What can occur in the weak area of the thoraco-lumbar fascia
lumbar hernia
What is the originof internal oblique muscle?
- thoracolumbar fascia
- iliac crest (anterior 2/3)
- lateral 2/3 of inguinal ligament
What is the insertion of the internal oblique muscle?
- inferior 3-4 ribs
- linea alba
- xiphoid process
- pubic crest
What is the nerve innervation of internal oblique muscle?
iliohypogastric (L1) nerve
How do the fibres of internal oblique muscle run?
supero-medially and inferioly to conjoint tendon
What is the origin of transversus abdominis
- thoracolumbar fascia
- iliac crest
- lateral 1/3 of inguinal ligmanet
- inferior 6 ribs and CC
What is the insertion of transversus abdominis
- linea alba
- xiphoid process
- pubic crest
What is the nerve innervation of transversus abdominis
- iliohypogastric (L1) nerves
- ilioinguinal nerve (supplies inferior most fibres)
Conjoint tendon =
inguinal falx
What is the conjoint tendon?
fibres of internal oblique arising from the inguinal ligament arch medially over the spermatic cord and unite with transversus abdominis aponeruosis to form the conjoint tendon
What does the conjoint tendon attach to?
attaches to the pubic crest and pectineal line behind the superificial inguinal ring
What is the function of the conjoint tendon?
supports the superficial inguinal ring
What is transverslais fascia
thin layer of CT that lines the transversus abdominis muscle internally
What is the inguinal canal?
passage tgrough the anterior abdominal wall
What does the inguinal canal connect the abdomen to?
- scotum in makes
- labia majoria in females
What are the two openings of the inguinal canal?
deep inguinal ring and superifical inguinal ring
What are the contents of the inguinal canal?
- Ductus deferens in males
- testicular artery in males
- round ligament of uterus un females (ligamentum teres)
- genital branch of genitofemoral nerves (L1/2)
- ilioinguinal nerve (doesnt pass through all of the canal)
Where is the deep inguinal ring?
opening in the transversalis fascia
Found in the lateral inguinal fossa
- lateral to the lateral umbilical fold
- 1cm above the midway between the ASIS and pubic symphysis (mid-inguinal portion)
Where is the superifical inguinal ring?
traingular opening ion the external oblique aponeurosis
What is the superifical inguinal ring supported by?
supported from behind by the conjoint tendon
What are the anterior relations of the inguinal canal
- external oblique
- internal oblique laterally
What are the posterior relations of the inguinal canal
- conjoint tendon medially
- transversalis fascia laterally
What is on the roof of the inguinal canal?
arching inferior edges of internal oblique and transversalis abdominis
What comprises the floor of the inguinal canal?
- inguinal ligament
- lacunar ligament medially
What is a hernia?
a condition which part of an organ is displcaed and protrudes through the wall of the cavity containing
Where does an inguinal hernia usually occur?
usually appears above & medial to the pubic tubercle
Where does a femoral hernia usually occur?
passes through the femoral canal & appears below & lateral to the pubic tubercle
Where does a direct inguinal hernia occur?
area on the posterior wall of the inguinal canal, medial to the inferior epigastric vessels - Hesselbach’s triangle
One the medial corner of Haselbach’s (inguinal) triangle is the inguinal falx (conjoint tendon)
Who is a weaker conjoint tendon more common in?
males
What occurs in a direct inguinal hernia?
Fat or small bowel pushes the peritoneum and transversalis fascia
May pass through the superficial inguinal ring to enter the scrotum
- Parallel to spermatic cord
- Covered by peritoneum, transversalis fascia (and conjoint tendon)
What occurs in an indirect inguinal hernia?
abdominal cintents pass through the deep inguinal ring
contents are covered by all layers of the spermatic cord


