Glaucoma Flashcards
(23 cards)
open angle glaucoma
implies optic neuropathy with the death of many retinal ganglion cells and their optic nerve axons
asymptomatic until visual fields are severely impaired, hence the need for screening
there are many different types, but all result in optic nerve damage, and therefore, visual loss

Definition/Pathogenesis of Open-Angle Type
the sclerocorneal angle is open, but there is resistance to outflow of aqueous in the trabecular meshwork

fundoscopy of retina in open angle glaucoma
cup-to-disc ratio is increased
as damage progresses the disc pales (atrophy), and the cup widens and deeps until eventually there is total (asymmetric) cupping of the disc
notching at the neuro-retinal rim of the cup and haemorrhaging at the disc may occur

IOP in glaucoma
may be raised, but this is not part of the definition
what is the only modfiable risk factor for glaucoma
IOP - any damage done by glaucoma cannot be reversed, the only option is to slow the progression by lowering the IOP
this is why screening is of the utmost importance
presentation of open-angle glaucoma
since the central field is intact, good acuity is maintained so presentation is often delayed until irreversible optic nerve damage has occurred
this is why screening is of the utmost importance

optic disc cupping
characterised by loss of disc substance, hence enlargement of the cup
as cupping develops the disc vessels are displaced nasally
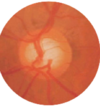
what does asymmetric cupping of optic disc suggest
glaucoma

bayoneting
sharp turning of vessels seen in optic disc cupping

treatment of open-angle
The system of aqueous humor is a closed system with no feedback. Therefore, medications either stop the production of aqueous humor from the ciliary body or open up the drainage system (trabecular meshwork).
- Prostanoids e.g. Latanoprost (‘Xalatan’)
- Beta blockers
- Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors e.g. topical Dorzolamide or systemic Acetazolamide
- Alpha2 adrenergic agonist e.g. Brimonidine
- Parasympathetic e.g. Pilocarpine
- Combination e.g. dorzolamide and timolol = Cosopt
action of prostanoid
- increases uveoscleral outflow
- can cause brown pigmentation of iris
beta blockres
- reduce aqueous production
- avoid in asthmatics and those with heart block
surgery available for open angle glaucoma
trabeculectomy - filtration surgery that establishes a pressure valve at the limbus so that aqueous can flow into a conjunctival bleb


patient has had trabeculectomy
Pathogenesis of Closed-Angle Type
aqueous humor encounters increased resistance through iris/lens channel, this increased pressure gradient causes the iris to bow forward obstructing the trabecular meshwork and drainage to canal of Schlemm - ‘closed angle’
there is a rapid build up in pressure - acute - ophthalmic emergency

how does pupillary dilation affect angle, and what are the consequences of this
pupillary dilation makes the angle smaller, this means symptoms are worse at night/when in dark etc
risk factors for close angle glaucoma
shallow anterior chamber, therefore smaller angle
- hypermetropic people have a shallow anterior chamber
older people also
what drugs can induce angle closure in predisposed individuals
nebulised ipatropium and tricyclic anti-depressants
presentation of closed angle glaucoma
very painful red eye (one), visual loss, acute onset headache, nausea and vomiting, mid-dilated pupil/milky cornea
haloes around lights

what is closed angle glaucoma often preceded by
blurry vision or haloes around lights (especially at night)

treatment of closed angle glaucoma
pilocarpine - miosis opens a blocked ‘close’ drainage angle and improves the flow of aqueous humour
mannitol - lowers ICP
topical steroids and anti-hypertensive drugs
what surgery is available for acute closed angle glaucoma
peripheral laser irodotomy is performed once IOP is controlled
peice of iris removed at 12 o’clock in both eyes to allow aqueous to flow


irodotomy


