Ocular Trauma Flashcards
(35 cards)
initial assessment
good history of incident
visual acuities
examination of eye
use fluorescein drops and a bright blue light to examine cornea
what is a quick but sensitive test to examine clarity of vision
ability to read news print with refractive errors corrected
if the patient cannot open the eye to be examined what can be done
fews drops of local anaesthetic (eg tetracaine 1%)
which imaging is good and which should be avoided
CT is good
avoid MRI as FB may be magnetic
what must be done if there is a suspicion of IOFB
X ray of orbit
orbital blowout fracture
blunt injury can cause a sudden increase in pressure in the orbit, and may cause blowout fracture withn the orbital contents herniating into the maxillary sinus
typically affects medial wall (ethmoid bone) and floor (maxillary bone)
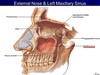
signs of orbital blowout fracture
pain
muscle entrapment
decreased visual acuity
hypoesthesia in the infraorbital region due to infraorbital nerve (CNV2) injury
periorbital ecchymosis (discolouration of skin due to bleeding underneath)

what does this CT scan show

orbital blowout fracture and herniation of contents into maxillary sinus
what is a classical orbital blowout fracture CT sign
tear drop sign - herniation or orbital fat inferiorly

which muscle is often trapped in an orbital blowout fracture and what clinical feature does this result in
often entraps inferior rectus/inferior oblique muscles
pain on upward gaze and diploplia
investigation and treatment of orbital blowout fracture
CT
fracture reduction and muscle release

hyphaema
blood in anterior chamber
may affect acuity

clinical features of traumatic uveitis
acute pain, photophobia, decreased acuity, lacrimation (not sticky), circumcorneal redness, small/irregular pupils
commotion retinae
bruised retina
degeneration of the layers of the retina secondary to shock waves caused by blunt trauma/blast injury


optic nerve avulsion
globe rupture
any full thickness injury of the cornea/sclera is considered a globe rupture
must be handled with care
where is a scleral rupture most common
insertion of intraocular muscles or at the limbus, where the sclera is thinnest

indications of globe rupture
hyphema, loss of anterior chamber depth or deviation of pupil towards laceration or irregular pupil (tear drop shape)
must be handled with care

what must be done on presentration with penetrating trauma
history and examination
X ray to exclude intra-ocular foreign bodies (±skull x ray and CT to exclude intracranial involvement)
what autoimmune inflammatory response is there a risk of in uveal injury
sympathetic ophthalmia
bilateral granulomatous uveitis that is thought to be an autoimmune inflammatory response towards ocular antigens
may lead to bilateral blindness

how should a large foreign body be dealt with
done remove it, support it with padding
pad the unaffected eye to prevent damage from conjugate movement
chemosis
swelling of conjunctiva

when should a foreign body be considered to have penetrated
irregular pupil, shallow anterior chamber, localised cataract or gross inflammation
what must be done to all IOFB
X ray




